|
Fibronectin
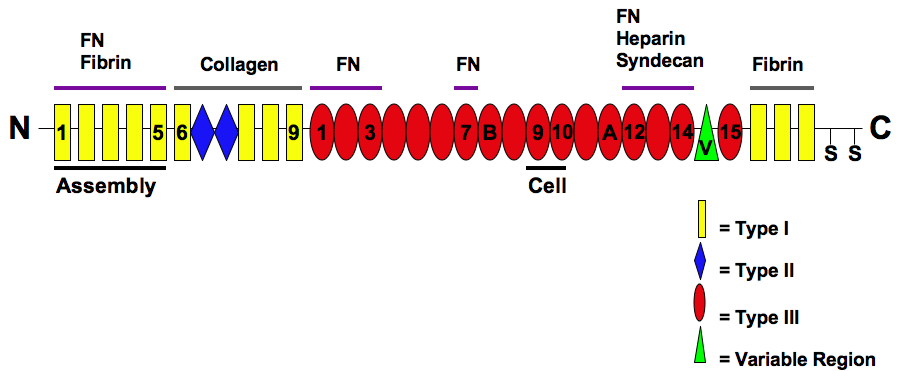
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g. syndecans). Fibronectin exists as a protein dimer, consisting of two nearly identical monomers linked by a pair of disulfide bonds. The fibronectin protein is produced from a single gene, but alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA leads to the creation of several isoforms. Two types of fibronectin are present in vertebrates: * soluble plasma fibronectin (formerly called "cold-insoluble globulin", or CIg) is a major protein component of blood plasma (300 μg/ml) and is produced in the liver by hepatocytes. * insoluble cellular fibronectin is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is secreted by various cells, primarily fibroblasts, as a soluble protein dimer and is then ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wound Healing
Wound healing refers to a living organism's replacement of destroyed or damaged tissue by newly produced tissue. In undamaged skin, the epidermis (surface, epithelial layer) and dermis (deeper, connective layer) form a protective barrier against the external environment. When the barrier is broken, a regulated sequence of biochemical events is set into motion to repair the damage. This process is divided into predictable phases: blood clotting (hemostasis), inflammation, tissue growth ( cell proliferation), and tissue remodeling (maturation and cell differentiation). Blood clotting may be considered to be part of the inflammation stage instead of a separate stage. The wound healing process is not only complex but fragile, and it is susceptible to interruption or failure leading to the formation of non-healing chronic wounds. Factors that contribute to non-healing chronic wounds are diabetes, venous or arterial disease, infection, and metabolic deficiencies of old age.Enoch, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrins
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, organization of the intracellular cytoskeleton, and movement of new receptors to the cell membrane. The presence of integrins allows rapid and flexible responses to events at the cell surface (''e.g''. signal platelets to initiate an interaction with coagulation factors). Several types of integrins exist, and one cell generally has multiple different types on its surface. Integrins are found in all animals while integrin-like receptors are found in plant cells. Integrins work alongside other proteins such as cadherins, the immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules, selectins and syndecans, to mediate cell–cell and cell–matrix interaction. Ligands for integrins include fibronectin, vitronectin, collagen and laminin. Structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndecans
Syndecans are single transmembrane domain proteins that are thought to act as coreceptors, especially for G protein-coupled receptors. More specifically, these core proteins carry three to five heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate chains, i.e. they are proteoglycans, which allow for interaction with a large variety of ligands including fibroblast growth factors, vascular endothelial growth factor, transforming growth factor-beta, fibronectin and antithrombin-1. Interactions between fibronectin and some syndecans can be modulated by the extracellular matrix protein tenascin C. Family members and Structure The syndecan protein family has four members. Syndecans 1 and 3 and syndecans 2 and 4, making up separate subfamilies, arose by gene duplication and divergent evolution from a single ancestral gene. The syndecan numbers reflect the order in which the cDNAs for each family member were cloned. All syndecans have an N-terminal signal peptide, an ectodomain, a single hydroph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the Interstitial fluid, interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in connective tissue such as cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Depending upon the degree of mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to two percent of muscle tissue and accounts for 6% of the weight of the skeletal muscle tissue. The fibroblast is the most common cell that crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
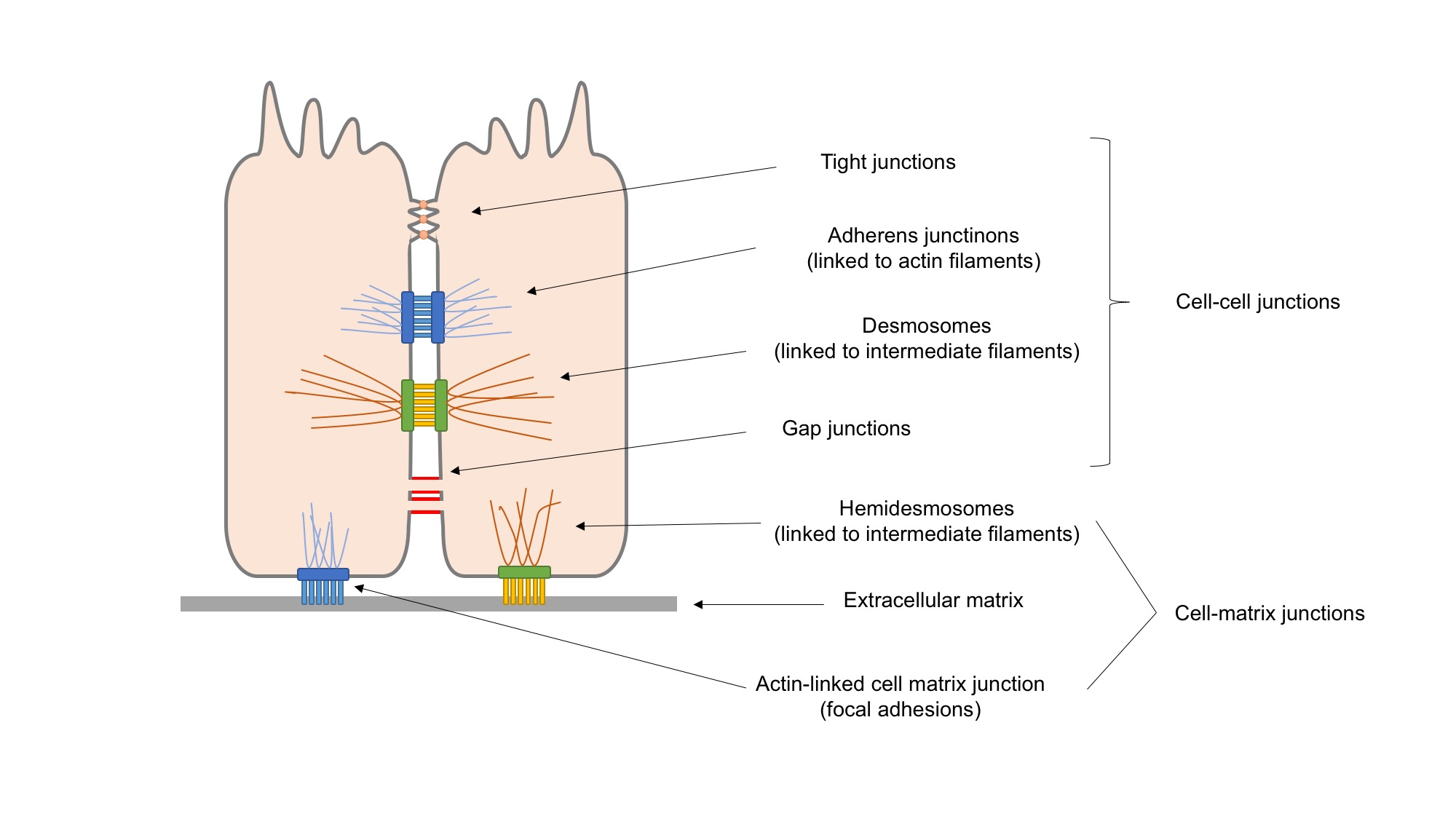
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heparan Sulfate
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan (HSPG, i.e. Heparan Sulfate ProteoGlycan) in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. It is in this form that HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB (Granzyme B), and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2. Proteoglycans The major cell membrane HSPGs are the transmembrane syndecans and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored glypicans. Other minor forms of membrane HSPG include betaglycan and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Modular Structure Of Fibronectin And Its Binding Domains
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocytes
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass. These cells are involved in: * Protein synthesis * Protein storage * Transformation of carbohydrates * Synthesis of cholesterol, bile salts and phospholipids * Detoxification, modification, and excretion of exogenous and endogenous substances * Initiation of formation and secretion of bile Structure The typical hepatocyte is cubical with sides of 20-30 μm, (in comparison, a human hair has a diameter of 17 to 180 μm).The diameter of human hair ranges from 17 to 181 μm. The typical volume of a hepatocyte is 3.4 x 10−9 cm3. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is abundant in hepatocytes, in contrast to most other cell types. Microanatomy Hepatocytes display an eosinophilic cytoplasm, reflecting numerous mitochondria, and basophilic stippling due to large amounts of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and free ribosomes. Brown lipofuscin granules are also observed ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblasts
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum. Inactive fibroblasts (called fibrocytes) are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have a reduced amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Although disjointed and scattered when they have to cover a large space, fibroblasts, when crowded, often locally align in parallel clusters. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a polarizing attachment to a basal lamina on one side, although they may contribute to basal lamina components in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)

.jpg)