|
Cyclone Gwenda
Severe Tropical Cyclone Gwenda is tied with Cyclone Inigo as the most intense Australian tropical cyclone on record (with the possible exception of Cyclone Mahina), with a barometric pressure of 900 hPa (mbar) and was the most intense storm worldwide in 1999. Forming out of a tropical disturbance over the Arafura Sea on 2 April 1999, the precursor to Gwenda tracked slowly westward and gradually became more organised. On 4 April, the system developed into a Category 1 cyclone and was named Gwenda. It began to undergo explosive intensification the following day, and in a 30-hour span ending early on 7 April, the storm's maximum 10-minute sustained wind speed increased from to and its barometric pressure decreased to 900 hPa (mbar). The Joint Typhoon Warning Center reported that the storm had peaked as a high-end Category 4 equivalent on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale. Increasing wind shear and an acceleration in forward speed caused Gwenda to quickly weaken. Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone Inigo
Cyclone Inigo is tied with Cyclone Gwenda for being the most intense recorded cyclone in the Australian region in terms of pressure, with the possible exception of Cyclone Mahina. Inigo developed from a tropical low that crossed eastern Indonesia in late March 2003. Becoming a named tropical cyclone on 1 April, Inigo rapidly intensified as it tracked southwestward, reaching a minimum central pressure of 900 hPa on 4 April with maximum 1 minute sustained winds of 170mph. An approaching trough weakened the cyclone and turned it to the southeast, and on 8 April, Inigo dissipated after making landfall on Western Australia, as a minimal tropical storm. The precursor disturbance dropped heavy rainfall across eastern Indonesia, causing widespread flooding and mudslides. The worst of the damage was on Flores island, though damage was also reported on West Timor and Sumba. The flooding and mudslides damaged or destroyed thousands of houses, forcing many to leave their homes. A t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Meteorology (Australia)
The Bureau of Meteorology (BOM or BoM) is an executive agency of the Australian Government responsible for providing weather services to Australia and surrounding areas. It was established in 1906 under the Meteorology Act, and brought together the state meteorological services that existed before then. The states officially transferred their weather recording responsibilities to the Bureau of Meteorology on 1 January 1908. History The Bureau of Meteorology was established on 1 January 1908 following the passage of the ''Meteorology Act 1906''. Prior to Federation in 1901, each colony had had its own meteorological service, with all but two colonies also having a subsection devoted to astronomy. In August 1905, federal home affairs minister Littleton Groom surveyed state governments for their willingness to cede control, finding South Australia and Victoria unwilling. However, at a ministerial conference in April 1906 the state governments agreed to transfer responsibility for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Emergency Service
The State Emergency Service (SES) is the name used by a number of organisations in Australia that provide assistance during and after major incidents. Specifically, the service deals with floods, storms and tsunamis, but can also assist in other emergencies, such as vertical rescue and road crash rescues, missing persons searches, and medical evacuations. In other scenarios the SES may provide a support role to other agencies, particularly police and fire. The SES is operational 24 hours a day. The SES is constituted as separate organisations operating in the various Australian states and territories. Eight of the SES organisations co-ordinate through the Australian Council of State and Territory Emergency Services (ACSES). History During World War II the National Emergency Service was created on 1 February 1939 to provide air raid wardens. The organisation was disbanded six months after the end of the war. The Civil Defence Service began in Australia in 1955. It was form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exmouth, Western Australia
Exmouth is a town on the tip of the North West Cape and on Exmouth Gulf in Western Australia, north of the state capital Perth and southwest of Darwin. The town was established in 1967 to support the nearby United States Naval Communication Station Harold E. Holt. It is named after Exmouth Gulf. Beginning in the late 1970s, the town began hosting United States Air Force personnel assigned to Learmonth Solar Observatory, a defence science facility jointly operated with Australia's Ionospheric Prediction Service. The town is served by Learmonth Airport. History In 1618, Dutch East India Company ship ''Mauritius'', under command of Willem Janszoon, landed near North West Cape, just proximate to what would be Exmouth, and named Willem's River, which was later renamed Ashburton River. The location was first used as a military base in World War II. US Admiral James F. Calvert in his memoir, '' Silent Running: My Years on a World War II Attack Submarine'', and US Vice Admira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone Vance
Severe Tropical Cyclone Vance was a tropical cyclone that struck Western Australia during the active 1998–99 Australian region cyclone season, and was also one of six tropical cyclones to form off the coast of Australia during that season. When making landfall the Learmonth Meteorological Office (35 km south of Exmouth) recorded the highest Australian wind gust of .Bureau of Meteorologybr>Tropical Cyclone Vance in Review March 2000. URL Accessed: 30 December 2006 The previous highest gust was at nearby Mardie during Cyclone Trixie.Bureau of Meteorologybr>BoM Report on Vance March 2000. URL Accessed: 19 July 2006 This record was surpassed in 2010 after a world record wind-gust of at Barrow Island during Cyclone Olivia in 1996 was declared official by the World Meteorological Organisation. Forming on 19 March 1999, in the Timor Sea, Vance then curved west-southwest where it recurved and struck the Gascoyne and Pilbara coasts of Western Australia on 22 March as a Category& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Sustained Wind
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unlike gusts, the value of these winds are determined via their sampling and averaging the sampled results over a period of time. Wind measuring has been standardized globally to reflect the winds at above the Earth's surface, and the maximum sustained wind represents the highest average wind over either a one-minute (US) or ten-minute time span (see the definition, below), anywhere within the tropical cyclone. Surface winds are highly variable due to friction between the atmosphere and the Earth's surface, as well as near hills and mountains over land. Over the ocean, satellite imagery determines the value of the maximum sustained winds within a tropical cyclone. Land, ship, aircraft reconnaissance observations, and radar imagery can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilbara
The Pilbara () is a large, dry, thinly populated region in the north of Western Australia. It is known for its Aboriginal peoples; its ancient landscapes; the red earth; and its vast mineral deposits, in particular iron ore. It is also a global biodiversity hotspot for subterranean fauna. Definitions of the Pilbara region At least two important but differing definitions of "the Pilbara" region exist. Administratively it is one of the nine regions of Western Australia defined by the '' Regional Development Commissions Act 1993''; the term also refers to the Pilbara shrublands bioregion (which differs in extent) under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA). General The Pilbara region, as defined by the Regional Development Commissions Act 1993 and administered for economic development purposes by the Pilbara Development Commission, has an estimated population of 61,688 , and covers an area of . It contains some of Earth's oldest rock formations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category 5 Hurricane
Category, plural categories, may refer to: Philosophy and general uses *Categorization, categories in cognitive science, information science and generally *Category of being * ''Categories'' (Aristotle) * Category (Kant) *Categories (Peirce) * Category (Vaisheshika) *Stoic categories *Category mistake Mathematics * Category (mathematics), a structure consisting of objects and arrows * Category (topology), in the context of Baire spaces * Lusternik–Schnirelmann category, sometimes called ''LS-category'' or simply ''category'' * Categorical data, in statistics Linguistics * Lexical category, a part of speech such as ''noun'', ''preposition'', etc. *Syntactic category, a similar concept which can also include phrasal categories *Grammatical category, a grammatical feature such as ''tense'', ''gender'', etc. Other * Category (chess tournament) * Objective-C categories, a computer programming concept * Pregnancy category * Prisoner security categories in the United Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone Gwenda 1999 Near Landfall
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone). Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale (the synoptic scale). Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within smaller mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process of cyclone formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
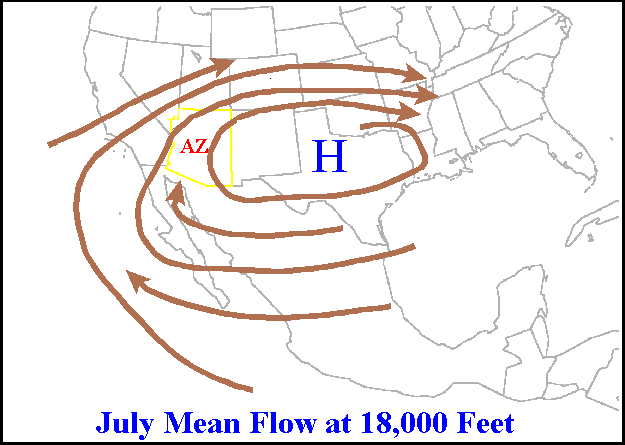
Ridge (meteorology)
A ridge or barometric ridge is a term in meteorology describing an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure compared to the surrounding environment, without being a closed circulation. It is associated with an area of maximum anticyclonic curvature of wind flow. The ridge originates in the center of an anticyclone and sandwiched between two low-pressure areas, and the locus of the maximum curvature is called the ''ridge line''. This phenomenon is the opposite of a trough. Description Ridges can be represented in two ways: * On surface weather maps, the pressure isobars form contours where the maximum pressure is found along the axis of the ridge. * In upper-air maps, geopotential height isohypses form similar contours where the maximum defines the ridge. Related weather Given the direction of the winds around an anticyclonic circulation and the fact that weather systems move from west to east: *ahead of an upper-ridge, the airflow that comes from the polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical Cyclone
A subtropical cyclone is a weather system that has some characteristics of both tropical and an extratropical cyclone. As early as the 1950s, meteorologists were uncertain whether they should be characterized as tropical or extratropical cyclones. They were officially recognized and titled by the National Hurricane Center in 1972. Beginning in 2002, subtropical cyclones received names from the official tropical cyclone lists in the North Atlantic, South-west Indian Ocean, and South Atlantic basins. There are two definitions currently used for subtropical cyclones depending on their location. Across the north Atlantic and southwest Indian Ocean, they require some central convection fairly near the center surrounding a warming core existing in the mid-levels of the troposphere. Across the eastern half of the northern Pacific however, they require a mid-tropospheric cyclone to be cut off from the main belt of the westerlies and with only a weak surface circulation. Subtropical cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outflow (meteorology)
Outflow, in meteorology, is air that flows outwards from a storm system. It is associated with ridging, or anticyclonic flow. In the low levels of the troposphere, outflow radiates from thunderstorms in the form of a wedge of rain-cooled air, which is visible as a thin rope-like cloud on weather satellite imagery or a fine line on weather radar imagery. For observers on the ground, a thunderstorm outflow boundary often approaches in otherwise clear skies as a low, thick cloud that brings with it a gust front. Low-level outflow boundaries can disrupt the center of small tropical cyclones. However, outflow aloft is essential for the strengthening of a tropical cyclone. If this outflow is restricted or undercut, the tropical cyclone weakens. If two tropical cyclones are in close proximity, the upper-level outflow from the upwind system can limit the development of the other system. Thunderstorms For thunderstorms, outflow tends to indicate the development of a system. Large qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |