|
Cystoisospora Belli
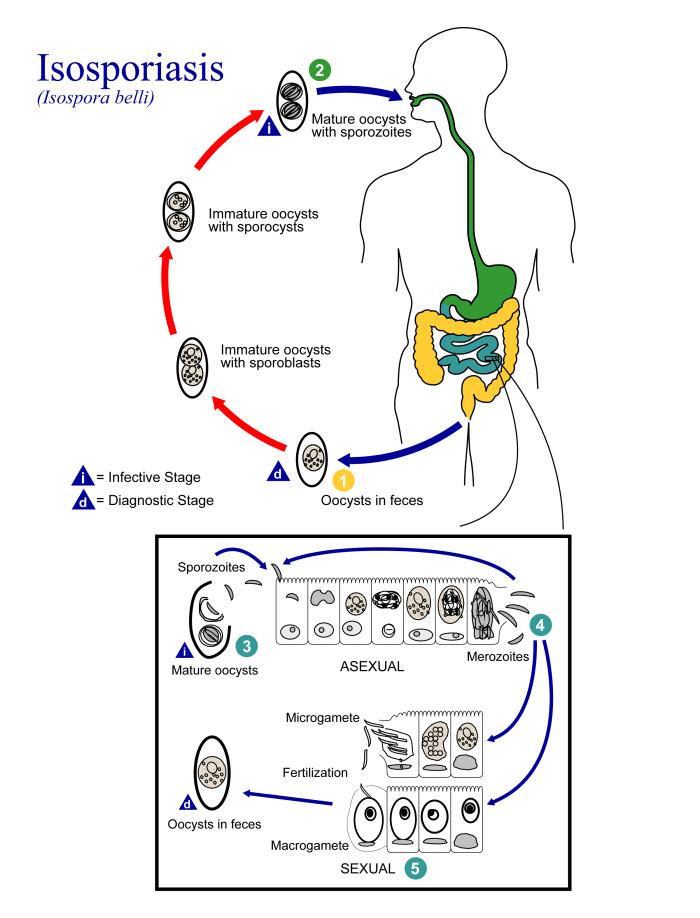
''Cystoisospora belli'', previously known as ''Isospora belli'', is a parasite that causes an intestinal disease known as cystoisosporiasis.Centers For Disease Control: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cystoisospora/index.html This protozoan parasite is opportunistic in immune suppressed human hosts. It primarily exists in the epithelial cells of the small intestine, and develops in the cell cytoplasm. The distribution of this coccidian parasite is cosmopolitan, but is mainly found in tropical and subtropical areas of the world such as the Caribbean, Central and S. America, India, Africa, and S.E. Asia. In the U.S., it is usually associated with HIV infection and institutional living. Morphology A fully mature (sporulated) oocyst of genus ''Isospora'' is a spindle-shaped body that has two sporocysts that contain four sporozoites each. The oocysts of ''Cystoisospora belli'' are long and oval shaped. They measure between 20 and 33 micrometers in length and between 10 and 19 microme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oocyst
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is typified by a ''cellular variety'' with a distinct morphology and biochemistry. Not all apicomplexa develop all the following cellular varieties and division methods. This presentation is intended as an outline of a hypothetical generalised apicomplexan organism. Methods of asexual replication Apicomplexans (sporozoans) replicate via ways of multiple fission (also known as schizogony). These ways include , and , although the latter is sometimes referred to as schizogony, despite its general meaning. Merogony is an asexually reproductive process of apicomplexa. After infecting a host cell, a trophozoite ( see glossary below) increases in size while repeatedly replicating its nucleus and other organelles. During this process, the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fission (biology)
Fission, in biology, is the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts to separate entities resembling the original. The object experiencing fission is usually a cell, but the term may also refer to how organisms, bodies, populations, or species split into discrete parts. The fission may be ''binary fission'', in which a single organism produces two parts, or ''multiple fission'', in which a single entity produces multiple parts. Binary fission Organisms in the domains of Archaea and Bacteria reproduce with binary fission. This form of asexual reproduction and cell division is also used by some organelles within eukaryotic organisms (e.g., mitochondria). Binary fission results in the reproduction of a living prokaryotic cell (or organelle) by dividing the cell into two parts, each with the potential to grow to the size of the original. Fission of prokaryotes The single DNA molecule first replicates, then attaches each copy to a differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual may not notice any symptoms, or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged incubation period with no symptoms. If the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors which are rare in people who have normal immune function. These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss. HIV is spread primarily by unprotected sex (including anal and vaginal sex), contaminated blood transfusions, hypodermic needles, and from mother to child duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Co-trimoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the brand name Bactrim among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It consists of one part trimethoprim to five parts sulfamethoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract infections, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infections, travelers' diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, and cholera, among others. It is used both to treat and prevent pneumocystis pneumonia and toxoplasmosis in people with HIV/AIDS and other causes of immunosuppression. It can be given by mouth or intravenously. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines and is also available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 121st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. Medical uses ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' pneumonia Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) is the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosinophilia
Eosinophilia is a condition in which the eosinophil count in the peripheral blood exceeds . Hypereosinophilia is an elevation in an individual's circulating blood eosinophil count above 1.5 x 109/ L (i.e. 1,500/μL). The hypereosinophilic syndrome is a sustained elevation in this count above 1.5 x 109/L (i.e. 1,500/μL) that is also associated with evidence of eosinophil-based tissue injury. Eosinophils usually account for less than 7% of the circulating leukocytes. A marked increase in non-blood tissue eosinophil count noticed upon histopathologic examination is diagnostic for tissue eosinophilia. Several causes are known, with the most common being some form of allergic reaction or parasitic infection. Diagnosis of eosinophilia is via a complete blood count (CBC), but diagnostic procedures directed at the underlying cause vary depending on the suspected condition(s). An absolute eosinophil count is not generally needed if the CBC shows marked eosinophilia. The location of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporogony
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is typified by a ''cellular variety'' with a distinct morphology and biochemistry. Not all apicomplexa develop all the following cellular varieties and division methods. This presentation is intended as an outline of a hypothetical generalised apicomplexan organism. Methods of asexual replication Apicomplexans (sporozoans) replicate via ways of multiple fission (also known as schizogony). These ways include , and , although the latter is sometimes referred to as schizogony, despite its general meaning. Merogony is an asexually reproductive process of apicomplexa. After infecting a host cell, a trophozoite ( see glossary below) increases in size while repeatedly replicating its nucleus and other organelles. During this process, the orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizogony
Fission, in biology, is the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts to separate entities resembling the original. The object experiencing fission is usually a cell, but the term may also refer to how organisms, bodies, populations, or species split into discrete parts. The fission may be ''binary fission'', in which a single organism produces two parts, or ''multiple fission'', in which a single entity produces multiple parts. Binary fission Organisms in the domains of Archaea and Bacteria reproduce with binary fission. This form of asexual reproduction and cell division is also used by some organelles within eukaryotic organisms (e.g., mitochondria). Binary fission results in the reproduction of a living prokaryotic cell (or organelle) by dividing the cell into two parts, each with the potential to grow to the size of the original. Fission of prokaryotes The single DNA molecule first replicates, then attaches each copy to a differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplasm
Protoplasm (; ) is the living part of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is a mixture of small molecules such as ions, monosaccharides, amino acid, and macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, etc. In some definitions, it is a general term for the cytoplasm (e.g., Mohl, 1846), but for others, it also includes the nucleoplasm (e.g., Strasburger, 1882). For Sharp (1921), "According to the older usage the extra-nuclear portion of the protoplast 'the entire cell, excluding the cell wall''was called "protoplasm," but the nucleus also is composed of protoplasm, or living substance in its broader sense. The current consensus is to avoid this ambiguity by employing Strasburger's '(1882)''terms cytoplasm Albert_von_Kölliker.html"_;"title="'coined_by_Albert_von_Kölliker">Kölliker_(1863),_originally_as_synonym_for_protoplasm''and_nucleoplasm_([''term_coined_by_Edouard_Van_Beneden.html" ;"title="Albert von Kölliker">Kölliker (1863), originally as syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexan Life Cycle
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is typified by a ''cellular variety'' with a distinct morphology and biochemistry. Not all apicomplexa develop all the following cellular varieties and division methods. This presentation is intended as an outline of a hypothetical generalised apicomplexan organism. Methods of asexual replication Apicomplexans (sporozoans) replicate via ways of multiple fission (also known as schizogony). These ways include , and , although the latter is sometimes referred to as schizogony, despite its general meaning. Merogony is an asexually reproductive process of apicomplexa. After infecting a host cell, a trophozoite ( see glossary below) increases in size while repeatedly replicating its nucleus and other organelles. During this process, the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Morley Wenyon
Charles Morley Wenyon (1878–1948) was a distinguished English protozoologist. Honours and prizes Wenyon was awarded many honours and prizes for his work during his lifetime including: * The Makdougall-Brisbane Prize of the Royal Society of Edinburgh in 1927 * The Mary Kingsley Medal of the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine in 1929 * Officier de la Legion d'Honneur in 1933 * Elected Honorary Member of the Société Belge de Médecine Tropicale in 1934 * Honorary Life Member of the New York Academy of Sciences in 1945 * The Theobald Smith Gold Medal of the American Academy of Tropical Medicine in 1946 * Elected Honorary Fellow of the Royal Society of Medicine and Honorary Member of the Société de Pathologie Exotique in 1947 * Manson Medal of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene The Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, more commonly known by its acronym RSTMH, was founded in 1907 by Sir James Cantlie and George Carmichael Low. Sir Patrick Manso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporoblast
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |