|
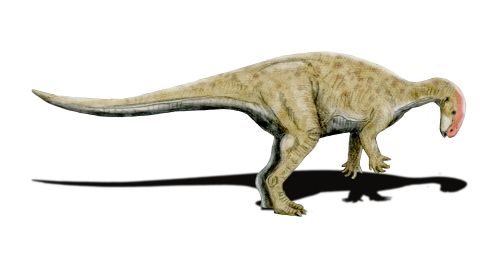
Cumnoria
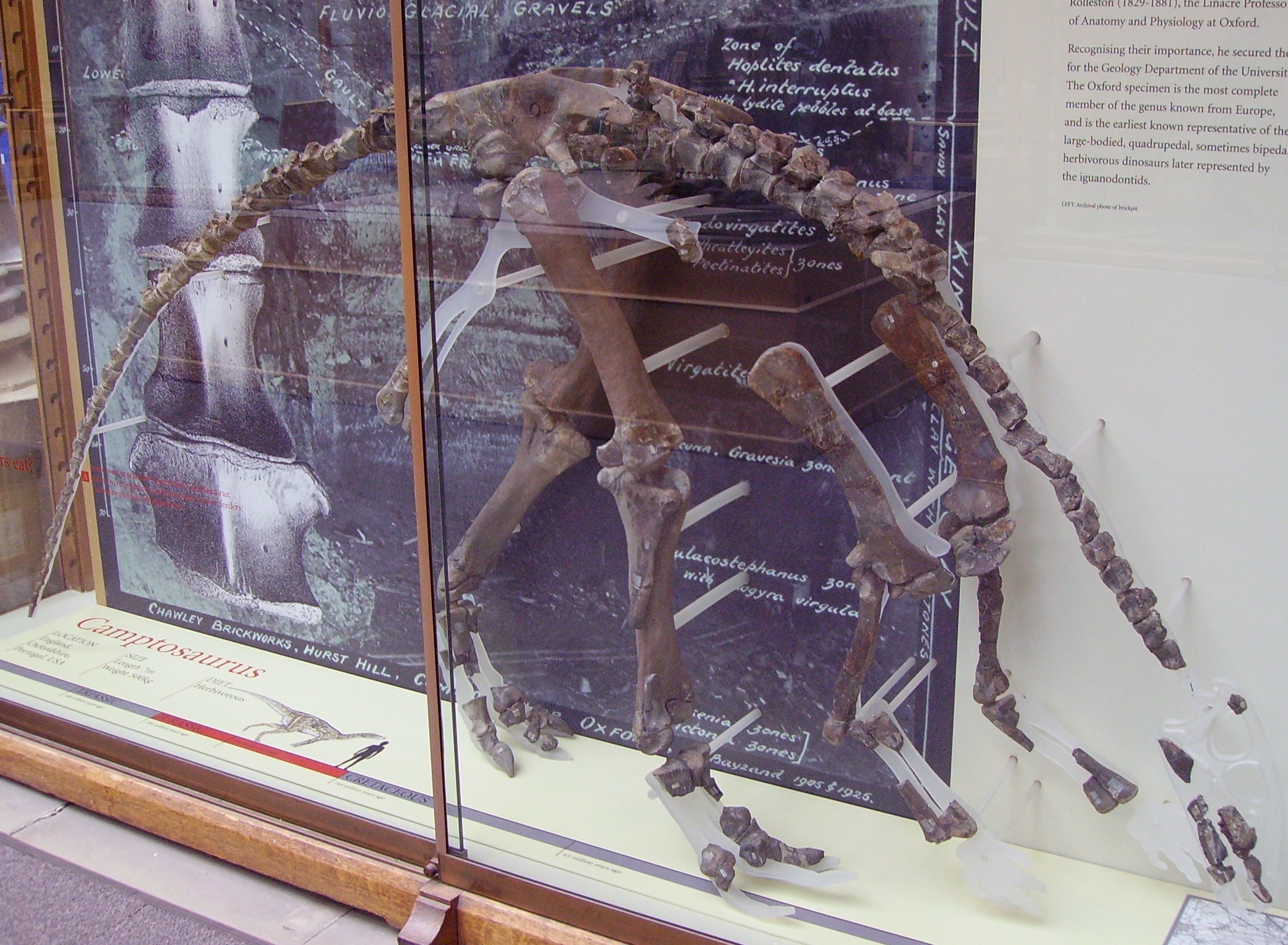
''Cumnoria'' is a genus of herbivorous iguanodontian dinosaur. It was a basal iguanodontian that lived during the Late Jurassic period (Kimmeridgian age) in what is now Oxfordshire, United Kingdom. Description The holotype of ''Cumnoria'' is of a rather small bipedal animal with a slender build. about 3.5 metres (11.4 feet) long, The specimen is probably that of a juvenile though. History of discovery ''Cumnoria'' is known from the holotype OXFUM J.3303, a partial skull and postcranium, recovered from the lower Kimmeridge Clay Formation, in the Chawley Brick Pits, Cumnor Hurst. Workers at first discarded the remains on a dump heap, but one of them later collected the bones in a sack and showed them to Professor George Rolleston, an anatomist at the nearby Oxford University. Rolleston in turn brought them to the attention of palaeontologist Professor Joseph Prestwich who in 1879 reported them as a new species of ''Iguanodon'', though without actually coining a species na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumnoria NT
''Cumnoria'' is a genus of herbivorous iguanodontian dinosaur. It was a basal iguanodontian that lived during the Late Jurassic period (Kimmeridgian age) in what is now Oxfordshire, United Kingdom. Description The holotype of ''Cumnoria'' is of a rather small bipedal animal with a slender build. about 3.5 metres (11.4 feet) long, The specimen is probably that of a juvenile though. History of discovery ''Cumnoria'' is known from the holotype OXFUM J.3303, a partial skull and postcranium, recovered from the lower Kimmeridge Clay Formation, in the Chawley Brick Pits, Cumnor Hurst. Workers at first discarded the remains on a dump heap, but one of them later collected the bones in a sack and showed them to Professor George Rolleston, an anatomist at the nearby Oxford University. Rolleston in turn brought them to the attention of palaeontologist Professor Joseph Prestwich who in 1879 reported them as a new species of ''Iguanodon'', though without actually coining a species name. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, Europe, and North America, taxonomic revision in the early 21st century has defined ''Iguanodon'' to be based on one well-substantiated species: ''I. bernissartensis'', which lived from the late Barremian to the earliest Aptian ages (Early Cretaceous) in Belgium, Germany, England, Spain, and possibly elsewhere in Europe, between about 126 and 122 million years ago. ''Iguanodon'' was a large, bulky herbivore, measuring up to in length and in body mass. Distinctive features include large thumb spikes, which were possibly used for defense against predators, combined with long prehensile fifth fingers able to forage for food. The genus was named in 1825 by English geologist Gideon Mantell but discovered by William Harding Bensted, ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camptosaurus
''Camptosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of plant-eating, beaked ornithischian dinosaurs of the Late Jurassic period of western North America and possibly also Europe. The name means 'flexible lizard' (Greek (') meaning 'bent' and (') meaning 'lizard'). Description ''Camptosaurus'' is a relatively heavily built form, with robust hindlimbs and broad feet, still having four toes. Due to the separate status of '' Uteodon'' it has become problematic which material from the Morrison Formation belongs to ''Camptosaurus''. The specimens with certainty belonging to ''Camptosaurus dispar'', from Quarry 13, have been recovered from very deep layers, probably dating to the Callovian- Oxfordian. The largest fragments from later strata indicate adult individuals more than long, and at the hips. The Quarry 13 individuals are smaller though. They have been described as reaching 6 meters (19.7 feet) in length and 785 – 874 kg in weight.Foster, J. (2007). "''Camptosaurus dispar''." ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumnor
Cumnor is a village and civil parish 3½ miles (5.6 km) west of the centre of Oxford, England. The village is about 2 miles (3.2 km) south-west of Botley and its centre is west of the A420 road to Swindon. The parish includes Cumnor Hill, (a ribbon development between Cumnor village and Botley), Chawley (at the top of Cumnor Hill), the Dean Court area on the edge of Botley and the outlying settlements of Chilswell, Farmoor, Filchampstead and Swinford. It was within Berkshire until the 1974 local government boundary changes transferred it to Oxfordshire. The 2011 Census recorded the parish population as 5,755. Amenities Cumnor has two public houses, the ''Vine'' and the ''Bear and Ragged Staff''. It has a butcher, a hairdresser, a sub-post office and greengrocer and a complementary health clinic. The newsagent closed in 2018. It has three churches: the Church of England parish church of St Michael in the centre of the village, Cumnor United Reformed Church in Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1888 In Paleontology
Newly named plants Dinosaurs Publications *Richard Lydekker published a catalogue of reptiles in the British Museum of Natural History The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museu ..., their collection information, and their classification. Newly named taxa Birds New taxa Plesiosaurs Newly named plesiosaurs Pterosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian See also References {{Reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimmeridge Clay Formation
The Kimmeridge Clay is a sedimentary deposit of fossiliferous marine clay which is of Late Jurassic to lowermost Cretaceous age and occurs in southern and eastern England and in the North Sea. This rock formation is the major source rock for North Sea oil. The fossil fauna of the Kimmeridge Clay includes turtles, crocodiles, sauropods, plesiosaurs, pliosaurs and ichthyosaurs, as well as a number of invertebrate species. Description Kimmeridge Clay is named after the village of Kimmeridge on the Dorset coast of England, where it is well exposed and forms part of the Jurassic Coast World Heritage Site. Onshore, it is of Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) age and outcrops across England, in a band stretching from Dorset in the south-west, north-east to North Yorkshire. Offshore, it extends into the Lower Cretaceous (Berriasian Stage) and it is found throughout the Southern, Central and Northern North Sea. The foundations of the Humber Bridge on the southern (Barton) side of the bridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomist
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the University of Oxford, the oldest university in the English-speaking world; it has buildings in every style of English architecture since late Anglo-Saxon. Oxford's industries include motor manufacturing, education, publishing, information technology and science. History The history of Oxford in England dates back to its original settlement in the Saxon period. Originally of strategic significance due to its controlling location on the upper reaches of the River Thames at its junction with the River Cherwell, the town grew in national importance during the early Norman period, and in the late 12th century became home to the fledgling University of Oxford. The city was besieged during The Anarchy in 1142. The university rose to domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Prestwich
Sir Joseph Prestwich, FRS (12 March 1812 – 23 June 1896) was a British geologist and businessman, known as an expert on the Tertiary Period and for having confirmed the findings of Boucher de Perthes of ancient flint tools in the Somme valley gravel beds. Biography Born in Clapham, Prestwich was educated in Paris and Reading before entering University College, London where he studied chemistry and natural philosophy. Whilst a student he founded the short-lived Zetetical Society. In 1830 he began working for the family wine business. This job required him to travel throughout the United Kingdom and also abroad to France and Belgium, and during the course of these travels he made many geological observations. He became a Fellow of Geological Society in 1833 and published his first paper there two years later. His 1836 memoir on the ''Geology of Coalbrookdale'', based upon observations made during 1831 and 1832, established his reputation as a geologist. From 1846 his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimmeridgian
In the geologic timescale, the Kimmeridgian is an age in the Late Jurassic Epoch and a stage in the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 157.3 ± 1.0 Ma and 152.1 ± 0.9 Ma (million years ago). The Kimmeridgian follows the Oxfordian and precedes the Tithonian. Stratigraphic definition The Kimmeridgian Stage takes its name from the village of Kimmeridge on the Dorset coast, England. The name was introduced into the literature by French geologist Alcide d'Orbigny in 1842. The Kimmeridge Clay Formation takes its name from the same type location (although this formation extends from the Kimmeridgian stage of the Upper Jurassic into the Lower Cretaceous). It is the source for about 95% of the petroleum in the North Sea. Historically, the term Kimmeridgian has been used in two different ways. The base of the interval is the same but the top was defined by British stratigraphers as the base of the Portlandian (''sensu anglico'') whereas in France the top was defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers ( strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |