|
Cuchulain Of Muirthemne
''Cuchulain of Muirthemne'' is a version of the Cú Chulainn legends based on previous oral and written versions, as collected and translated by Lady Augusta Gregory. First published in 1902, it is one of the earliest such collections to appear in English. The book covers the lifespan of the hero, from conception to death, and draws on folklore and oral tradition in addition to the stories of the Ulster Cycle. Background Lady Gregory considered herself a supporter of the Irish Literary Revival, rather than a writer. She recorded in her diary that "I dreamed that I had been writing some article & that W.B.Y. said 'It's not your business to write – Your business is to make an atmosphere'". She undertook the book only after William Butler Yeats refused an offer to translate his own edition of Irish myth. In 1900, a commission on education in Ireland issued a report, declaring Irish literature to be devoid of idealism or imagination. This report, written by Trinity College Professo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cú Chulainn
Cú Chulainn ( ), called the Hound of Ulster (Irish: ''Cú Uladh''), is a warrior hero and demigod in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology, as well as in Scottish and Manx folklore. He is believed to be an incarnation of the Irish god Lugh, who is also his father. His mother is the mortal Deichtine, sister of king Conchobar mac Nessa. Born Sétanta, he gained his better-known name as a child, after killing Culann's fierce guard dog in self defence and offering to take its place until a replacement could be reared, hence he became the "Hound (''cú'') of Culann". He was trained in martial arts by Scáthach, who gave him the spear Gáe Bulg. It was prophesied that his great deeds would give him everlasting fame, but that his life would be short. At the age of seventeen he defends Ulster single-handedly against the armies of queen Medb of Connacht in the famous ''Táin Bó Cúailnge'' ("Cattle Raid of Cooley"). He is known for his terrifying battle frenzy (''ríastrad''), in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Nationalism
Irish nationalism is a nationalist political movement which, in its broadest sense, asserts that the people of Ireland should govern Ireland as a sovereign state. Since the mid-19th century, Irish nationalism has largely taken the form of cultural nationalism based on the principles of national self-determination and popular sovereignty.Sa'adah 2003, 17–20.Smith 1999, 30. Irish nationalists during the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries such as the United Irishmen in the 1790s, Young Irelanders in the 1840s, the Fenian Brotherhood during the 1880s, Fianna Fáil in the 1920s, and Sinn Féin styled themselves in various ways after French left-wing radicalism and republicanism. Irish nationalism celebrates the culture of Ireland, especially the Irish language, literature, music, and sports. It grew more potent during the period in which all of Ireland was part of the United Kingdom, which led to most of the island gaining independence from the UK in 1922. Irish nationalists believ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
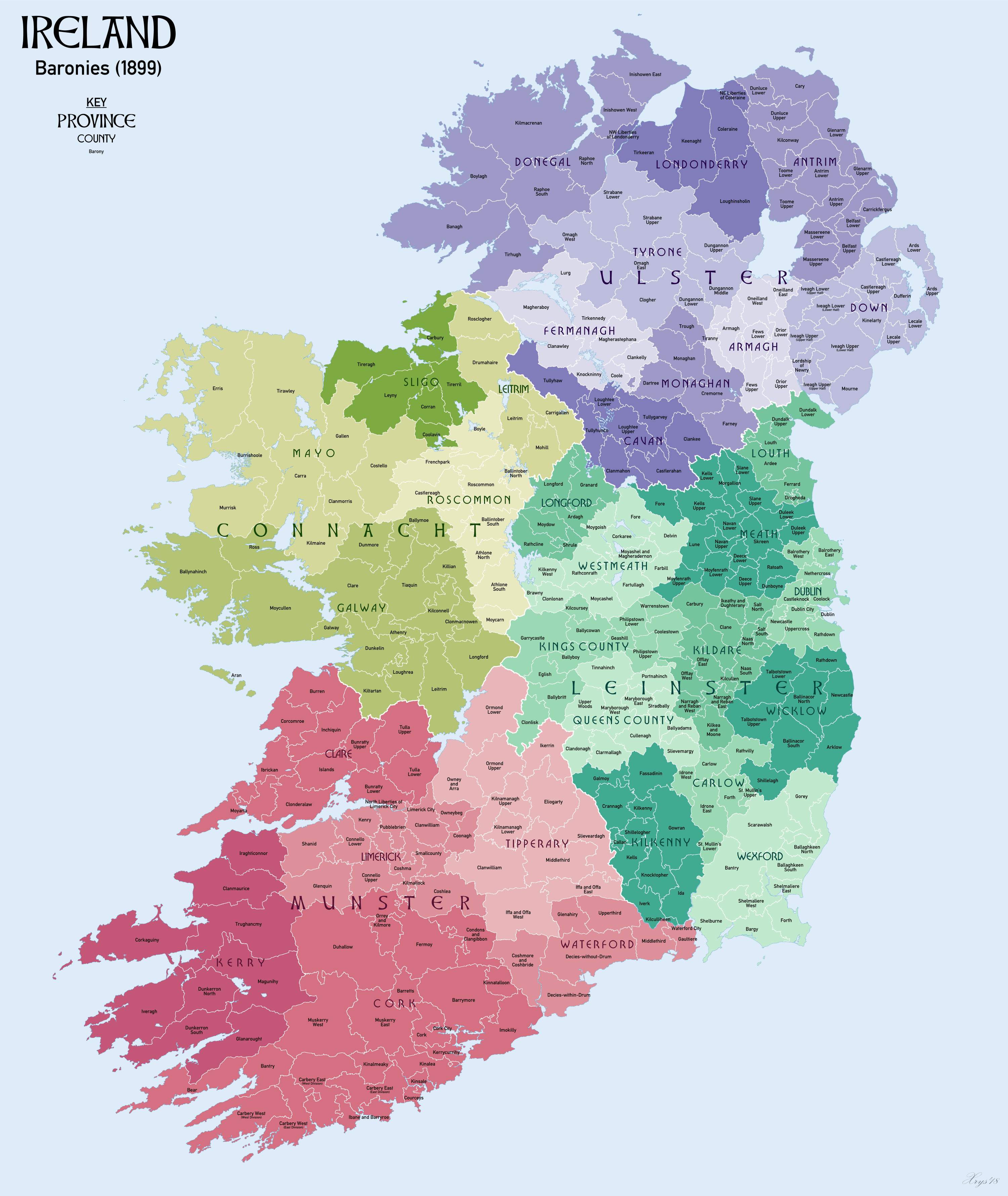
Barony (Ireland)
In Ireland, a barony ( ga, barúntacht, plural ) is a historical subdivision of a county, analogous to the hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion.Mac Cotter 2005, pp.327–330 Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Subsequent adjustments of county boundaries mean that some baronies now straddle two counties. The final catalogue of baronies numbered 331, with an average area of ; therefore, each county was divided, on average, into 10 or 11 baronies. Creation The island of Ireland was "shired" into counties in two distinct periods: the east and south duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Morte D'Arthur
' (originally written as '; inaccurate Middle French for "The Death of Arthur") is a 15th-century Middle English prose reworking by Sir Thomas Malory of tales about the legendary King Arthur, Guinevere, Lancelot, Merlin and the Knights of the Round Table, along with their respective folklore. In order to tell a "complete" story of Arthur from his conception to his death, Malory compiled, rearranged, interpreted and modified material from various French and English sources. Today, this is one of the best-known works of Arthurian literature. Many authors since the 19th-century revival of the legend have used Malory as their principal source. Apparently written in prison at the end of the medieval English era, ''Le Morte d'Arthur'' was completed by Malory around 1470 and was first published in a printed edition in 1485 by William Caxton. Until the discovery of the Winchester Manuscript in 1934, the 1485 edition was considered the earliest known text of ''Le Morte d'Arthur'' and that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Malory
Sir Thomas Malory was an English writer, the author of '' Le Morte d'Arthur'', the classic English-language chronicle of the Arthurian legend, compiled and in most cases translated from French sources. The most popular version of '' Le Morte d'Arthur'' was published by the famed London printer William Caxton in 1485. Much of Malory's life history is obscure, but he identified himself as a "knight prisoner", apparently reflecting that he was either a criminal or a prisoner-of-war. Malory's identity has never been confirmed. However, since modern scholars began researching his identity the most widely accepted candidate has been Sir Thomas Malory of Newbold Revel in Warwickshire, who was imprisoned at various times for criminal acts and possibly also for political reasons during the Wars of the Roses. Identity Most of what is known about Malory stems from the accounts describing him in the prayers found in the Winchester Manuscript of ''Le Morte d'Arthur''. He is described as a "" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mabinogion
The ''Mabinogion'' () are the earliest Welsh prose stories, and belong to the Matter of Britain. The stories were compiled in Middle Welsh in the 12th–13th centuries from earlier oral traditions. There are two main source manuscripts, created c. 1350–1410, as well as a few earlier fragments. The title covers a collection of eleven prose stories of widely different types, offering drama, philosophy, romance, tragedy, fantasy and humour, and created by various narrators over time. There is a classic hero quest, "Culhwch and Olwen"; a historic legend in "Lludd and Llefelys," complete with glimpses of a far off age; and other tales portray a very different King Arthur from the later popular versions. The highly sophisticated complexity of the Four Branches of the Mabinogi defies categorisation. The stories are so diverse that it has been argued that they are not even a true collection. Scholars from the 18th century to the 1970s predominantly viewed the tales as fragmentary p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady Charlotte Guest
Lady Charlotte Elizabeth Guest (née Bertie; 19 May 1812 – 15 January 1895), later Lady Charlotte Schreiber, was an English aristocrat who is best known as the first publisher in modern print format of the '' Mabinogion'', the earliest prose literature of Britain. Guest established the ''Mabinogion'' as a source literary text of Europe, claiming this recognition among literati in the context of contemporary passions for the chivalric romance of King Arthur and the Gothic movement. The name Guest used for the book was derived from a mediaeval copyist's error, already established in the 18th century by William Owen Pughe and the London Welsh societies. As an accomplished linguist, and the wife of a foremost Welsh ironmaster John Josiah Guest, she became a leading figure in the study of literature and the wider Welsh Renaissance of the 19th century. With her second husband, Charles Schreiber, she became a well known Victorian collector of porcelain; their collection is held in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleanor Hull
Eleanor Henrietta Hull also known as Eibhlín Ní Choill (15 January 1860 – 13 January 1935) was a writer, journalist and scholar of Old Irish. Life and family Hull was born on 15 January 1860 in Manchester, England. Her father, Edward Hull, was from County Antrim, and her mother, Catherine Henrietta Hull (née Cooke), was from Cheltenham. Hull had 3 sisters and 2 brothers. Hull's paternal grandfather, John Dawson Hull, was a Protestant minister and a poet. Whilst in Manchester, the family lives at 147 York Street, Cheetham. The family moved to Dublin while Hull was a child. She was likely educated at home before attending Alexandra College, Dublin from 1877 to 1882. She attended courses on electricity, power and light during the summer of 1879 at the Royal College of Science, Dublin. She died at her home, 3 Camp View, Wimbledon Common on 13 January 1935. Her funeral took place at the chapel of Wimbledon cemetery, Gap Road. Career In her early thirties, Hull moved to London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silva Gadelica
The ''Silva Gadelica'' are two volumes of medieval tales taken from Irish folklore, translated into modern English by Standish Hayes O'Grady and published in 1892. The volumes contain many stories that together comprise the Fenian Cycle. Contents The ''Silva Gadelica'' contains two volumes, the first containing the medieval script and the second the English translations. The stories were translated from mostly vellum documents contained in the British Museum. When first published the ''Silva Gadelica'' included 31 tales and, in the second volume containing translations, over 600 pages of fine print. The largest and most important translation in ''Silva Gadelica'' is of the ''Acallam na Senórach'' or ''"Colloquy of the Ancients"''. Reception The ''Journal of the Royal Society of Antiquaries of Ireland'' described the volumes as containing "many passages of great beauty." Referencing the opening passage of the poem Caeilte's lay, The journal writes that it "cannot recall any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standish Hayes O'Grady
Standish Hayes O'Grady ( ga, Anéislis Aodh Ó Grádaigh; 19 May 1832 – 16 October 1915) was an Irish antiquarian. He was born at Erinagh House, Castleconnell, County Limerick, the son of Admiral Hayes O'Grady. He was a cousin of the writer Standish James O'Grady, with whom he is sometimes confused. As a child, he learnt Irish from the native speakers of his locality. He was educated at Rugby School and Trinity College Dublin. Although qualified as a civil engineer, he is best remembered for ''Silva Gadelica'' (two volumes, 1892), a collection of tales from medieval Irish manuscripts. He was a friend of antiquaries John O'Donovan and Eugene O'Curry. In 1853, he became a founding member of the Ossianic Society. He would later become its president in 1855. In 1857 he moved to the United States where he remained for 30 years. In 1901 he contributed an essay on ''Anglo-Irish Aristocracy'' to a collection entitled ''Ideals in Ireland'' edited by Augusta, Lady Gregory. He died in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medb
Medb (), later spelled Meadhbh (), Méibh () and Méabh (), and often anglicised as Maeve ( ), is queen of Connacht in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology. Her husband in the core stories of the cycle is Ailill mac Máta, although she had several husbands before him who were also kings of Connacht. She rules from Cruachan (now Rathcroghan, County Roscommon). She is the enemy (and former wife) of Conchobar mac Nessa, king of Ulster, and is best known for starting the ''Táin Bó Cúailnge'' ("The Cattle Raid of Cooley") to steal Ulster's prize stud bull Donn Cúailnge. Medb is strong-willed, ambitious, cunning and promiscuous, and is an archetypal warrior queen. She is believed by some to be a manifestation of the sovereignty goddess.Ó hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth, Legend & Romance: An encyclopaedia of the Irish folk tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. pp. 294–295Monaghan, Patricia. ''The Encyclopedia of Celtic Mythology and Folklore''. Infobase Publishing, 2004. p.319Koch, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deirdre
Deirdre ( , Irish: ; sga, Derdriu ) is the foremost tragic heroine in Irish legend and probably its best-known figure in modern times. She is known by the epithet "Deirdre of the Sorrows" (). Her story is part of the Ulster Cycle, the best-known stories of pre-Christian Ireland. In legend Deirdre was the daughter of the royal storyteller Fedlimid mac Daill. Before she was born, Cathbad the chief druid at the court of Conchobar mac Nessa, king of Ulster, prophesied that Fedlimid's daughter would grow up to be very beautiful, but that kings and lords would go to war over her, much blood would be shed because of her, and Ulster's three greatest warriors would be forced into exile for her sake. Hearing this, many urged Fedlimid to kill the baby at birth, but Conchobar, aroused by the description of her future beauty, decided to keep the child for himself. He took Deirdre away from her family and had her brought up in seclusion by Leabharcham, a poet and wise woman, and planned to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |