|
Cryptotethya Crypta
''Tectitethya crypta'' is a species of demosponge belonging to the family Tethyidae. Its classified family is characterized by fourteen different known genera, one of them being ''Tectitethya''. It is a massive, shallow-water sponge found in the Caribbean Sea. This sponge was first discovered by Werner Bergmann in 1945 and later classified by de Laubenfels in 1949. It is located in reef areas situated on softer substrates such as sand or mud. Oftentimes, it is covered in sand and algae. This results in an appearance that is cream colored/ gray colored; however, when the animal is washed free of its sediment coverings, its body plan appears more green and gray. It's characterized with ostia peaking out of its body cavity, with the ability to abruptly open or close, changing its desired water flow rate through its mesohyl. This sponge is widely known for its contributions to the field of medicine as a source for potent nucleoside analogues used in treating H.I.V, Acute Myeloid Leuke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Walker De Laubenfels
Max Walker de Laubenfels (1894–1960) was an American spongiologist. He received his undergraduate degree from Oberlin College and his doctorate from Stanford University. He was among the most prolific identifiers of new species of Caribbean sponges, describing 60 species from 1932-1954. He was a Professor of Zoology at Oregon State College (now Oregon State University) from 1950 to 1958. Publications * , 1954 : The sponges of the west-central Pacific. Studies in zoology, no.7: 320pg. * , 1929 : The sponges of California. Dept. of Zoology. 634 pg. See also * David John de Laubenfels David John de Laubenfels or D. J. de Laubenfels (1925 – February 6, 2016) was an American botanist known as an expert on tropical conifers. See also * Max Walker de Laubenfels Max Walker de Laubenfels (1894–1960) was an American spongi ... References Spongiologists 20th-century American zoologists Oregon State University faculty 1894 births 1960 deaths {{US-zoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ''leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia— acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myeloi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animals Described In 1949
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadromerida
Heteroscleromorpha is a subclass of demosponges within the phylum Porifera Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through th ....van Soest, R. (2016)Heteroscleromorpha.Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species on 2017-02-17. References Sponge subclasses Taxa named by Nicole Boury-Esnault {{Demosponge-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectitethya Crypta In Medicine
''Tectitethya'' is a genus of sea sponges belonging to the family Tethyidae. There are five described species in this genus with the first member having been described in 1900. Species Species in this genus include: * ''Tectitethya crypta'' (de Laubenfels, 1949) * ''Tectitethya keyensis'' Sarà & Bavestrello, 1996 * ''Tectitethya macrostella'' Sarà & Bavestrello, 1996 * ''Tectitethya raphyroides'' Sarà & Bavestrello, 1996 * ''Tectitethya topsenti ''Tectitethya'' is a genus of sea sponges belonging to the family Tethyidae. There are five described species in this genus with the first member having been described in 1900. Species Species in this genus include: * ''Tectitethya crypta'' (de ...'' (Thiele, 1900) References Hadromerida {{demosponge-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budding
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is known as a bud. Since the reproduction is asexual, the newly created organism is a clone and excepting mutations is genetically identical to the parent organism. Organisms such as hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction in the process of budding. In hydra, a bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site. These buds develop into tiny individuals and, when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent individuals. Internal budding or endodyogeny is a process of asexual reproduction, favored by parasites such as ''Toxoplasma gondii''. It involves an unusual process in which two daughter cells are produced inside a mother cell, which is then consumed by the offspring prior to their s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
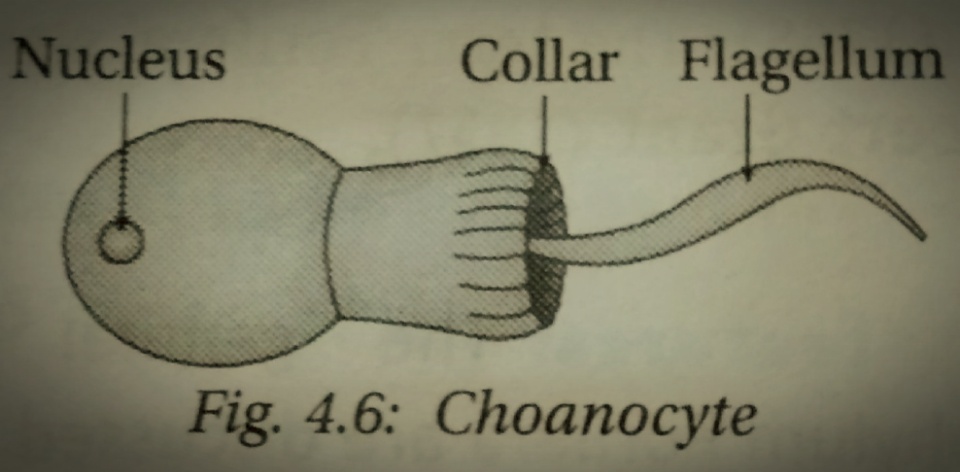
Choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a thin membrane. They make up the choanoderm, a type of cell layer found in sponges. The cell has the closest resemblance to the choanoflagellates which are the closest related single celled protists to the animal kingdom (metazoans). The flagellae beat regularly, creating a water flow across the microvilli which can then filter nutrients from the water taken from the collar of the sponge. Food particles are then phagocytosed by the cell. Anderson, D. (2001) ''Invertebrate Zoology'' Oxford University Press Location Choanocytes are found dotting the surface of the spongocoel in asconoid sponges and the radial canals in syconoid sponges, but they comprise entirely the chambers in leuconoid sponges. Function By cooperatively moving their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osculum
The osculum (plural "oscula") is an excretory structure in the living sponge, a large opening to the outside through which the current of water exits after passing through the spongocoel. Wastes diffuse into the water and the water is pumped through the osculum carrying away with it the sponge's wastes. Sponges pump large volumes of water: typically a volume of water equal to the sponge's body size is pumped every five seconds. The size of the osculum is regulated by contractile myocytes. Its size, in turn, is one of the factors which determines the amount of water flowing through the sponge Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through t .... It can be closed completely in response to excess silt in the water. References Sponge anatomy {{animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge Spicule
Spicules are structural elements found in most sponges. The meshing of many spicules serves as the sponge's skeleton and thus it provides structural support and potentially defense against predators. Sponge spicules are made of calcium carbonate or silica. Large spicules visible to the naked eye are referred to as megascleres, while smaller, microscopic ones are termed microscleres. The composition, size, and shape of spicules are major characters in sponge systematics and taxonomy. Overview Sponges are a species-rich clade of the earliest-diverging (most basal) animals. They are distributed globally, with diverse ecologies and functions, and a record spanning at least the entire Phanerozoic. Most sponges produce skeletons formed by spicules, structural elements that develop in a wide variety of sizes and three dimensional shapes. Among the four sub-clades of Porifera, three (Demospongiae, Hexactinellida, and Homoscleromorpha) produce skeletons of amorphous silica and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemcitabine
Gemcitabine, with brand names including Gemzar, is a chemotherapy medication. It treats cancers including testicular cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and bladder cancer. It is administered by intravenous infusion. It acts against neoplastic growth, and it inhibits the replication of Orthohepevirus A, the causative agent of Hepatitis E, through upregulation of interferon signaling. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, liver and kidney problems, nausea, fever, rash, shortness of breath, mouth sores, diarrhea, neuropathy, and hair loss. Use during pregnancy will likely result in fetal harm. Gemcitabine is in the nucleoside analog family of medication. It works by blocking the creation of new DNA, which results in cell death. Gemcitabine was patented in 1983 and was approved for medical use in 1995. Generic versions were introduced in Europe in 2009 and in the US in 2010. It is on the WHO Model List of Essentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night. Many subtypes of lymphomas are known. The two main categories of lymphomas are the non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (90% of cases) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (10%). The World Health Organization (WHO) includes two other categories as types of lymphoma – multiple myeloma and immunoproliferative diseases. Lymphomas and leukemias are a part of the broader group of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include infection with Epstein–Barr virus and a history of the disease in the family. Risk factors for common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytarabine
Cytarabine, also known as cytosine arabinoside (ara-C), is a chemotherapy medication used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is given by injection into a vein, under the skin, or into the cerebrospinal fluid. There is a liposomal formulation for which there is tentative evidence of better outcomes in lymphoma involving the meninges. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, vomiting, diarrhea, liver problems, rash, ulcer formation in the mouth, and bleeding. Other serious side effects include loss of consciousness, lung disease, and allergic reactions. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Cytarabine is in the antimetabolite and nucleoside analog families of medication. It works by blocking the function of DNA polymerase. Cytarabine was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1969. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |