|
Culture Theory
Culture theory is the branch of comparative anthropology and semiotics (not to be confused with cultural sociology or cultural studies) that seeks to define the heuristic concept of culture in operational and/or scientific terms. Overview In the 19th century, "culture" was used by some to refer to a wide array of human activities, and by some others as a synonym for "civilization". In the 20th century, anthropologists began theorizing about culture as an object of scientific analysis. Some used it to distinguish human adaptive strategies from the largely instinctive adaptive strategies of animals, including the adaptive strategies of other primates and non-human hominids, whereas others used it to refer to symbolic representations and expressions of human experience, with no direct adaptive value. Both groups understood culture as being definitive of human nature. According to many theories that have gained wide acceptance among anthropologists, culture exhibits the way tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of behavior, while cultural anthropology studies cultural meaning, including norms and values. A portmanteau term sociocultural anthropology is commonly used today. Linguistic anthropology studies how language influences social life. Biological or physical anthropology studies the biological development of humans. Archaeological anthropology, often termed as 'anthropology of the past', studies human activity through investigation of physical evidence. It is considered a branch of anthropology in North America and Asia, while in Europe archaeology is viewed as a discipline in its own right or grouped under other related disciplines, such as history and palaeontology. Etymology The abstract noun ''anthropology'' is first attested in reference t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Nature
Human nature is a concept that denotes the fundamental dispositions and characteristics—including ways of thinking, feeling, and acting—that humans are said to have naturally. The term is often used to denote the essence of humankind, or what it 'means' to be human. This usage has proven to be controversial in that there is dispute as to whether or not such an essence actually exists. Arguments about human nature have been a central focus of philosophy for centuries and the concept continues to provoke lively philosophical debate. While both concepts are distinct from one another, discussions regarding human nature are typically related to those regarding the comparative importance of genes and environment in human development (i.e., ' nature versus nurture'). Accordingly, the concept also continues to play a role in academic fields, such as the natural sciences, social sciences, history, and philosophy, in which various theorists claim to have yielded insight into hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Behaviour
Human behavior is the potential and expressed capacity ( mentally, physically, and socially) of human individuals or groups to respond to internal and external stimuli throughout their life. Kagan, Jerome, Marc H. Bornstein, and Richard M. Lerner.Human Behaviour." ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2020. Retrieved 5 June 2020. Behavior is driven by genetic and environmental factors that affect an individual. Behavior is also driven, in part, by thoughts and feelings, which provide insight into individual psyche, revealing such things as attitudes and values. Human behavior is shaped by psychological traits, as personality types vary from person to person, producing different actions and behavior. Social behavior accounts for actions directed at others. It is concerned with the considerable influence of social interaction and culture, as well as ethics, interpersonal relationships, politics, and conflict. Some behaviors are common while others are unusual. The acceptability of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sexuality
Human sexuality is the way people experience and express themselves sexually. This involves biological, psychological, physical, erotic, emotional, social, or spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied with historical contexts over time, it lacks a precise definition. The biological and physical aspects of sexuality largely concern the human reproductive functions, including the human sexual response cycle. Someone's sexual orientation is their pattern of sexual interest in the opposite or same sex. Physical and emotional aspects of sexuality include bonds between individuals that are expressed through profound feelings or physical manifestations of love, trust, and care. Social aspects deal with the effects of human society on one's sexuality, while spirituality concerns an individual's spiritual connection with others. Sexuality also affects and is affected by cultural, political, legal, philosophical, moral, ethical, and religious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-human Animal Sexuality
Animal sexual behaviour takes many different forms, including within the same species. Common mating or reproductively motivated systems include monogamy, polygyny, polyandry, polygamy and promiscuity. Other sexual behaviour may be reproductively motivated (e.g. sex apparently due to duress or coercion and situational sexual behaviour) or non-reproductively motivated (e.g. homosexual sexual behaviour, bisexual sexual behaviour, cross-species sex, sexual arousal from objects or places, sex with dead animals, etc.). When animal sexual behaviour is reproductively motivated, it is often termed ''mating'' or ''copulation''; for most non-human mammals, mating and copulation occur at oestrus (the most fertile period in the mammalian female's reproductive cycle), which increases the chances of successful impregnation. Some animal sexual behaviour involves competition, sometimes fighting, between multiple males. Females often select males for mating only if they appear strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
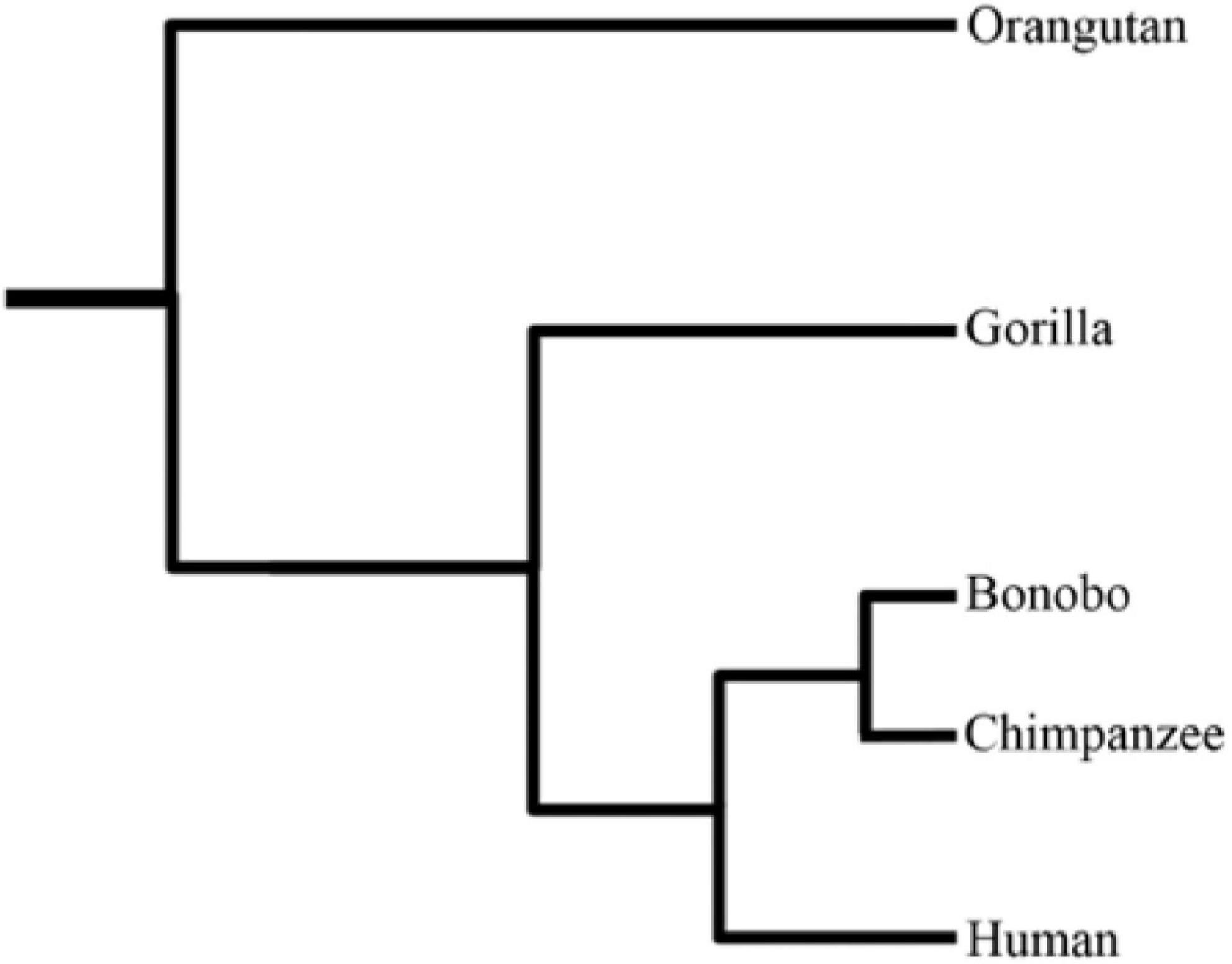
Bonobo
The bonobo (; ''Pan paniscus''), also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee and less often the dwarf chimpanzee or gracile chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus '' Pan,'' the other being the common chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''). While bonobos are now recognized as a distinct species in their own right, they were initially thought to be a subspecies of chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes)'' due to the physical similarities between the two species. Taxonomically, the members of the chimpanzee/bonobo subtribe Panina (composed entirely by the genus '' Pan'') are collectively termed ''panins''. The bonobo is distinguished by relatively long legs, pink lips, dark face, tail-tuft through adulthood, and parted long hair on its head. The bonobo is found in a area of the Congo Basin in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Central Africa. The species is frugivorous and inhabits primary and secondary forests, including seasonally inundated sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of Hominidae, great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative the bonobo was more commonly known as the pygmy chimpanzee, this species was often called the common chimpanzee or the robust chimpanzee. The chimpanzee and the bonobo are the only species in the genus Pan (genus), ''Pan''. Evidence from fossils and DNA sequencing shows that ''Pan'' is a sister taxon to the Human evolution, human lineage and is humans' closest living relative. The chimpanzee is covered in coarse black hair, but has a bare face, fingers, toes, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It is larger and more Robustness (morphology), robust than the bonobo, weighing for males and for females and standing . The chimpanzee lives in groups that range in size from 15 to 150 members, although individuals travel and forag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Evolution
Human evolution is the evolutionary process within the history of primates that led to the emergence of ''Homo sapiens'' as a distinct species of the hominid family, which includes the great apes. This process involved the gradual development of traits such as human bipedalism and language, as well as interbreeding with other hominins, which indicate that human evolution was not linear but a web.Human Hybrids (PDF). Michael F. Hammer. ''Scientific American'', May 2013. The study of human evolution involves scientific disciplines, including [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an Discipline (academia), academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the historiography, nature of history as an end in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Change
Social change is the alteration of the social order of a society which may include changes in social institutions, social behaviours or social relations. Definition Social change may not refer to the notion of social progress or sociocultural evolution, the philosophical idea that society moves forward by evolutionary means. It may refer to a paradigmatic change in the socio-economic structure, for instance the transition from feudalism to capitalism, or hypothetical future transition to some form of post-capitalism. Social development refers to how people develop social and emotional skills across the lifespan, with particular attention to childhood and adolescence. Healthy social development allows us to form positive relationships with family, friends, teachers, and other people in our lives. Accordingly, it may also refer to social revolution, such as the Socialist revolution presented in Marxism, or to other social movements, such as women's suffrage or the civil ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Existentialism
Existentialism ( ) is a form of philosophical inquiry that explores the problem of human existence and centers on human thinking, feeling, and acting. Existentialist thinkers frequently explore issues related to the meaning, purpose, and value of human existence, and the role of personal agency in transforming one's life. In the view of an existentialist, the individual's starting point is phenomenological, grounded in the immediate direct experience of life. Key concepts include " existential angst", a sense of dread, disorientation, confusion, or anxiety in the face of an apparently meaningless or absurd world, and also authenticity, courage, and human-heartedness. Existentialism is associated with several 19th- and 20th-century European philosophers who shared an emphasis on the human subject, despite often profound differences in thought. Among the earliest figures associated with existentialism are philosophers Søren Kierkegaard and Friedrich Nietzsche and novel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)






.jpg)
