|
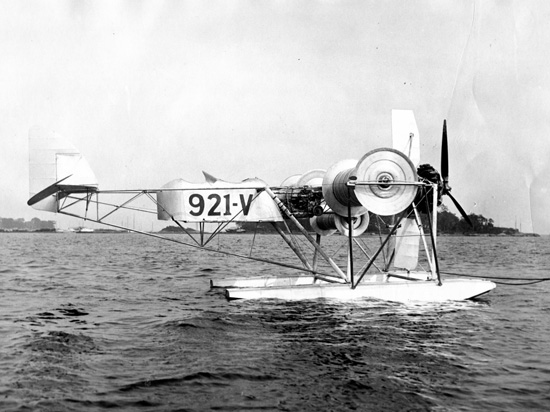
Flettner Aircraft
A Flettner airplane is a type of rotor airplane which uses a Flettner rotor to provide lift. The rotor comprises a spinning cylinder with circular end plates and, in an aircraft, spins about a spanwise horizontal axis. When the aircraft moves forward, the Magnus effect creates lift. Anton Flettner, after whom the rotor is named, used it successfully as the sails of a rotor ship. He also suggested its use as a wing for a rotor airplane. The Butler Ames Aerocycle was built in 1910 and tested aboard a warship. There is no record of it having flown. The Plymouth A-A-2004 was built for Zaparka in 1930 by three anonymous American inventors. It was reported to have made successful flights over Long Island Sound. An inherent safety concern is that if power to the rotating drums were lost—even if thrust was maintained—the aircraft would lose its ability to generate lift as the drum slowed and it would not be able to sustain flight. See also * Cyclogyro * FanWing * Servo tab __N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flettner Rotor Aircraft
Anton Flettner, Flugzeugbau GmbH was a German helicopter and autogyro manufacturer during World War II, founded by Anton Flettner. Flettner aircraft included: *Flettner Fl 184 - Reconnaissance autogyro, prototype *Flettner Fl 185 - Reconnaissance helicopter, prototype *Flettner Fl 265 - Reconnaissance helicopter, prototype *Flettner Fl 282 ''Kolibri'' (Hummingbird) - Reconnaissance helicopter *Flettner Fl 339 - Reconnaissance helicopter, project *Flettner Gigant - Experimental helicopter Anton Flettner's interest in aerodynamics (specifically the Magnus effect, which produces a force from a cylinder rotating in a fluid flow) also led him to invent the Flettner rotor which he used to power a Flettner ship which crossed the Atlantic, and the Flettner ventilator which is still widely used as a cooling device for buses, vans and other commercial vehicles and which is based upon the Savonius principle. See also * Gyrodyne * List of RLM aircraft designations References Defunct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotor Airplane
A rotor wing is a lifting rotor or wing which spins to provide aerodynamic lift. In general, a rotor may spin about an axis which is aligned substantially either vertically or side-to-side (spanwise). All three classes have been studied for use as lifting rotors and several variations have been flown on full-size aircraft, although only the vertical-axis rotary wing has become widespread on rotorcraft such as the helicopter. Some types provide lift at zero forward airspeed, allowing for vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL), as in the helicopter. Others, especially unpowered free-spinning types, require forward airspeed in the same manner as a fixed-wing aircraft, as in the autogyro. Many can also provide forward thrust if required. Types Many ingenious ways have been devised to convert the spinning of a rotor into aerodynamic lift. The various types of such rotor wings may be classified according to the axis of the rotor. Types include:Foshag & Boehler (1969)Seifert (2012) ;Verti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flettner Rotor
A Flettner rotor is a smooth cylinder with disc end plates which is spun along its long axis and, as air passes at right angles across it, the Magnus effect causes an aerodynamic force to be generated in the direction perpendicular to both the long axis and the direction of airflow.Seifert, Jost;A review of the Magnus effect in aeronautics, ''Progress in Aerospace Sciences'' Vol. 55, 2012, pp.17–45. The rotor sail is named after the German aviation engineer and inventor Anton Flettner, who started developing the rotor sail in the 1920s. In a rotor ship, the rotors stand vertically and lift is generated at right angles to the wind, to drive the ship forwards. In a rotor airplane, the rotor extends sideways in place of a wing and upwards lift is generated. Magnus effect The Magnus effect is named after Gustav Magnus, the German physicist who investigated it. It describes the force generated by fluid flow over a rotating body, at right angles to both the direction of flow and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnus Effect
The Magnus effect is an observable phenomenon commonly associated with a spinning object moving through a fluid. The path of the spinning object is deflected in a manner not present when the object is not spinning. The deflection can be explained by the difference in pressure of the fluid on opposite sides of the spinning object. The Magnus effect is dependent on the speed of rotation. The most readily observable case of the Magnus effect is when a spinning sphere (or cylinder) curves away from the arc it would follow if it were not spinning. It is often used by association football and volleyball players, baseball pitchers, and cricket bowlers. Consequently, the phenomenon is important in the study of the physics of many ball sports. It is also an important factor in the study of the effects of spinning on guided missiles—and has some engineering uses, for instance in the design of rotor ships and Flettner aeroplanes. Topspin in ball games is defined as spin about a ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Flettner
Anton Flettner (November 1, 1885 – December 29, 1961) was a German aviation engineer and inventor. Born in Eddersheim (today a district of Hattersheim am Main), Flettner made important contributions to airplane, helicopter, vessel, and automobile designs. After serving Germany in both World Wars, Anton Flettner emigrated to the United States post World War II as a consultant to the office of Naval Research at the United States Navy. Anton Flettner attended the Fulda State Teachers College in Fulda, Germany. He was the village teacher in Pfaffenwiesbach from 1906 to 1909. Flettner subsequently taught high school mathematics and physics in Frankurt, where he developed ideas that would assist Germany in World War I. Flettner revolutionized the art of harnessing the wind, used essentially in an unaltered form for thousands of years—the canvas sail—by a modern machine—the Flettner Rotor ship—that could permit ocean liners to reduce their crews by two-thirds and save 90 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress In Aerospace Sciences
''Progress in Aerospace Sciences'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all areas of aerospace and aerospace engineering. It covers all areas of aerospace and aerospace engineering, particularly with respect to new theoretical and experimental developments and their applications in research, industry, and university. The journal aims to serve as a general-purpose aerospace journal, condensing the ever-expanding, increasingly multidisciplinary field of aerospace into one publication. The journal is intended for a broad readership - generally anyone either active or simply interested in the aerospace field. The editors-in-chief are K.J. Badcock (University of Liverpool) and M.F. Platzer ( Naval Postgraduate School). It was established in 1961 and is published by Elsevier. Originally the journal published articles written in English, French, and German, but since 1972 it has been published entirely in English. About The first edition of ''Progress in Aerospace S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth A-A-2004
Plymouth () is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Island Sound
Long Island Sound is a marine sound and tidal estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It lies predominantly between the U.S. state of Connecticut to the north and Long Island in New York to the south. From west to east, the sound stretches from the East River in New York City, along the North Shore of Long Island, to Block Island Sound. A mix of freshwater from tributaries and saltwater from the ocean, Long Island Sound is at its widest point and varies in depth from . Shoreline Major Connecticut cities on the Sound include Stamford, Norwalk, Bridgeport, New Haven, and New London. Cities on the New York side of the Sound include Rye, Glen Cove, New Rochelle, Larchmont and portions of Queens and the Bronx in New York City. Climate and geography The climate of Long Island Sound is warm temperate or Cfa in the Köppen climate classification. Summers are hot and humid often with convective showers and strong sunshine, while the cooler months feature cold temperatures and a mix o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that system. The force applied on a surface in a direction perpendicular or normal to the surface is also called thrust. Force, and thus thrust, is measured using the International System of Units (SI) in newtons (symbol: N), and represents the amount needed to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at the rate of 1 meter per second per second. In mechanical engineering, force orthogonal to the main load (such as in parallel helical gears) is referred to as static thrust. Examples A fixed-wing aircraft propulsion system generates forward thrust when air is pushed in the direction opposite to flight. This can be done by different means such as the spinning blades of a propeller, the propelling jet of a jet engine, or by ejecting hot gases from a rocket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclogyro
The cyclogyro, or cyclocopter, is an aircraft configuration that uses a horizontal-axis cyclorotor as a rotor wing to provide lift and sometimes also propulsion and control. In principle, the cyclogyro is capable of vertical take off and landing and hovering performance like a helicopter, while potentially benefiting from some of the advantages of a fixed-wing aircraft. The cyclogyro is distinct from the Flettner airplane which uses a cylindrical wing rotor to harness the Magnus effect. Principles of operation The cyclogyro wing resembles a paddle wheel, with airfoil blades replacing the paddles. Like a helicopter, the blade pitch (angle of attack) can be adjusted either collectively all together or cyclically as they move around the rotor's axis. In normal forward flight the blades are given a slight positive pitch at the upper and forward portions of their arc producing lift and, if powered, also forward thrust. They are given flat or negative pitch at the bottom, and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FanWing
The FanWing is an aircraft configuration in which a horizontal-axis cross-flow fan is used in close conjunction with a fixed wing. The fan forces airflow over the fixed surface to provide both lift and forward thrust. The concept was initially developed around 1997 by designer Patrick Peebles and is under development by his company FanWing Ltd. As of December 2018, only experimental drones have been flown. Principles of operation A cross-flow fan comprises blades radiating from a central axis and aligned with the axis, similar to those of a cylinder mower. It is contained in a duct which is shaped so that when the fan spins, it induces a directional airflow. In the FanWing, the fan is set above the leading section of a fixed wing and extends the full span of the wing. The wing upper surface is shaped around the fan to form a half-duct. The wing chord extends approximately as far again back from the fan, with the rear section shaped as a wedge-like fairing that extends to the trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |