|
Cymo Melanodactylus
''Cymo melanodactylus'', the furry coral crab, is a species of small decapod crustacean in the family Xanthidae. It is found in the Indo-Pacific Ocean and lives in crevices and on the surface of corals in the genus ''Acropora''. Description The carapace and limbs of ''Cymo melanodactylus'' have the appearance of being covered with short fur. It has large pale blue, stalked eyes, a spiny carapace with a shallow groove down the middle and grows to about wide. It typically has black fingers to its claws but is difficult to distinguish from the rather similar '' Cymo andreossyi'' on claw colour alone as some individuals have white finger tips and others have white fingers with black bases. A more reliable feature to distinguish between the two is the orange granulations on the carapace of ''Cymo melanodactylus''. Distribution ''Cymo melanodactylus'' is found in the Indo-Pacific Ocean. Its range extends from the Red Sea and Madagascar to New Caledonia, French Polynesia and Wallis an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Dwight Dana
James Dwight Dana Royal Society of London, FRS FRSE (February 12, 1813 – April 14, 1895) was an American geologist, mineralogist, volcanologist, and zoologist. He made pioneering studies of mountain-building, volcano, volcanic activity, and the origin and structure of continents and oceans around the world. His zoological author abbreviation is Dana. Early life and career Dana was born February 12, 1813, in Utica, New York. His father was merchant James Dana (1780–1860) and his mother was Harriet Dwight (1792–1870). Through his mother he was related to the Dwight New England family of missionaries and educators including uncle Harrison Gray Otis Dwight and first cousin Henry Otis Dwight. He showed an early interest in science, which had been fostered by Fay Edgerton, a teacher in the Utica high school, and in 1830 he entered Yale College in order to study under Benjamin Silliman the elder. Graduating in 1833, for the next two years he was teacher of mathematics to midshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallis And Futuna
Wallis and Futuna, officially the Territory of the Wallis and Futuna Islands (; french: Wallis-et-Futuna or ', Fakauvea and Fakafutuna: '), is a French island collectivity in the South Pacific, situated between Tuvalu to the northwest, Fiji to the southwest, Tonga to the southeast, Samoa to the east, and Tokelau to the northeast. Mata Utu is its capital and largest city. Its land area is . It had a population of 11,558 at the 2018 census (down from 14,944 at the 2003 census). The territory is made up of three main volcanic tropical islands and a number of tiny islets. It is divided into two island groups that lie about apart: the Wallis Islands (also known as Uvea) in the northeast; and the Hoorn Islands (also known as the Futuna Islands) in the southwest, including Futuna Island proper and the mostly uninhabited Alofi Island. Since 28 March 2003, Wallis and Futuna has been a French overseas collectivity (''collectivité d'outre-mer'', or ''COM''). Between 1961 and 2003, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acropora Formosa
''Acropora muricata'', commonly called staghorn coral, is a species of acroporid coral found in the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, Persian Gulf, Australia, central Indo-Pacific, Japan, Southeast Asia, the East China Sea and the oceanic central and western Pacific Ocean. It is found in tropical shallow reefs, slopes of reefs, and in lagoons, from depths of 5 to 30 m. It was described by Dana in 1846. Description It occurs in arborescent colonies forming thickets with diameters of up to . Its branches vary from being short in shallower water to being less clumped in deeper water. Its axial corallites protrude from the branches and the radial corallites are tube-shaped. It is blue, brown or cream, and the ends of branches are pale. It looks similar to '' Acropora teres''. Distribution It is classed as a near threatened species on the IUCN Red List The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (french: link=no, République des Seychelles; Creole: ''La Repiblik Sesel''), is an archipelagic state consisting of 115 islands in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, is east of mainland Africa. Nearby island countries and territories include the Comoros, Madagascar, Mauritius, and the French overseas departments of Mayotte and Réunion to the south; and Maldives and the Chagos Archipelago (administered by the United Kingdom as the British Indian Ocean Territory) to the east. It is the least populated sovereign African country, with an estimated 2020 population of 98,462. Seychelles was uninhabited prior to being encountered by Europeans in the 16th century. It faced competing French and British interests until coming under full British control in the late 18th century. Since proclaiming independence from the United Kingdom in 1976, it has developed from a largely agricultural society to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Band Disease
White band disease is a coral disease that affects acroporid corals and is distinguishable by the white band of exposed coral skeleton that it forms. The disease completely destroys the coral tissue of Caribbean acroporid corals, specifically elkhorn coral (''Acropora palmata'') and staghorn coral (''A. cervicornis''). The disease exhibits a pronounced division between the remaining coral tissue and the exposed coral skeleton. These symptoms are similar to white plague, except that white band disease is only found on acroporid corals, and white plague has not been found on any acroporid corals. It is part of a class of similar disease known as "white syndromes", many of which may be linked to species of ''Vibrio'' bacteria. While the pathogen for this disease has not been identified, ''Vibrio carchariae'' may be one of its factors. The degradation of coral tissue usually begins at the base of the coral, working its way up to the branch tips, but it can begin in the middle of a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
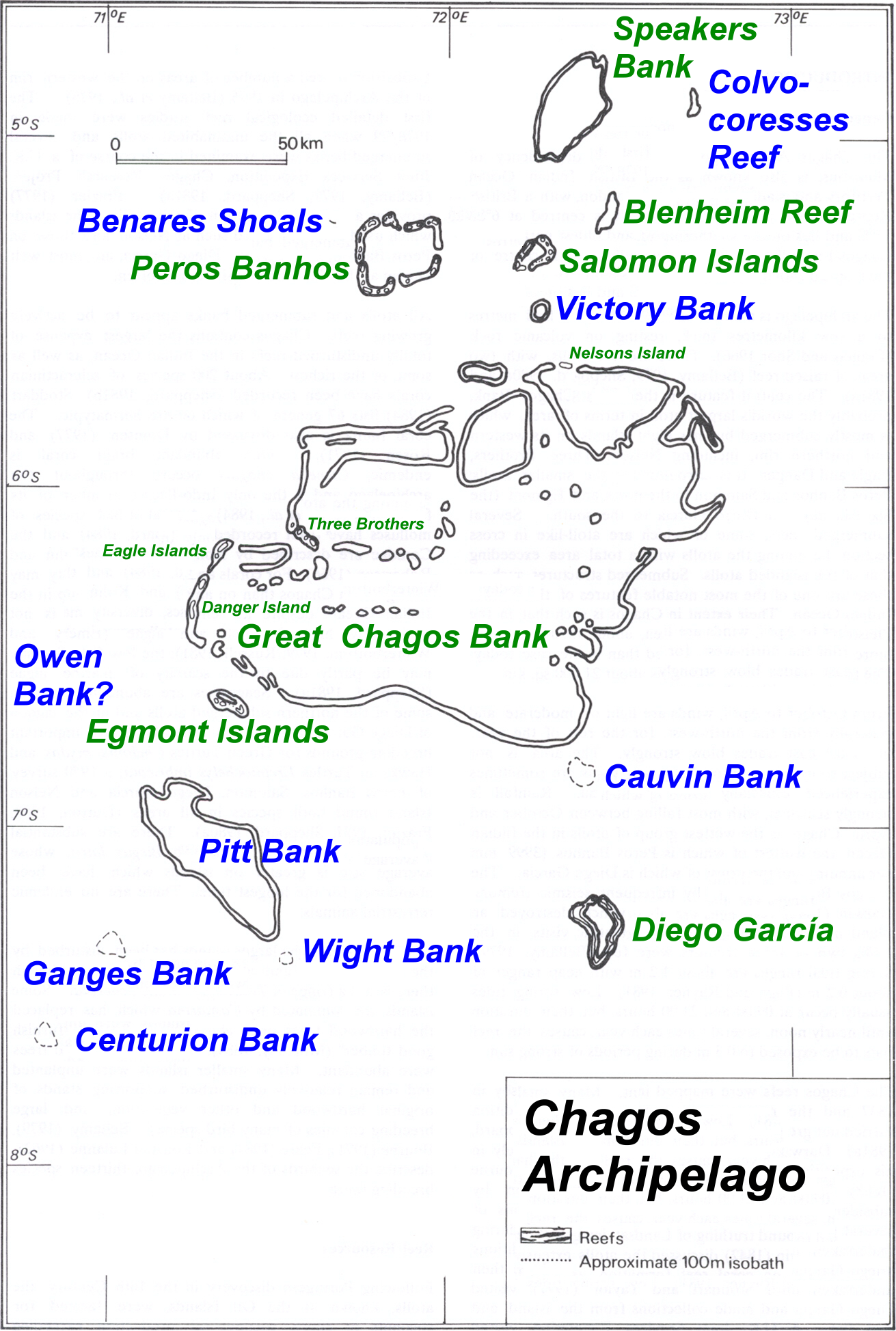
Chagos Archipelago
The Chagos Archipelago () or Chagos Islands (formerly the Bassas de Chagas, and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelson's Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle, Egmont and Danger Island(s); southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons. The Chagos Islands had been home to the native Chagossians, a Bourbonnais Creole-speaking people, until the United Kingdom expelled them from the archipelago at the request of the United States between 1967 and 1973 to allow the United States to build a military base on Diego Garcia. Since 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes (such as lysozymes), immunoglobulins (especially IgA), and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Amphibians, fish, snails, slugs, and some other invertebrates also produce external mucus from their epidermis as protection against pathogens, and to help in movement and is also produced in fish to line the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acropora Cytherea
''Acropora cytherea'' is a stony coral which forms horizontal table like structures. It occurs in the Indo-Pacific Ocean in areas with little wave action, favouring back reef environments from depth. Description ''Acropora cytherea'' is a colonial species of coral that grows in large horizontal plates. These are formed of many tiny branchlets growing vertically or at an angle and others growing horizontally to extend the colony. They may branch and link together and near the centre the plates may become a solid mass of joined branchlets. The surface of the coral is covered by a thin layer of living tissue. This has a rough surface and contains ''zooxanthella'', symbiotic, unicellular, photosynthetic algae. These give the coral its cream or pale brown colour (occasionally pale blue). The calcium carbonate skeleton is secreted by many small polyps which are joined together through an interconnecting network of channels inside the skeleton. At night, and sometimes during the day, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commensalism
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit from each other; amensalism, where one is harmed while the other is unaffected; parasitism, where one is harmed and the other benefits, and parasitoidism, which is similar to parasitism but the parasitoid has a free-living state and instead of just harming its host, it eventually ends up killing it. The commensal (the species that benefits from the association) may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is substantially unaffected. The commensal relation is often between a larger host and a smaller commensal; the host organism is unmodified, whereas the commensal species may show great structural adaptation consistent with its habits, as in the remoras that ride attached to sharks and other fishes. Remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze") , anthem = , song_type = Regional anthem , song = " Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui" , image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg , map_alt = Location of French Polynesia , map_caption = Location of French Polynesia (circled in red) , mapsize = 290px , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title = Protectorate proclaimed , established_date = 9 September 1842 , established_title2 = Territorial status , established_date2 = 27 October 1946 , established_title3 = Collectivity status , established_date3 = 28 March 2003 , established_title4 = Country status (nominal title) , established_date4 = 27 February 2004 , official_languages = French , regional_languages = , capital = Papeete , coordinates = , largest_city = Fa'a'ā , demonym = French Polynesian , ethnic_groups = 66.5% unmixed Polynesians7.1% mixed Polynesians9.3% Demis1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decapoda
The Decapoda or decapods (literally "ten-footed") are an order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, including many familiar groups, such as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is estimated to contain nearly 15,000 species in around 2,700 genera, with around 3,300 fossil species. Nearly half of these species are crabs, with the shrimp (about 3,000 species) and Anomura including hermit crabs, porcelain crabs, squat lobsters (about 2500 species) making up the bulk of the remainder. The earliest fossil decapod is the Devonian ''Palaeopalaemon''. Anatomy Decapods can have as many as 38 appendages, arranged in one pair per body segment. As the name Decapoda (from the Greek , ', "ten", and , '' -pod'', "foot") implies, ten of these appendages are considered legs. They are the pereiopods, found on the last five thoracic segments. In many decapods, one pair of these "legs" has enlarged pincers, called chelae, with the legs be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |