|
Cryoneurolysis
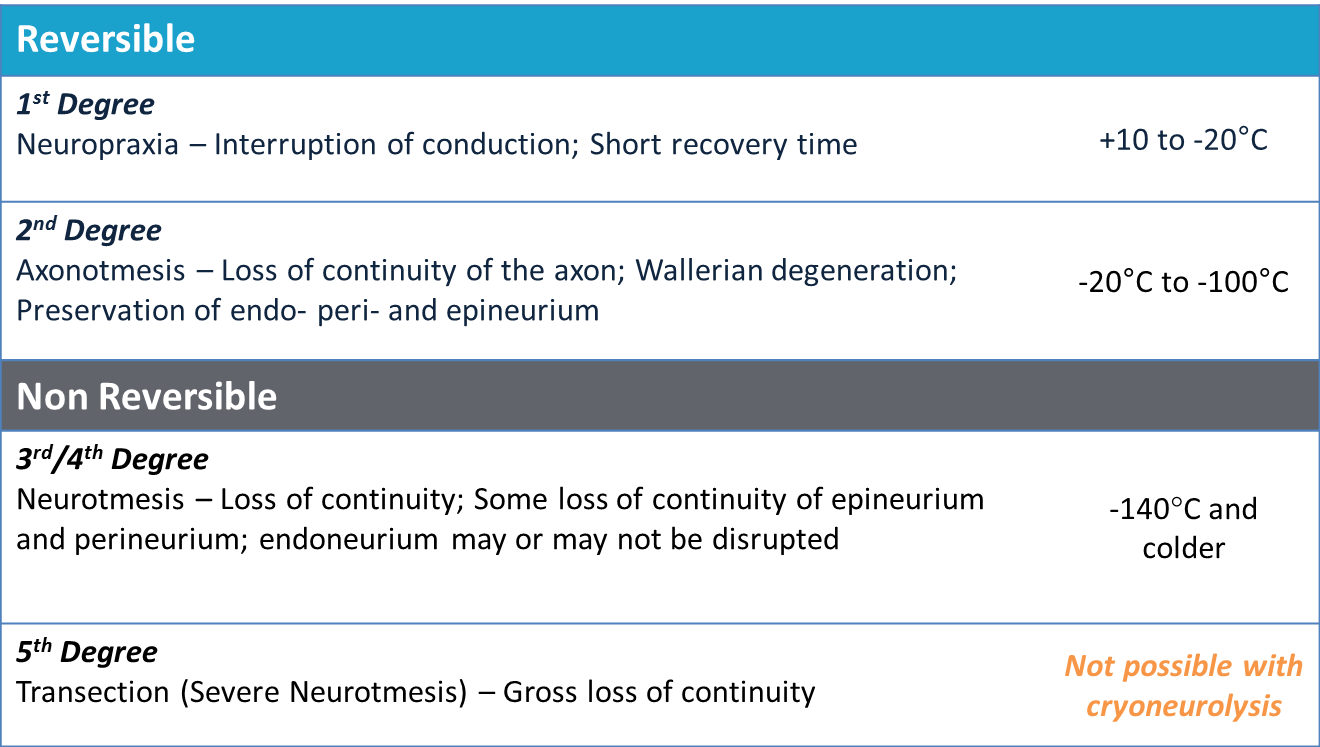
Cryoneurolysis, also referred to as cryoanalgesia, is a medical procedure that temporarily blocks nerve conduction along peripheral nerve pathways. The procedure, which inserts a small probe to freeze the target nerve, can facilitate complete regeneration of the structure and function of the affected nerve. Cryoneurolysis has been used to treat a variety of painful conditions. Medical uses A similar procedure that uses radiofrequency energy for back pain appears to have short-term benefit, but it is unclear if it has a long-term effect. Mechanisms of action Nerve anatomy Each nerve is composed of a bundle of axons. Each axon is surrounded by the endoneurium connective tissue layer. These axons are bundled into fascicles surrounded by the perineurium connective tissue layer. Multiple fascicles are then surrounded by the epineurium, which is the outermost connective tissue layer of the nerve. The axons of myelinated nerves have a myelin sheath made up of Schwann cells that coat the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryoprobe
Cryosurgery is the use of extreme cold in surgery to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue; thus, it is the surgical application of cryoablation. The term comes from the Greek words cryo (κρύο) ("icy cold") and surgery (''cheirourgiki'' – χειρουργική) meaning "hand work" or "handiwork". Cryosurgery has been historically used to treat a number of diseases and disorders, especially List of skin diseases, a variety of benign and malignant skin conditions. Uses Warts, mole (skin marking), moles, skin tags, solar keratosis, solar keratoses, molluscum contagiosum, molluscum, Morton's neuroma and small skin cancers are candidates for cryosurgical treatment. Several internal medicine, internal disorders are also treated with cryosurgery, including Hepatocellular carcinoma, liver cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, oral cancers, Cervix, cervical disorders and, more commonly in the past, hemorrhoids. Soft tissue conditions such as plantar fasciitis (jogger's heel) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiofrequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an Alternating current, alternating electric current or voltage or of a Magnetic field, magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequency, audio frequencies and the lower limit of infrared frequencies; these are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range. Electric current Electric currents that oscillate at radio frequencies (RF currents) have special properties not shared by direct current or lower audio frequency alternating current, such as the 50 or 60 Hz current used in electrical power distribution. * Energy from RF currents in conductors can radiate into space as electromagnetic waves (radio waves). This is the basis of radio technology. * RF cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has a slightly sweet scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen. Nitrous oxide has significant medical uses, especially in surgery and dentistry, for its anaesthetic and pain-reducing effects. Its colloquial name, "laughing gas", coined by Humphry Davy, is due to the euphoric effects upon inhaling it, a property that has led to its recreational use as a dissociative anaesthetic. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is also used as an oxidiser in rocket propellants, and in motor racing to increase the power output of engines. Nitrous oxide's atmospheric concentration reached 333 parts per billion (ppb) in 2020, increasing at a rate of abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Arnott (physician)
James Arnott (1797-1883) was an English physician and pioneer of cryotherapy. Regarded as “the father of modern cryosurgery”, Arnott was the first to utilize extreme cold locally for the destruction of tissue. In 1819, Arnott began his practice of cryotherapy Cryotherapy, sometimes known as cold therapy, is the local or general use of low temperatures in medical therapy. Cryotherapy may be used to treat a variety of tissue lesions. The most prominent use of the term refers to the surgical treatment, s ... to freeze tumors in the treatment of breast and uterine cancers. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Arnott, James 1797 births 1883 deaths 19th-century English medical doctors Cryotherapy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referred to as the "Father of Medicine" in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field, such as the use of prognosis and clinical observation, the systematic categorization of diseases, or the formulation of humoral theory. The Hippocratic school of medicine revolutionized ancient Greek medicine, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields with which it had traditionally been associated (theurgy and philosophy), thus establishing medicine as a profession. However, the achievements of the writers of the Hippocratic Corpus, the practitioners of Hippocratic medicine, and the actions of Hippocrates himself were often conflated; thus very little is known about what Hippocrates actually t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is widely used as a coolant. Physical properties The diatomic character of the N2 molecule is retained after liquefaction. The weak van der Waals interaction between the N2 molecules results in little interatomic interaction, manifested in its very low boiling point. The temperature of liquid nitrogen can readily be reduced to its freezing point by placing it in a vacuum chamber pumped by a vacuum pump. Liquid nitrogen's efficiency as a coolant is limited by the fact that it boils immediately on contact with a warmer object, enveloping the object in an insulating layer of nitrogen gas bubbles. This effect, known as the Leidenfrost effect, occurs when any liquid comes in contact with a surface which is significantly hotter than its boiling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryoablation
Cryoablation is a process that uses extreme cold to destroy tissue. Cryoablation is performed using hollow needles (cryoprobes) through which cooled, thermally conductive, fluids are circulated. Cryoprobes are positioned adjacent to the target in such a way that the freezing process will destroy the diseased tissue. Once the probes are in place, the attached cryogenic freezing unit removes heat from ("cools") the tip of the probe and by extension from the surrounding tissues. Ablation occurs in tissue that has been frozen by at least three mechanisms: # formation of ice crystals within cells thereby disrupting membranes, and interrupting cellular metabolism among other processes; # coagulation of blood thereby interrupting bloodflow to the tissue in turn causing ischemia and cell death; and # induction of apoptosis, the so-called programmed cell death cascade. The most common application of cryoablation is to ablate solid tumors found in the lung, liver, breast, kidney and prosta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin Sheath
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Rather, myelin sheaths the nerve in segments: in general, each axon is encased with multiple long myelinated sections with short gaps in between called nodes of Ranvier. Myelin is formed in the central nervous system (CNS; brain, spinal cord and optic nerve) by glial cells called oligodendrocytes and in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) by glial cells called Schwann cells. In the CNS, axons carry electrical signals from one nerve cell body to another. In the PNS, axons carry signals to muscles and glands or from sensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallerian Degeneration
Wallerian degeneration is an active process of degeneration that results when a nerve fiber is cut or crushed and the part of the axon distal to the injury (i.e. farther from the neuron's cell body) degenerates. A related process of dying back or retrograde degeneration known as 'Wallerian-like degeneration' occurs in many neurodegenerative diseases, especially those where axonal transport is impaired such as ALS and Alzheimer's disease. Primary culture studies suggest that a failure to deliver sufficient quantities of the essential axonal protein NMNAT2 is a key initiating event. Wallerian degeneration occurs after axonal injury in both the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS). It occurs in the section of the axon distal to the site of injury and usually begins within 24–36 hours of a lesion. Prior to degeneration, the distal section of the axon tends to remain electrically excitable. After injury, the axonal skeleton disintegrates, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotmesis
Neurotmesis (in Greek tmesis signifies "to cut") is part of Seddon's classification scheme used to classify nerve damage. It is the most serious nerve injury in the scheme. In this type of injury, both the nerve and the nerve sheath are disrupted. While partial recovery may occur, complete recovery is impossible. Symptoms Symptoms of neurotmesis include but are not limited to pain, dysesthesias (uncomfortable sensations), and complete loss of sensory and motor function of the affected nerve. Anatomy Neurotmesis occurs in the peripheral nervous system and most often in the upper-limb (arms), accounting for 73.5% of all peripheral nerve injury cases. Of these cases, the ulnar nerve was most often injured. Peripheral nerves are structured so that the axons are surrounded by most often a myelinated sheath and then an endoneurium. A perineurium surrounds that and the outermost layer is considered the epineurium. When injury occurs, "local vascular trauma leads to hemorrhage and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |