|
Cultural Christianity
Cultural Christians are nonreligious persons who adhere to Christian values and appreciate Christian culture. As such, these individuals usually identify themselves as culturally Christians, and are often seen by practicing believers as nominal Christians. This kind of identification may be due to various factors, such as family background, personal experiences, and the social and cultural environment in which they grew up. Contrasting terms are "biblical Christian", "committed Christian", or "believing Christian". The term "Cultural Christian" may be specified further by Christian denomination, e.g. "Cultural Catholic", "Cultural Lutheran", and "Cultural Anglican". Usage Belarus The President of Belarus, Alexander Lukashenko, has identified as cultural Christian, calling himself an "Orthodox atheist" in one of his interviews. France French Deists of the 18th and early 19th centuries include Napoleon. The current President of France, Emmanuel Macron, identified himself as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Values
Christian values historically refers to values derived from the teachings of Jesus Christ. The term has various applications and meanings, and specific definitions can vary widely between denominations, geographical locations and different schools of thought. The terms Christian values and family values are often used as a euphemism for familialism by the Christian right. Christian values also relate to the Christian identity in identity politics. Paul Since the first century, The Bible has summarized Christians values as the Fruit of the Spirit. The list, written by the Apostle Paul in his letter to the Galatians includes: * Love * Joy * Peace * Patience * Kindness * Goodness * Faithfulness * Gentleness * Self-control Modern use in worldwide conservative or right-wing politics In the 21st century United States, Australia, United Kingdom and other countries, the phrases Christian values and family values are used by Christian right and conservative parties to describe some o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Xiaofeng (academic)
Liu Xiaofeng (born 1956; ) is a contemporary Chinese scholar and a professor at Renmin University of China. He has been considered the prototypical example of what is called a cultural Christian (), meaning a believer who may lack a specific church identification or affiliation, and was, along with He Guanghu, one of the main forerunners of the academic field of Sino-Christian Theology (). However, in recent years, his interest has shifted from studies in Christian theology to the political theories of Leo Strauss and Carl Schmitt. Biography Liu Xiaofeng was born in Chongqing, China, in April 1956. He completed his Bachelor of Arts degree in German language and literature at Sichuan International Studies University before beginning his Master of Arts in aesthetics at Peking University in 1982, completing it in 1985. He later received a scholarship to study at the University of Basel in Switzerland in April 1989, where he completed his Ph.D in Christian theology in 1993 on a the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theism
Theism is broadly defined as the belief in the existence of a supreme being or deities. In common parlance, or when contrasted with ''deism'', the term often describes the classical conception of God that is found in monotheism (also referred to as classical theism) – or gods found in polytheistic religions—a belief in God or in gods without the rejection of revelation as is characteristic of deism. Gnosticism is the belief in personal spiritual knowledge. Atheism is commonly understood as non-acceptance or rejection of theism in the broadest sense of theism, i.e. non-acceptance or rejection of belief in God or gods. Related, but separate, is the claim that the existence of any deity is unknown or unknowable: agnosticism.(page 56 in 1967 edition) Combined with theism, is agnostic theism. Etymology The term ''theism'' derives from the Greek (''theós'') or ''theoi'' meaning "god" or "gods". The term ''theism'' was first used by Ralph Cudworth (1617–1688). In Cudworth's de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnival In The Netherlands
Carnival in the Netherlands ( nl, Carnaval; also called "vastenavond" – eve of the fasting or li, "vastelaovend") is a festival held mainly in the Southern and Eastern regions of the Netherlands with an emphasis on role-reversal and the suspension of social norms, as part of celebrations of Carnival. The feast was assimilated by the Catholic Church, taking elements from ancient pagan spring festivals and is celebrated in the three days preceding the Christian holidays of Ash Wednesday and Lent. From an anthropological point of view, Carnival is a reversal ritual, in which social roles are reversed and norms about desired behavior are suspended. Winter was thought of as the reign of the winter spirits that were to be driven out for summer to return. Carnival can thus be regarded as a rite of passage from darkness to light, from winter to summer: a fertility celebration, the first spring festival of the new year. It precedes the Christian penitential season of Lent. The firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secularization
In sociology, secularization (or secularisation) is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The ''secularization thesis'' expresses the idea that as societies progress, particularly through modernization, rationalization, and advances in science and technology, religious authority diminishes in all aspects of social life and governance."The Secularization Debate" chapter 1 (pp 3 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the '' Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X until January 1521. The Diet of Worms of May 152 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, taxation, and the rights and privileges of the nobility and cities. After the initial stages, Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Netherlands, deployed his armies and regained control over most of the rebel-held territories. However, widespread mutinies in the Spanish army caused a general uprising. Under the leadership of the exiled William the Silent, the Catholic- and Protestant-dominated provinces sought to establish religious peace while jointly opposing the king's regime with the Pacification of Ghent, but the general rebellion failed to sustain itself. Despite Governor of Spanish Netherlands and General for Spain, the Duke of Parma's steady military and diplomatic successes, the Union of Utrecht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church In The Netherlands
, native_name_lang = , image = Catharijnekerk Utrecht.jpg , imagewidth = 200px , alt = , caption = St Catherine's Cathedral, Utrecht. , abbreviation = , type = National polity , main_classification = Catholic , orientation = , scripture = , theology = , polity = , governance = Episcopal , structure = , leader_title = Pope , leader_name = Pope Francis , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Bishop Hans van den Hende , leader_title2 = Primate , leader_name2 = Archbishop Wim Eijk , leader_title3 = Apostolic Nuncio , leader_name3 = Aldo Cavalli , fellowships_type = , fellowships = , fellowships_type1 = , fellowships1 = , division_type = , division = , division_type1 = , division1 = , division_type2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands , established_title = Before independence , established_date = Spanish Netherlands , established_title2 = Act of Abjuration , established_date2 = 26 July 1581 , established_title3 = Peace of Münster , established_date3 = 30 January 1648 , established_title4 = Kingdom established , established_date4 = 16 March 1815 , established_title5 = Liberation Day (Netherlands), Liberation Day , established_date5 = 5 May 1945 , established_title6 = Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Kingdom Charter , established_date6 = 15 December 1954 , established_title7 = Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, Caribbean reorganisation , established_date7 = 10 October 2010 , official_languages = Dutch language, Dutch , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = , languages2_type = Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
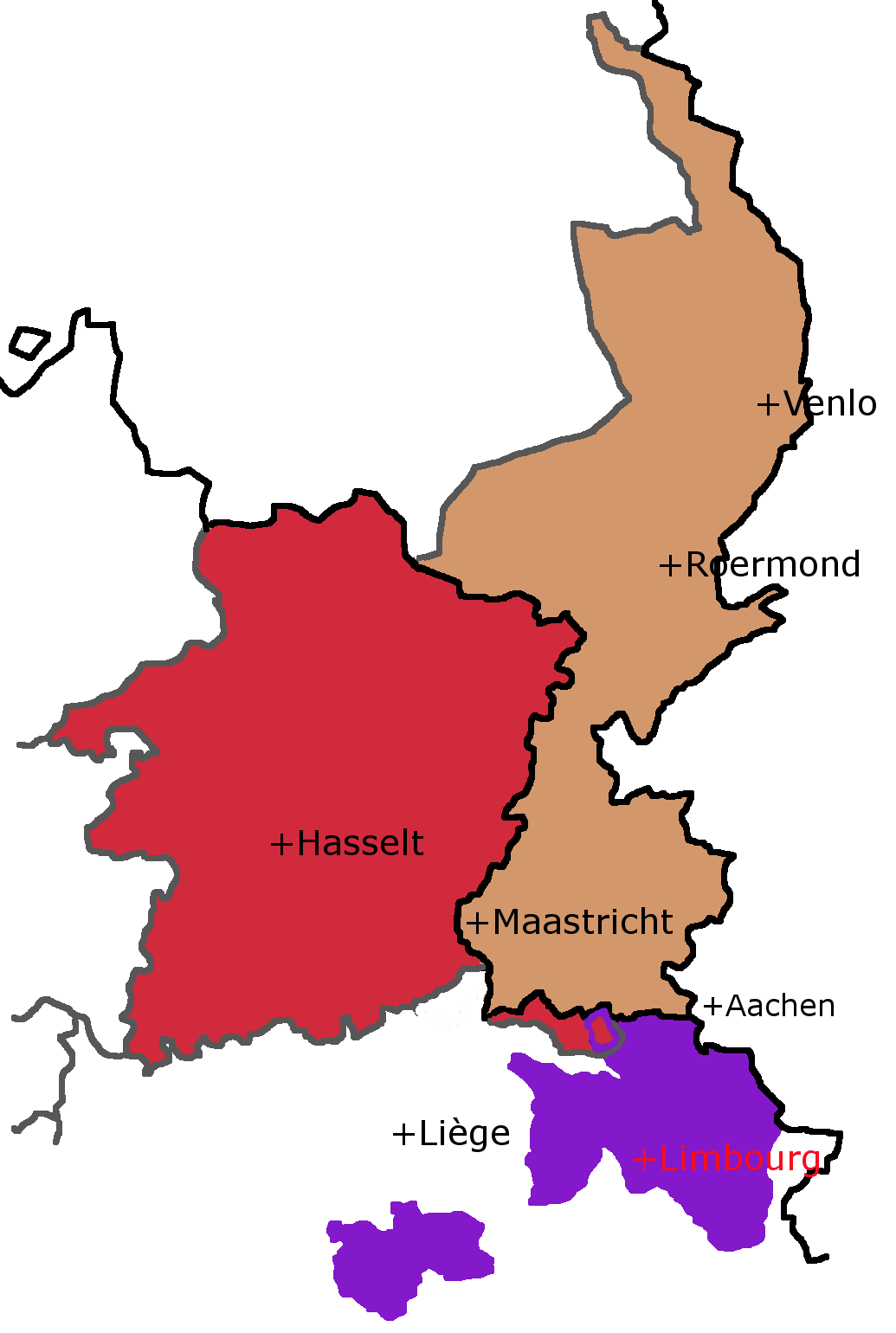
Limburg (Netherlands)
Limburg (, ) is the southernmost of the twelve provinces of the Netherlands. It is bordered by Gelderland to the north and by North Brabant to its west. Its long eastern boundary forms the international border with the state of North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. To the west is the international border with the similarly named Belgian province of Limburg, part of which is delineated by the river Meuse. The Vaalserberg is on the extreme southeastern point, marking the tripoint of the Netherlands, Germany and Belgium. Limburg's main municipalities are the provincial capital Maastricht (population 120,837 as of January 2022), Venlo (population 102,176) in the northeast, as well as Sittard-Geleen (population 91,760, bordering both Belgium and Germany) and Heerlen (population 86,874) in the south. More than half of the population, approximately 650,000 people, live in the south of Limburg, which corresponds to roughly one-third of the province's area proper. In South Limburg, most peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Brabant
North Brabant ( nl, Noord-Brabant ; Brabantian: ; ), also unofficially called Brabant, is a province in the south of the Netherlands. It borders the provinces of South Holland and Gelderland to the north, Limburg to the east, Zeeland to the west, and the Flemish provinces of Antwerp and Limburg to the south. The northern border follows the Meuse westward to its mouth in the Hollands Diep strait, part of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. North Brabant has a population of 2,562,566 as of November 2019. Major cities in North Brabant are Eindhoven (pop. 231,642), Tilburg (pop. 217,259), Breda (pop. 183,873) and its provincial capital 's-Hertogenbosch (pop. 154,205). History The Duchy of Brabant was a state of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183 or 1190. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was split up after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)