|
Cubes (OLAP Server)
Cubes is a light-weight open source multidimensional modelling and OLAP toolkit for development reporting applications and browsing of aggregated data written in Python programming language released under the MIT License. Cubes provides to an analyst or any application end-user "understandable and natural way of reporting using concept of data Cubes – multidimensional data objects". Cubes was first publicly released in March 2011. The project was originally developed for Public Procurements of Slovakia. Cubes 1.0 was released in September 2014 and presented on the PyData Conference in New York Features * OLAP and aggregated browsing (default is ROLAP) * logical model of OLAP cubes in JSON or provided from external sources * hierarchical dimensions (attributes that have hierarchical dependencies, such as category-subcategory or country-region) * multiple hierarchies in a dimension * arithmetic expressions for computing derived measures and aggregates * localizable metadata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language and first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000 and introduced new features such as list comprehensions, cycle-detecting garbage collection, reference counting, and Unicode support. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision that is not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2 was discontinued with version 2.7.18 in 2020. Python consistently ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser. Development of HTTP was initiated by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in 1989 and summarized in a simple document describing the behavior of a client and a server using the first HTTP protocol version that was named 0.9. That first version of HTTP protocol soon evolved into a more elaborated version that was the first draft toward a far future version 1.0. Development of early HTTP Requests for Comments (RFCs) started a few years later and it was a coordinated effort by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), with work later moving t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language) Scientific Libraries
Python may refer to: Snakes * Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia ** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia * Python (mythology), a mythical serpent Computing * Python (programming language), a widely used programming language * Python, a native code compiler for CMU Common Lisp * Python, the internal project name for the PERQ 3 computer workstation People * Python of Aenus (4th-century BCE), student of Plato * Python (painter), (ca. 360–320 BCE) vase painter in Poseidonia * Python of Byzantium, orator, diplomat of Philip II of Macedon * Python of Catana, poet who accompanied Alexander the Great * Python Anghelo (1954–2014) Romanian graphic artist Roller coasters * Python (Efteling), a roller coaster in the Netherlands * Python (Busch Gardens Tampa Bay), a defunct roller coaster * Python (Coney Island, Cincinnati, Ohio), a steel roller coaster Vehicles * Python (automobile maker), an Australian car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
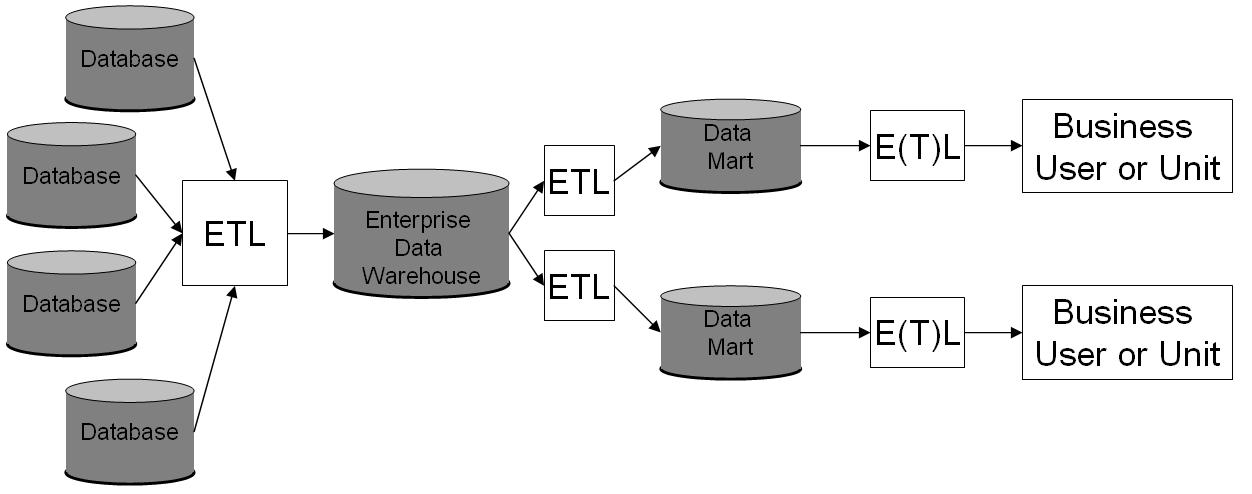
Data Warehousing
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. The data stored in the warehouse is uploaded from the operational systems (such as marketing or sales). The data may pass through an operational data store and may require data cleansing for additional operations to ensure data quality before it is used in the DW for reporting. Extract, transform, load (ETL) and extract, load, transform (ELT) are the two main approaches used to build a data warehouse system. ETL-based data warehousing The typical extract, transform, load (ETL)-based data warehouse uses staging, data integration, and access layers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Analysis Software
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted. A datum is an individual value in a collection of data. Data is usually organized into structures such as tables that provide additional context and meaning, and which may themselves be used as data in larger structures. Data may be used as variables in a computational process. Data may represent abstract ideas or concrete measurements. Data is commonly used in scientific research, economics, and in virtually every other form of human organizational activity. Examples of data sets include price indices (such as consumer price index), unemployment rates, literacy rates, and census data. In this context, data represents the raw facts and figures which can be used in such a manner in order to capture the useful information out of it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SQLAlchemy
SQLAlchemy is an open-source SQL toolkit and object-relational mapper (ORM) for the Python programming language released under the MIT License. Description SQLAlchemy's philosophy is that relational databases behave less like object collections as the scale gets larger and performance starts being a concern, while object collections behave less like tables and rows as more abstraction is designed into them. For this reason it has adopted the data mapper pattern (similar to Hibernate for Java) rather than the active record pattern used by a number of other object-relational mappers.iThe architecture of open source applications/ref> History SQLAlchemy was first released in February 2006 Example The following example represents an n-to-1 relationship between movies and their directors. It is shown how user-defined Python classes create corresponding database tables, how instances with relationships are created from either side of the relationship, and finally how the data can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowflake Schema
In computing, a snowflake schema is a logical arrangement of tables in a multidimensional database such that the entity relationship diagram resembles a snowflake shape. The snowflake schema is represented by centralized fact tables which are connected to multiple dimensions. "Snowflaking" is a method of normalizing the dimension tables in a star schema. When it is completely normalized along all the dimension tables, the resultant structure resembles a snowflake with the fact table in the middle. The principle behind snowflaking is normalization of the dimension tables by removing low cardinality attributes and forming separate tables. The snowflake schema is similar to the star schema. However, in the snowflake schema, dimensions are normalized into multiple related tables, whereas the star schema's dimensions are denormalized with each dimension represented by a single table. A complex snowflake shape emerges when the dimensions of a snowflake schema are elaborate, havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Schema
In computing, the star schema is the simplest style of data mart schema and is the approach most widely used to develop data warehouses and dimensional data marts. The star schema consists of one or more fact tables referencing any number of dimension tables. The star schema is an important special case of the snowflake schema, and is more effective for handling simpler queries. The star schema gets its name from the physical model's", p. 708 resemblance to a star shape with a fact table at its center and the dimension tables surrounding it representing the star's points. Model The star schema separates business process data into facts, which hold the measurable, quantitative data about a business, and dimensions which are descriptive attributes related to fact data. Examples of fact data include sales price, sale quantity, and time, distance, speed and weight measurements. Related dimension attribute examples include product models, product colors, product sizes, geograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology
In mathematics, topology (from the Greek words , and ) is concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a set endowed with a structure, called a ''topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of a topological space, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a topological property. Basic examples of topological properties are: the dimension, which allows distinguishing between a line and a surface; compactness, which allows distinguishing between a line and a circle; connectedne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ROLAP
Online analytical processing, or OLAP (), is an approach to answer multi-dimensional analytical (MDA) queries swiftly in computing. OLAP is part of the broader category of business intelligence, which also encompasses relational databases, report writing and data mining. Typical applications of OLAP include business reporting for sales, marketing, management reporting, business process management (BPM), budgeting and forecasting, financial reporting and similar areas, with new applications emerging, such as agriculture. The term ''OLAP'' was created as a slight modification of the traditional database term online transaction processing (OLTP). OLAP tools enable users to analyze multidimensional data interactively from multiple perspectives. OLAP consists of three basic analytical operations: consolidation (roll-up), drill-down, and slicing and dicing.O'Brien, J. A., & Marakas, G. M. (2009). Management information systems (9th ed.). Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Consolidatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flask (web Framework)
Flask is a micro web framework written in Python. It is classified as a microframework because it does not require particular tools or libraries. It has no database abstraction layer, form validation, or any other components where pre-existing third-party libraries provide common functions. However, Flask supports extensions that can add application features as if they were implemented in Flask itself. Extensions exist for object-relational mappers, form validation, upload handling, various open authentication technologies and several common framework related tools. Applications that use the Flask framework include Pinterest and LinkedIn. History Flask was created by Armin Ronacher of Pocoo, an international group of Python enthusiasts formed in 2004. According to Ronacher, the idea was originally an April Fool's joke that was popular enough to make into a serious application. The name is a play on the earlier Bottle framework. When Ronacher and Georg Brandl created a bull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |