|
1888 In Paleontology
Newly named plants Dinosaurs Publications *Richard Lydekker published a catalogue of reptiles in the British Museum of Natural History The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum an ..., their collection information, and their classification. Newly named taxa Birds New taxa Plesiosaurs Newly named plesiosaurs Pterosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian See also References {{Reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aachenosaurus
''Nicolia'' is a genus of Fossil wood, fossilized wood from the Late Cretaceous (Santonian-Campanian). At one time, specimens were misidentified as a jaw fragments of a hadrosaur and named ''Aachenosaurus''.H. N. Andrews. (1970). Index of Generic Names of Fossil Plants, 1820-1965. ''Geological Survey Bulletin'' 1-354 Taxonomy The genus and Monotypic taxon, sole species ''Nicolia aegyptiaca'' were named in 1842 by Unger. Independently in 1887, the name ''Aachenosaurus'' was created by the scientist (and abbé) Gerard Smets based on fossilized fragments of material that he thought were jaw fragments from a duck-billed dinosaur (a hadrosaur). However, the fossils turned out to be petrified wood, to the great embarrassment of the discoverer. The name ''Aachenosaurus'' means "Aachen lizard", named for the Aachen Formation of Moresnet (which was a neutral territory between Belgium and Germany), where the fossils were found. Smets considered that the specimen was a hadrosaur reaching an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleurocoelus
''Astrodon'' (aster: star, odon: tooth) is a genus of large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur, measuring in length, in height and in body mass. It lived in what is now the eastern United States during the Early Cretaceous period, and fossils have been found in the Arundel Formation, which has been dated through palynomorphs to the Albian about 112 to 110 million years ago. Discovery and species Two dinosaur teeth were received in late November 1858 by chemist Philip Thomas Tyson from John D. Latchford. They had been found in Latchford's open iron ore pit in the Arundel Formation at Swampoodle (Maryland), Swampoodle near Muirkirk, Maryland, Muirkirk in Prince George's County, Maryland. Tyson let them be studied by the dentist Christopher Johnston, professor at the Baltimore Dental College, who cut one tooth in half and thereby discovered a characteristic star-formed cross-section. Johnston named ''Astrodon'' in 1859. However, he did not attach a specific name (zoology), specific e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeohatteria
''Palaeohatteria'' is an extinct genus of basal sphenacodonts known from the Early Permian period (Sakmarian stage) of Saxony, Germany. It contains a single species, ''Palaeohatteria longicaudata''. Discovery ''Palaeohatteria'' is based on very young individuals including skulls and partial postcranial skeletons. All specimens were collected at Niederhäslich locality, in Dresden, from the Niederhäslich Limestone Member of the Niederhäslich Formation, Rotliegend Group (Döhlen Basin), dating to the Sakmarian stage of the Cisuralian series, about 295.0 -290.1 million years old. Description ''Palaeohatteria'' was a fairly small synapsid, up to 60 cm in length and with a mass of about 3 kg. The affinities of ''Palaeohatteria'' to the pelycosaur were first described in details by Alfred Sherwood Romer & Llewellyn Price (1940). They revised the taxonomy of pelycosaurs and synonymized ''Palaeohatteria'' (alongside with '' Pantelosaurus'' and others) with ''Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
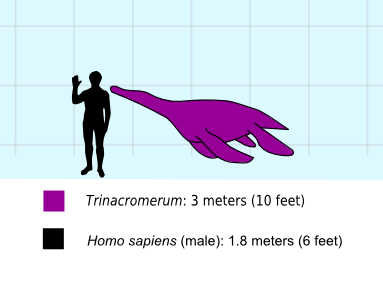
Trinacromerum BW
''Trinacromerum'' is an extinct genus of sauropterygian reptile, a member of the polycotylid plesiosaurs. It contains two species, ''T. bentonianum'' and ''T. kirki''. Specimens have been discovered in the Late Cretaceous fossil deposits of what is now modern Kansas and Manitoba. Description ''Trinacromerum'' was long. Its teeth show that it fed on small fish. The long flippers of ''Trinacromerum'' enabled it to achieve high swimming speeds. Its physical appearance was described by Richard Ellis as akin to a "four-flippered penguin."Ellis, 190 Its name means "three tipped femur". Classification Below is a cladogram of polycotylid relationships from Ketchum & Benson, 2011. See also * List of plesiosaur genera * Timeline of plesiosaur research This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinacromerum
''Trinacromerum'' is an extinct genus of sauropterygian reptile, a member of the polycotylid plesiosaurs. It contains two species, ''T. bentonianum'' and ''T. kirki''. Specimens have been discovered in the Late Cretaceous fossil deposits of what is now modern Kansas and Manitoba. Description ''Trinacromerum'' was long. Its teeth show that it fed on small fish. The long flippers of ''Trinacromerum'' enabled it to achieve high swimming speeds. Its physical appearance was described by Richard Ellis as akin to a "four-flippered penguin."Ellis, 190 Its name means "three tipped femur". Classification Below is a cladogram of polycotylid relationships from Ketchum & Benson, 2011. See also * List of plesiosaur genera * Timeline of plesiosaur research This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oluf Winge
Gustav Oluf Bang Winge (14 May 1855 Copenhagen – 16 February 1889)Collin, J. (1905) Winge, Gustav Oluf Bang. In: Bricka, C. F. (ed.) Dansk biografisk Lexikon, tillige omfattende, Norge for tidsrummet 1537-1814, XIX. BIND: 34. was a Danish zoologist. Biography The older brother of the zoologist Herluf Winge, Oluf also had since childhood a great interest in animals. He took in 1881 the title of "Magisterkonferens" in Natural History and in 1883 became assistant at the Zoologisk Museum. He worked mainly with ornithology, such as the birds recovered from the lighthouses in Denmark and his most important work, "Fugle fra Knoglehuler i Brasilien" (1888), on the fossil birds discovered in the caves in of the state of Minas Gerais in Brazil by his compatriot paleontologist Peter Wilhelm Lund.Winge, O. (1888) Fugle fra Knoglehuler i Brasilien – E Museo Lundii 1 (2): 1-54. He died in 1889, 33 years old, from an "incurable breast suffering". The Pleistocene condor genus ''Wingegyps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neochen Pugil
''Neochen pugil'' is an extinct species of goose from the Late Pleistocene or possibly the Early Holocene of Brazil. The fossils were discovered by Danish paleontologist Peter Wilhelm Lund near Lagoa Santa, Minas Gerais state, and described by Danish ornithologist Oluf Winge in 1888. It was related to the living Orinoco goose The Orinoco goose (''Neochen jubata'') is a Near-threatened species, Near Threatened species of waterfowl in tribe Tadornini of subfamily Anserinae.HBW and BirdLife International (2021) Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife Internatio ..., but much larger.Winge, O. (1888) Fugle fra Knoglehuler i Brasilien – E Museo Lundii 1 (2): 1-54. References External links * * Tadorninae Pleistocene birds Quaternary birds of South America Pleistocene Brazil Fossils of Brazil Fossil taxa described in 1888 {{Paleo-bird-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priconodon
''Priconodon'' (meaning "saw cone tooth") is an extinct genus of dinosaur (perhaps nodosaurid), known from its large teeth. Its remains have been found in the Aptian-Albian age Lower Cretaceous Arundel Formation of Muirkirk, Prince George's County, Maryland, USA and the Potomac Group, also located in Maryland. History O. C. Marsh named the genus for USNM 2135, a large worn tooth from what was then called the Potomac Formation. As ankylosaurians were by and large unknown at the time, he compared it to '' Diracodon'' (=''Stegosaurus'') teeth.Marsh, O.C. (1888). Notice of a new genus of Sauropoda and other new dinosaurs from the Potomac Formation. ''American Journal of Science'' 135:89-94. It was not identified as an ankylosaurian until Walter Coombs assigned it to Nodosauridae in 1978.Coombs, Jr., W.P. (1978). The families of the ornithischian dinosaur order Ankylosauria. ''Palaeontology'' 21(1):143-170. In 1998 Kenneth Carpenter and James Kirkland, in a review of North American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrodon
''Astrodon'' (aster: star, odon: tooth) is a genus of large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur, measuring in length, in height and in body mass. It lived in what is now the eastern United States during the Early Cretaceous period, and fossils have been found in the Arundel Formation, which has been dated through palynomorphs to the Albian about 112 to 110 million years ago. Discovery and species Two dinosaur teeth were received in late November 1858 by chemist Philip Thomas Tyson from John D. Latchford. They had been found in Latchford's open iron ore pit in the Arundel Formation at Swampoodle near Muirkirk in Prince George's County, Maryland. Tyson let them be studied by the dentist Christopher Johnston, professor at the Baltimore Dental College, who cut one tooth in half and thereby discovered a characteristic star-formed cross-section. Johnston named ''Astrodon'' in 1859. However, he did not attach a specific epithet, so Joseph Leidy is credited with naming ''Astrodon joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
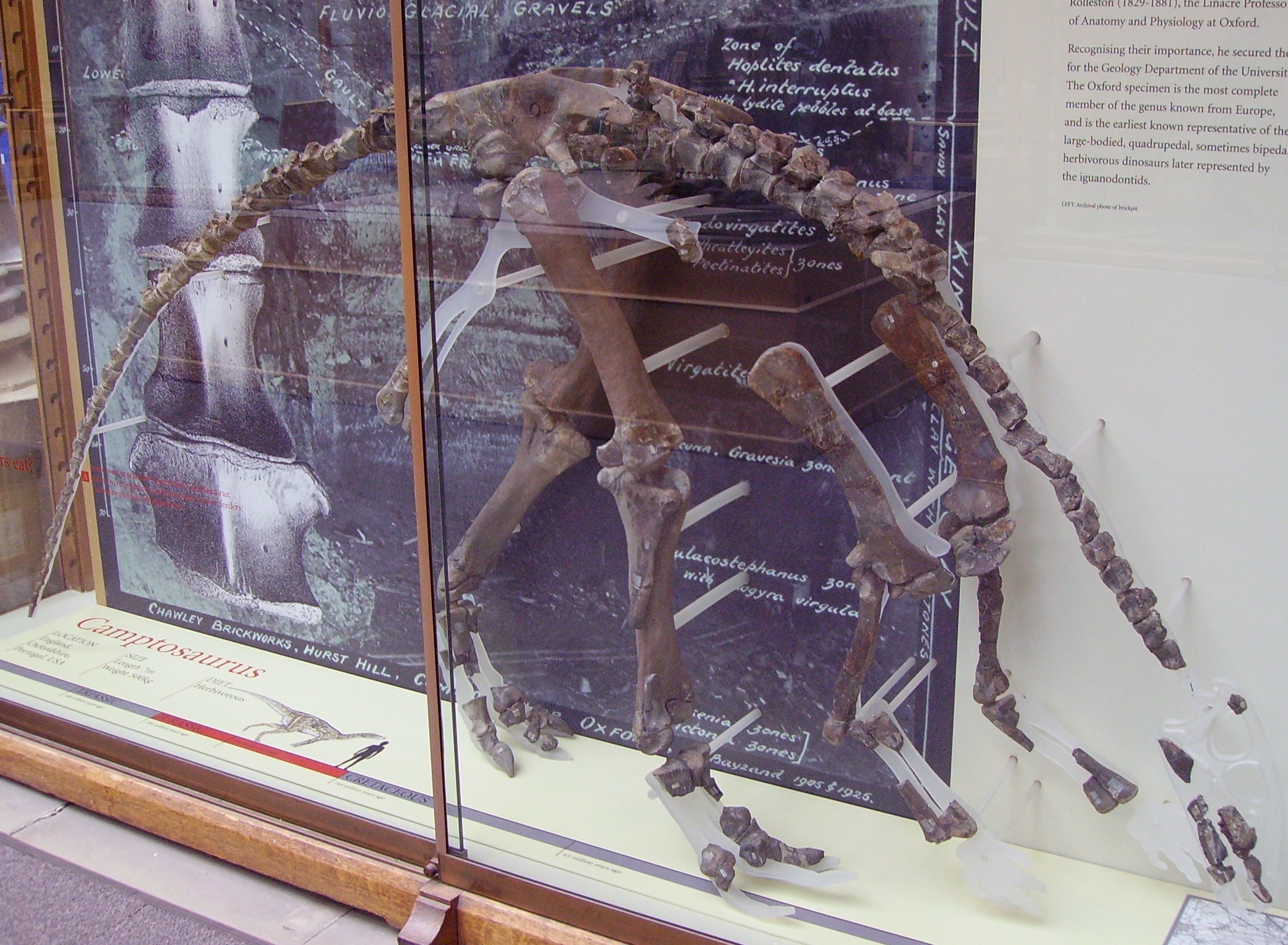
Cumnoria Incomplete Skeleton
''Cumnoria'' is a genus of herbivorous iguanodontian dinosaur. It was a basal iguanodontian that lived during the Late Jurassic period (Kimmeridgian age) in what is now Oxfordshire, United Kingdom. Description The holotype of ''Cumnoria'' is of a rather small bipedal animal with a slender build. about 3.5 metres (11.4 feet) long, The specimen is probably that of a juvenile though. History of discovery ''Cumnoria'' is known from the holotype OXFUM J.3303, a partial skull and postcranium, recovered from the lower Kimmeridge Clay Formation, in the Chawley Brick Pits, Cumnor Hurst. Workers at first discarded the remains on a dump heap, but one of them later collected the bones in a sack and showed them to Professor George Rolleston, an anatomist at the nearby Oxford University. Rolleston in turn brought them to the attention of palaeontologist Professor Joseph Prestwich who in 1879 reported them as a new species of ''Iguanodon'', though without actually coining a species name. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen Dubium
In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application. Zoology In case of a ''nomen dubium'' it may be impossible to determine whether a specimen belongs to that group or not. This may happen if the original type series (i. e. holotype, isotype, syntype or paratype) is lost or destroyed. The zoological and botanical codes allow for a new type specimen, or neotype, to be chosen in this case. A name may also be considered a ''nomen dubium'' if its name-bearing type is fragmentary or lacking important diagnostic features (this is often the case for species known only as fossils). To preserve stability of names, the ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature'' allows a new type specimen, or neotype, to be chosen for a ''nomen dubium'' in this case. 75.5. Replacement of unidentifiable name-bearing type by a neotype. When an author considers that the taxonomic identity of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |