|
Cryosupernatant
The term cryosupernatant (also called cryo-poor plasma, cryoprecipitate depleted, cryoprecipitate reduced plasma) refers to plasma from which the cryoprecipitate has been removed. It is used to treat thrombocytopenic purpura. __TOC__ Components The resulting plasma has reduced levels of factor VIII (FVIII), von Willebrand factor (VWF), factor XIII (FXIII), fibronectin and fibrinogen. While the levels of FVIII are greatly reduced, levels of fibrinogen can be as much as 70% of original levels. Uses Cryosupernatant plasma can be used when replacement of FVIII is not required, and is indicated for plasma exchange for patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a blood disorder that results in blood clots forming in small blood vessels throughout the body. This results in a low platelet count, low red blood cells due to their breakdown, and often kidney, h ... (TTP) as well as for treatment of hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) by p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a blood disorder that results in blood clots forming in small blood vessels throughout the body. This results in a low platelet count, low red blood cells due to their breakdown, and often kidney, heart, and brain dysfunction. Symptoms may include large bruises, fever, weakness, shortness of breath, confusion, and headache. Repeated episodes may occur. In about half of cases a trigger is identified, while in the remainder the cause remains unknown. Known triggers include bacterial infections, certain medications, autoimmune diseases such as lupus, and pregnancy. The underlying mechanism typically involves antibodies inhibiting the enzyme ADAMTS13. This results in decreased break down of large multimers of von Willebrand factor (vWF) into smaller units. Less commonly TTP is inherited from a person's parents, known as Upshaw–Schulman syndrome, such that ADAMTS13 dysfunction is present from birth. Diagnosis is typically based on sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intravascular part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains important dissolved proteins (6–8%; e.g., serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (, , , , , etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood-related disorders. Blood plasma is separated from the blood by spinning a vessel of fresh blood containing an anticoagulant in a centrifuge until the blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube. The blood plasma is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryoprecipitate
Cryoprecipitate, also called cryo for short, is a frozen blood product prepared from blood plasma. To create cryoprecipitate, fresh frozen plasma thawed to 1–6 °C is then centrifuged and the precipitate is collected. The precipitate is resuspended in a small amount of residual plasma (generally 10–15 mL) and is then re-frozen for storage. It is often transfused to adults as two 5-unit pools instead of as a single product. One of the most important constituents is factor VIII (also called antihaemophilic factor or AHF), which is why cryoprecipitate is sometimes called cryoprecipitated antihaemophilic factor or cryoprecipitated AHF. In many clinical contexts, use of whole cryoprecipitate has been replaced with use of clotting factor concentrates made therefrom (where available), but the whole form is still routinely stocked by many, if not most, hospital blood banks. Cryo can be stored at −18 °C or colder for 12 months from the original collection date. After thawi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Thrombocytopenic purpura are purpura associated with a reduction in circulating blood platelets which can result from a variety of causes, such as kaposi sarcoma. Types By tradition, the term idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is used when the cause is idiopathic. However, most cases are now considered to be immune-mediated. Another form is thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Diagnosis Diagnosis is done by the help of symptoms and only blood count abnormality is thrombocytopenia. Treatment See also * Aspirin * Hematopoietic ulcer * Thrombocyte Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby ini ... References External links Vascular-related cutaneous conditions Coagulopathies {{blood-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor VIII
Factor VIII (FVIII) is an essential blood-clotting protein, also known as anti-hemophilic factor (AHF). In humans, factor VIII is encoded by the ''F8'' gene. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A, a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. Factor VIII is produced in liver sinusoidal cells and endothelial cells outside the liver throughout the body. This protein circulates in the bloodstream in an inactive form, bound to another molecule called von Willebrand factor, until an injury that damages blood vessels occurs. In response to injury, coagulation factor VIII is activated and separates from von Willebrand factor. The active protein (sometimes written as coagulation factor VIIIa) interacts with another coagulation factor called factor IX. This interaction sets off a chain of additional chemical reactions that form a blood clot. Factor VIII participates in blood coagulation; it is a cofactor for factor IXa, which, in the presence of Ca2+ and phospholipids, forms a complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Willebrand Factor
Von Willebrand factor (VWF) () is a blood glycoprotein involved in hemostasis, specifically, platelet adhesion. It is deficient and/or defective in von Willebrand disease and is involved in many other diseases, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, Heyde's syndrome, and possibly hemolytic–uremic syndrome. Increased plasma levels in many cardiovascular, neoplastic, metabolic (e.g. diabetes), and connective tissue diseases are presumed to arise from adverse changes to the endothelium, and may predict an increased risk of thrombosis. Biochemistry Synthesis VWF is a large multimeric glycoprotein present in blood plasma and produced constitutively as ultra-large VWF in endothelium (in the Weibel–Palade bodies), megakaryocytes (α-granules of platelets), and subendothelial connective tissue. Structure The basic VWF monomer is a 2050-amino acid protein. Every monomer contains a number of specific domains with a specific function; elements of note are: * the D'/D3 do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor XIII
Factor XIII or fibrin stabilizing factor is a zymogen found in blood of humans and some other animals. It is activated by thrombin to factor XIIIa. Factor XIIIa is an enzyme of the blood coagulation system that crosslinks fibrin. Deficiency of XIII worsens clot stability and increases bleeding tendency. Human XIII is a heterotetramer. It consists of 2 enzymatic A peptides and 2 non-enzymatic B peptides. XIIIa is a dimer of activated A peptides. Function Within blood, thrombins cleave fibrinogens to fibrins during coagulation and a fibrin-based blood clot forms. Factor XIII is a transglutaminase that circulates in human blood as a heterotetramer of two A and two B subunits. Factor XIII binds to the clot via their B units. In the presence of fibrins, thrombin efficiently cleaves the R37– G38 peptide bond of each A unit within a XIII tetramer. A units release their N-terminal activation peptides. Both of the non-covalently bound B units are now able to dissociate from the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
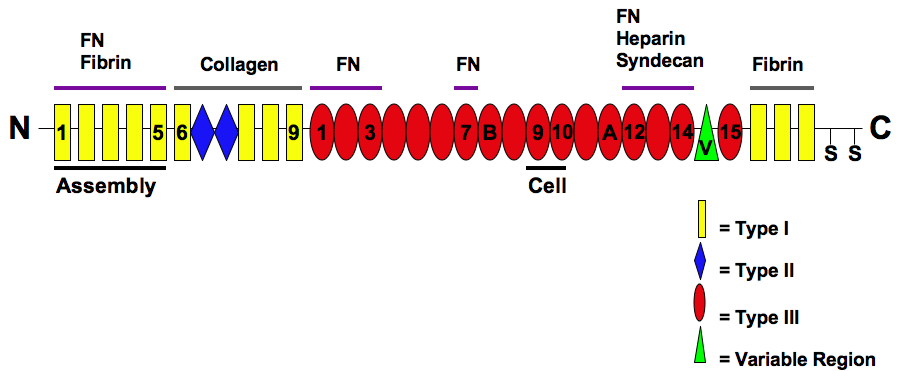
Fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g. syndecans). Fibronectin exists as a protein dimer, consisting of two nearly identical monomers linked by a pair of disulfide bonds. The fibronectin protein is produced from a single gene, but alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA leads to the creation of several isoforms. Two types of fibronectin are present in vertebrates: * soluble plasma fibronectin (formerly called "cold-insoluble globulin", or CIg) is a major protein component of blood plasma (300 μg/ml) and is produced in the liver by hepatocytes. * insoluble cellular fibronectin is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is secreted by various cells, primarily fibroblasts, as a soluble protein dimer and is then ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (factor I) is a glycoprotein complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and then to a fibrin-based blood clot. Fibrin clots function primarily to occlude blood vessels to stop bleeding. Fibrin also binds and reduces the activity of thrombin. This activity, sometimes referred to as antithrombin I, limits clotting. Fibrin also mediates blood platelet and endothelial cell spreading, tissue fibroblast proliferation, capillary tube formation, and angiogenesis and thereby promotes revascularization and wound healing. Reduced and/or dysfunctional fibrinogens occur in various congenital and acquired human fibrinogen-related disorders. These disorders represent a group of rare conditions in which individuals may present with severe episodes of pathological bleeding and thrombosis; these conditions are treated by supplementing blood fibrinogen levels an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Products
A blood product is any therapeutic substance prepared from human blood. This includes whole blood; blood components; and plasma derivatives. Whole blood is not commonly used in transfusion medicine. Blood components include: red blood cell concentrates or suspensions; platelets produced from whole blood or via apheresis; plasma; and cryoprecipitate. Plasma derivatives are plasma proteins prepared under pharmaceutical manufacturing conditions, these include: albumin; coagulation factor concentrates; and immunoglobulins. __TOC__ Relation to other substances Blood products may also be called blood-based products to differ from blood substitutes, which generally refer to artificially produced products. Also, although many blood products have the effect of volume expansion, the group is usually distinguished from volume expanders, which generally refers to artificially produced substances and are thereby within the scope of ''blood substitutes''. See also * Cryoprecipitate * Cryosupe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |