|
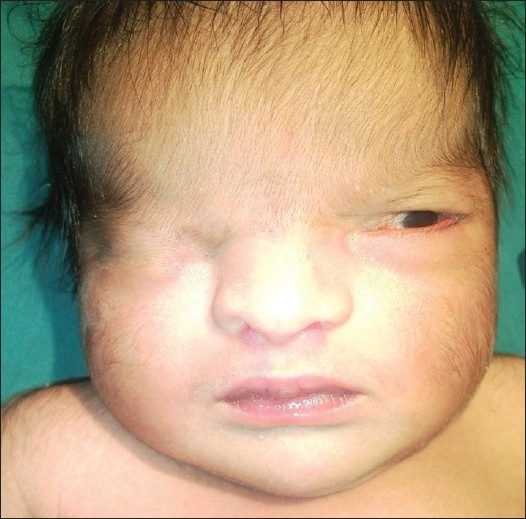
Cryptophthalmos
Cryptophthalmos is a rare congenital anomaly in which the skin is continuous over the eyeball with absence of Palpebral fissure, palpebral fissures and presence of eyelashes. It is classified into three types: complete, incomplete and abortive. Failure of eyelid separation can be associated with maldevelopment of the underlying cornea and microphthalmia. Cryptophthalmos usually occurs on both sides and occurs in association with multiple other malformations collectively referred to as Fraser syndrome. Along with microphthalmia (small or underdeveloped Globe (human eye), globe), it may be associated with a tuft of hair. Signs and symptoms Complete cryptophthalmos is the most severe form of Cryptophthalomos. Complete cryptophthalmos is characterized by complete occlusion of the eye sockets and fusion of the skin on the forehead and cheeks. Those with Complete cryptophthalmos have no eyebrows, gland structures, or eyelashes. They also lack a connjunctival sac and the overlying skin fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch tics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specialty, predictive medicine. Scope Medical genetics encompasses many different areas, including clinical practice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many include research as part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different cellular differentiation, developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ (anatomy), organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpebral Fissure
The palpebral fissure is the elliptic space between the medial and lateral canthi of the two open eyelids. In simple terms, it is the opening between the eyelids. In adult humans, this measures about 10 mm vertically and 30 mm horizontally. Variations Congenital dysmorphisms It can be reduced (short, "narrow") in horizontal size by fetal alcohol syndrome and in Williams syndrome. The chromosomal conditions trisomy 9 and trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) can cause the palpebral fissures to be upslanted, whereas Marfan syndrome can cause a downslant. An increase in vertical height can be seen in genetic disorders such as cri-du-chat syndrome. Acquired The fissure may be increased in vertical height in Graves' disease, which is manifested as Dalrymple's sign. It is seen in disorders such as cri-du-chat syndrome. In animal studies using four times the therapeutic concentration of the ophthalmic solution latanoprost, the size of the palpebral fissure can be increased. The condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its focus is fixed. Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "'' kerat-''" from the Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a touch of the cornea causes an involuntary reflex to close the eyelid. Because transparency is of prime importance, the healthy cornea does not have or need blood vessels with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microphthalmia
Microphthalmia (Greek: grc, μικρός, mikros, small, label=none, grc, ὀφθαλμός, ophthalmos, eye, label=none, also referred as microphthalmos, is a developmental disorder of the eye in which one (unilateral microphthalmia) or both (bilateral microphthalmia) eyes are abnormally small and have anatomic malformations. Microphthalmia is a distinct condition from anophthalmia and nanophthalmia. Although sometimes referred to as 'simple microphthalmia', nanophthalmia is a condition in which the size of the eye is small but no anatomical alterations are present. Presentation Microphthalmia is a congenital disorder in which the globe of the eye is unusually small and structurally disorganized. While the axis of an adult human eye has an average length of about , a diagnosis of microphthalmia generally corresponds to an axial length below in adults. Additionally, the diameter of the cornea is about in affected newborns and in adults with the condition. The presence of a sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraser Syndrome
Fraser syndrome (also known as Meyer-Schwickerath's syndrome, Fraser-François syndrome, or Ullrich-Feichtiger syndrome) is an autosomal recessive congenital disorder, identified by several developmental anomalies. Fraser syndrome is named for the geneticist George R. Fraser, who first described the syndrome in 1962. Signs and symptoms It is characterized by developmental defects including cryptophthalmos (where the eyelids fail to separate in each eye), and intersex development in the genitals (such as micropenis, or clitoromegaly) and cryptorchidism Congenital malformations of the nose, ears, larynx and renal system, as well as developmental delays, manifest occasionally. Syndactyly (fused fingers or toes) has also been noted. Genetics The genetic background of this disease has been linked to a gene called FRAS1, which seems to be involved in skin epithelial morphogenesis during early development. It has also been associated with FREM2 and with GRIP1. Mapping By autozyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globe (human Eye)
The globe of the eye, or bulbus oculi, is the eyeball apart from its appendages. A hollow structure, the bulbus oculi is composed of a wall enclosing a cavity filled with fluid with three coats: the sclera, choroid, and the retina. Normally, the bulbus oculi is bulb-like structure. However, the bulbus oculi is not completely spherical. Its anterior surface, transparent and more curved, is known as the cornea of the bulbus oculi. See also * Sclera * Choroid * Retina The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Globe (Human Eye) Human eye anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |