|
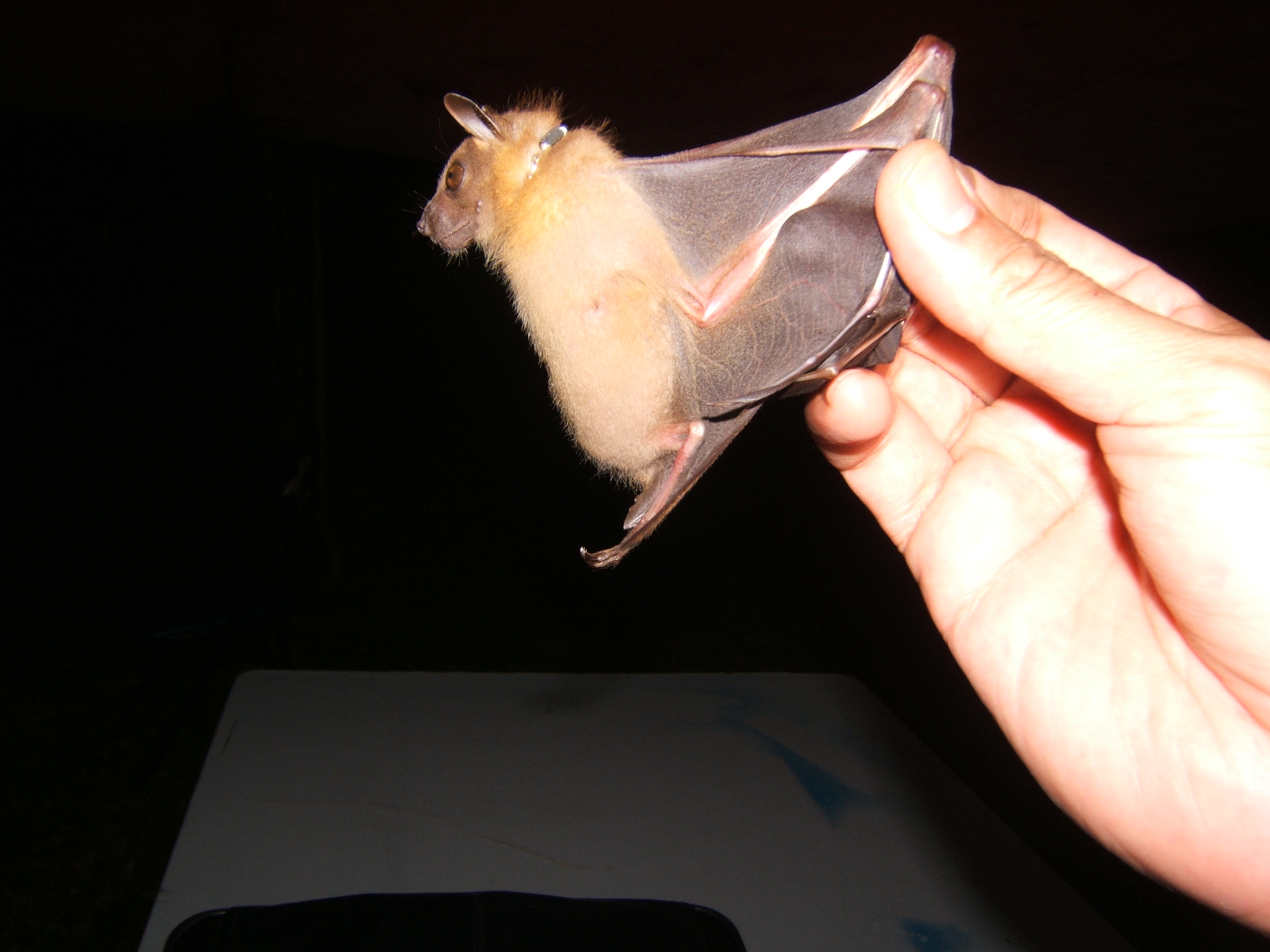
Cynopterus Horsfieldii
Horsfield's fruit bat (''Cynopterus horsfieldii'') is a species of megabat native to South East Asia. It is named for Thomas Horsfield, an American naturalist who presented the type specimen to the British Museum. Description Horsfield's fruit bat is a medium-sized megabat, intermediate in size between flying foxes and pygmy fruit bats. Adults weigh around , and have light-grey to brown fur, with a reddish-brown or orange mantle around the shoulders. In some males, the mantle extends across the chest, and the fur is often brighter in colour than in females. The rim of the ears and the skin overlying the metacarpals and phalanges within the wing are white. Juveniles have a more bland coat pattern, with uniformly dull buff or grey fur. The bats have a short, broad snout, ending in a pair of almost tubular nostrils. Both the eyes and ears are large, although the latter have a simpler structure than in most other bats, and lack tragi. The wings have a low aspect ratio and high w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabat
Megabats constitute the family Pteropodidae of the order Chiroptera (bats). They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genera ''Acerodon'' and ''Pteropus''—flying foxes. They are the only member of the superfamily Pteropodoidea, which is one of two superfamilies in the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. Internal divisions of Pteropodidae have varied since subfamilies were first proposed in 1917. From three subfamilies in the 1917 classification, six are now recognized, along with various tribes. As of 2018, 197 species of megabat had been described. The leading theory of the evolution of megabats has been determined primarily by genetic data, as the fossil record for this family is the most fragmented of all bats. They likely evolved in Australasia, with the common ancestor of all living pteropodids existing approximately 31 million years ago. Many of their lineages probably originated in Melanesia, then dispersed over time to mainland Asia, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumbawa
Sumbawa is an Indonesian island, located in the middle of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain, with Lombok to the west, Flores to the east, and Sumba further to the southeast. Along with Lombok, it forms the province of West Nusa Tenggara, but there have been plans by the Indonesian government to split the island off into a separate province. Traditionally, the island is known as the source of sappanwood, as well as honey and sandalwood. Its savanna-like climate and vast grasslands are used to breed horses and cattle, as well as to hunt deer. Sumbawa has an area (including minor offshore islands) of (three times the size of Lombok) with a population (at the 2020 Census) of 1,561,461.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. It marks the boundary between the islands to the west, which were influenced by religion and culture spreading from India, and the region to the east that was less influenced. In particular this applies to both Hinduism and Islam. Etymology Sumbawa is a Portuguese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Borneo
The mammal species of Borneo include 288 species of terrestrial and 91 species of marine mammals recorded within the territorial boundaries of Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia. The terrestrial mammals are dominated by the chiroptera (102 species of bats) and rodents (61 species of rats and mice). Introduction The high diversity and endemicity of mammals is related to the many niches found in the tropical rain forest of Borneo and past Pleistocene events within the Sundaland region. During interglacial and post-glacial periods, there was migration of animal from the Asian mainland into Borneo and into Sulawesi via the Philippines. Due to lack of favourable habitats and small founder population, some species of animals have become extinct and others have radiated into endemic species. Of the 57 mammal species that were identified from archaeological remains in the Niah Caves, Sarawak, 13 were bats. Four of these were megachiropterans, ''Pteropus vampyrus'', ''Rousettus amplexicauda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bats Of Malaysia
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox, ''Acerodon jubatus'', reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the order into Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiropter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bats Of Indonesia
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox, ''Acerodon jubatus'', reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the order into Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiropter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bats Of Southeast Asia
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out digits covered with a thin membrane or patagium. The smallest bat, and arguably the smallest extant mammal, is Kitti's hog-nosed bat, which is in length, across the wings and in mass. The largest bats are the flying foxes, with the giant golden-crowned flying fox, ''Acerodon jubatus'', reaching a weight of and having a wingspan of . The second largest order of mammals after rodents, bats comprise about 20% of all classified mammal species worldwide, with over 1,400 species. These were traditionally divided into two suborders: the largely fruit-eating megabats, and the echolocating microbats. But more recent evidence has supported dividing the order into Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiropter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynopterus
''Cynopterus'' (Latin meaning: ״flying dog״) is a genus of megabats. The cynopterine section is represented by 11 genera,Andersen K. 1912. Catalogue of the chiroptera in the collection of the British Museum. Second edition, British Museum of Natural History. five of which occur in Malaysia, namely, ''Chironax, Balionycteris, Penthetor, Dyacopterus'', and ''Cynopterus''. About 30 names for ''Cynopterus'' species have been proposed, but only 16 are taxonomically valid forms.Kitchener DJ, Maharadatunkamsi. 1991. Description of a new species of ''Cynopterus'' (Chiroptera: Pteropodidae) from Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Research Western Australian Museum 15(2):307-363. Species within this genus are: Genus ''Cynopterus'' *Lesser short-nosed fruit bat (''C. brachyotis'') * Horsfield's fruit bat (''C. horsfieldii'') * Peters's fruit bat (''C. luzoniensis'') * Minute fruit bat (''C. minutus'') * Nusatenggara short-nosed fruit bat (''C. nusatenggara'') *Greater short-nosed fruit bat ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguishing them from dessert bananas. The fruit is variable in size, color, and firmness, but is usually elongated and curved, with soft flesh rich in starch covered with a rind, which may be green, yellow, red, purple, or brown when ripe. The fruits grow upward in clusters near the top of the plant. Almost all modern edible seedless ( parthenocarp) bananas come from two wild species – ''Musa acuminata'' and ''Musa balbisiana''. The scientific names of most cultivated bananas are ''Musa acuminata'', ''Musa balbisiana'', and ''Musa'' × ''paradisiaca'' for the hybrid ''Musa acuminata'' × ''M. balbisiana'', depending on their genomic constitution. The old scientific name for this hybrid, ''Musa sapientum'', is no longer used. ''Musa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkia Speciosa
''Parkia speciosa'', the bitter bean, twisted cluster bean or stink bean, is a plant of the genus ''Parkia'' in the family Fabaceae. It bears long, flat edible beans with bright green seeds the size and shape of plump almonds which have a rather peculiar smell, similar to, but stronger than that of the shiitake mushroom, due to sulfur-containing compounds also found in shiitake, truffles and cabbage. Botanical description The petai tree can grow to about 30 metres. It bears flowers in a light bulb-shaped mass at the end of long stalks. The flowers secrete a nectar that attracts bats and other pollinators. The fruits emerge as long, twisted, translucent pods in a cluster of seven or eight pods. When those pods are mature, within them will reside the petai beans or seeds. Use in cooking The beans of other ''Parkia'' species (for example, ''Parkia javanica'' and ''Parkia singularis'') are also popular as culinary ingredient in Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Brunei, Laos, south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payena
''Payena'' is a genus of plants in the family Sapotaceae described as a genus in 1844. ''Payena'' is native to Southeast Asia Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ....Govaerts, R., Frodin, D.G. & Pennington, D. (2001 publ. 2002). World Checklist and Bibliography of Sapotaceae: 1-364. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. ;Species References * * Sapotaceae genera Trees of Indo-China Trees of Malesia Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Sapotaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elaeocarpus
''Elaeocarpus'' is a genus of nearly five hundred species of flowering plants in the family Elaeocarpaceae native to the Western Indian Ocean, Tropical and Subtropical Asia, and the Pacific. Plants in the genus ''Elaeocarpus'' are trees or shrubs with simple leaves, flowers with four or five petals usually, and usually blue fruit. Description Plants in the genus ''Elaeocarpus'' are mostly evergreen trees or shrubs, a few are epiphytes or lianes, and some are briefly deciduous. The leaves are arranged alternately, simple (strictly compound with only one leaflet) with a swelling where the petiole meets the lamina, often have toothed edges, usually have prominent veins and often turn red before falling. The flowers are usually arranged in a raceme, usually bisexual, have four or five sepals and petals and many stamens. The petals usually have finely-divided, linear lobes. The fruit is a oval to spherical drupe that is usually blue, sometimes black, with a sculptured endocarp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |