|
Cry1Ac
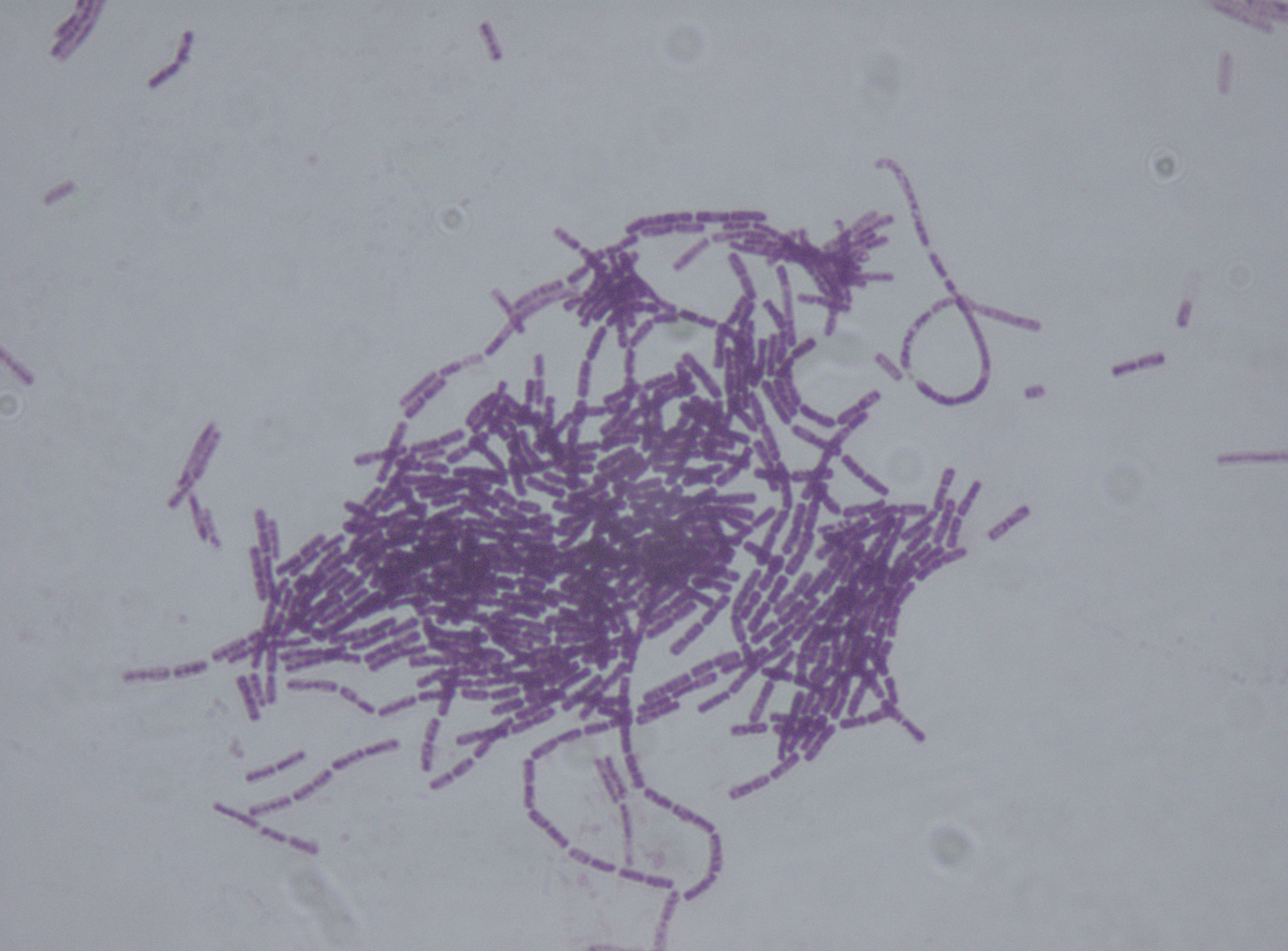
Cry1Ac protoxin is a crystal protein produced by the gram-positive bacterium, ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (Bt) during sporulation. Cry1Ac is one of the delta endotoxins produced by this bacterium which act as insecticides. Because of this, the genes for these have been introduced into commercially important crops by genetic engineering (such as cotton and corn) in order to confer pest resistance on those plants. Transgenic Bt cotton initially expressed a single Bt gene, which codes for Cry1Ac. Subsequently, Bt cotton has added other delta endotoxins. Products such as Bt cotton, Bt brinjal and genetically modified maize have received attention due to a number of issues, including genetically modified food controversies, and the Séralini affair. Cry1Ac is also a mucosal adjuvant (an immune-response enhancer) for humans. It has been used in research to develop a vaccine against the amoeba ''Naegleria fowleri''. This amoeba can invade and attack the human nervous system and brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as '' Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Endotoxin
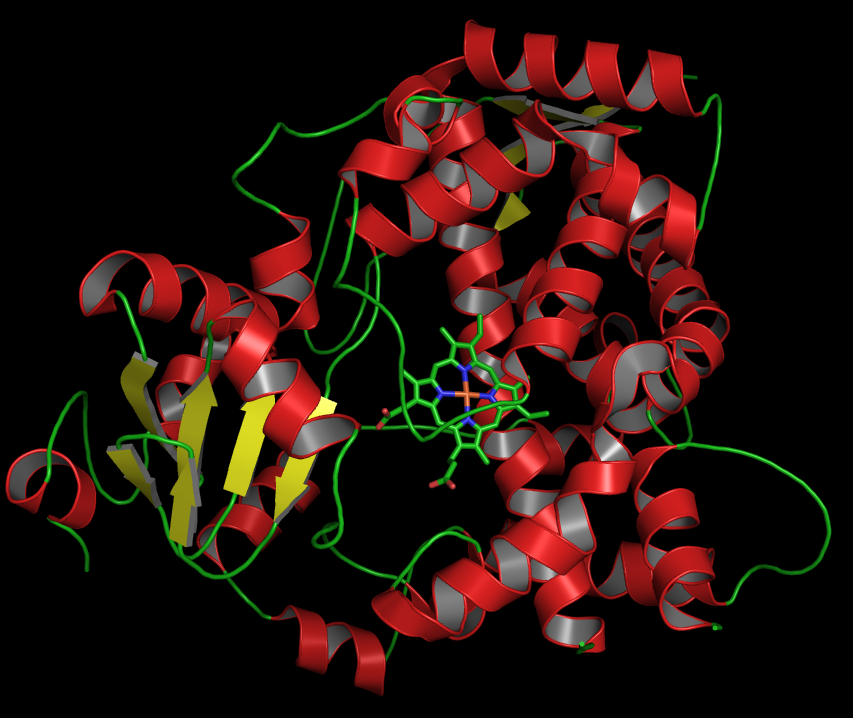
Delta endotoxins (δ-endotoxins) are pore-forming toxins produced by ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' species of bacteria. They are useful for their insecticidal action and are the primary toxin produced by Bt maize/corn. During spore formation the bacteria produce crystals of such proteins (hence the name Cry toxins) that are also known as parasporal bodies, next to the endospores; as a result some members are known as a parasporin. The Cyt (cytolytic) toxin group is a group of delta-endotoxins different from the Cry group. Mechanism of action When an insect ingests these proteins, they are activated by proteolytic cleavage. The N-terminus is cleaved in all of the proteins and a C-terminal extension is cleaved in some members. Once activated, the endotoxin binds to the gut epithelium and causes cell lysis by the formation of cation-selective channels, which leads to death. For many years there was no clarity as to the relationship between aminopeptidase N and Bt toxins. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bt Cotton
Bt cotton is a genetically modified pest resistant plant cotton variety, which produces an insecticide to combat bollworm. Description Strains of the bacterium ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' produce over 200 different Bt toxins, each harmful to different insects. Most notably, Bt toxins are insecticidal to the larvae of moths and butterflies, beetles, cotton bollworms and flies but are harmless to other forms of life. The gene coding for Bt toxin has been inserted into cotton as a transgene, causing it to produce this natural insecticide in its tissues. In many regions, the main pests in commercial cotton are lepidopteran larvae, which are killed by the Bt protein in the genetically modified cotton they eat. This eliminates the need to use large amounts of broad-spectrum insecticides to kill lepidopteran pests (some of which have developed pyrethroid resistance). This spares natural insect predators in the farm ecology and further contributes to noninsecticide pest management. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bt Brinjal
The genetically modified brinjal is a suite of transgenic brinjals (also known as an eggplant or aubergine) created by inserting a crystal protein gene ('' Cry1Ac'') from the soil bacterium ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' into the genome of various brinjal cultivars. The insertion of the gene, along with other genetic elements such as promoters, terminators and an antibiotic resistance marker gene into the brinjal plant is accomplished using ''Agrobacterium''-mediated genetic transformation. The Bt brinjal has been developed to give resistance against lepidopteron insects, in particular the Brinjal Fruit and Shoot Borer (''Leucinodes orbonalis'')(FSB) by forming pores in the digestive system. Mahyco, an Indian seed company based in Jalna, Maharashtra, has developed the Bt brinjal. The genetically modified brinjal event is termed Event EE 1, and Mahyco have also applied for approval of two brinjal hybrids. The Event EE 1 was introgressed by plant breeding into various local varieti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetically Modified Food Controversies
Genetically modified food controversies are disputes over the use of foods and other goods derived from genetically modified crops instead of conventional crops, and other uses of genetic engineering in food production. The disputes involve consumers, farmers, biotechnology companies, governmental regulators, non-governmental organizations, and scientists. The key areas of controversy related to genetically modified food (GM food or GMO food) are whether such food should be labeled, the role of government regulators, the objectivity of scientific research and publication, the effect of genetically modified crops on health and the environment, the effect on pesticide resistance, the impact of such crops for farmers, and the role of the crops in feeding the world population. In addition, products derived from GMO organisms play a role in the production of ethanol fuels and pharmaceuticals. Specific concerns include mixing of genetically modified and non-genetically modified pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetically Modified Maize
Genetically modified maize (corn) is a genetically modified crop. Specific maize strains have been genetically engineered to express agriculturally-desirable traits, including resistance to pests and to herbicides. Maize strains with both traits are now in use in multiple countries. GM maize has also caused controversy with respect to possible health effects, impact on other insects and impact on other plants via gene flow. One strain, called Starlink, was approved only for animal feed in the US but was found in food, leading to a series of recalls starting in 2000. Marketed products Herbicide-resistant maize Corn varieties resistant to glyphosate herbicides were first commercialized in 1996 by Monsanto, and are known as "Roundup Ready Corn". They tolerate the use of Roundup. Bayer CropScience developed "Liberty Link Corn" that is resistant to glufosinate. Pioneer Hi-Bred has developed and markets corn hybrids with tolerance to imidazoline herbicides under the trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis
Naegleriasis (also known as primary amoebic meningoencephalitis; PAM) is an almost invariably fatal infection of the brain by the free-living unicellular eukaryote ''Naegleria fowleri''. Symptoms are meningitis-like and include headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, a stiff neck, confusion, hallucinations and seizures. Symptoms progress rapidly over around five days, and death usually results within one to two weeks of symptoms. ''N. fowleri'' is typically found in warm bodies of fresh water, such as ponds, lakes, rivers and hot springs. It is also found in an amoeboid or temporary flagellate stage in soil, poorly maintained municipal water supplies, water heaters, near warm-water discharges of industrial plants and in poorly chlorinated or unchlorinated swimming pools. There is no evidence of it living in salt water. As the disease is rare, it is often not considered during diagnosis. Although infection occurs very rarely, it almost inevitably results in death. Of the 450 or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naegleria Fowleri
''Naegleria fowleri'', colloquially known as a "brain-eating amoeba", is a species of the genus '' Naegleria'', belonging to the phylum Percolozoa, which is technically not classified as true amoeba, but a shapeshifting amoeboflagellate excavate. It is a free-living, bacteria-eating microorganism that can be pathogenic, causing an extremely rare, sudden, severe and usually fatal brain infection called naegleriasis or primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). This microorganism is typically found in bodies of warm freshwater, such as ponds, lakes, rivers, hot springs, warm water discharge from industrial or power plants, geothermal well water, poorly maintained or minimally chlorinated (under 0.5 mg/m3 residual) swimming pools, water heaters, soil, and pipes connected to tap water. It can be seen in either an amoeboid or temporary flagellate stage. Etymology The organism was named after Malcolm Fowler, an Australian pathologist at Adelaide Children's Hospital, who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjuvants, Immunologic
In immunology, an adjuvant is a substance that increases or modulates the immune response to a vaccine. The word "adjuvant" comes from the Latin word ''adiuvare'', meaning to help or aid. "An immunologic adjuvant is defined as any substance that acts to accelerate, prolong, or enhance antigen-specific immune responses when used in combination with specific vaccine antigens." In the early days of vaccine manufacture, significant variations in the efficacy of different batches of the same vaccine were correctly assumed to be caused by contamination of the reaction vessels. However, it was soon found that more scrupulous cleaning actually seemed to ''reduce'' the effectiveness of the vaccines, and some contaminants actually enhanced the immune response. There are many known adjuvants in widespread use, including aluminium salts, oils and virosomes. Overview Adjuvants in immunology are often used to modify or augment the effects of a vaccine by stimulating the immune system to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes (such as lysozymes), immunoglobulins (especially IgA), and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Amphibians, fish, snails, slugs, and some other invertebrates also produce external mucus from their epidermis as protection against pathogens, and to help in movement and is also produced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Séralini Affair
The Séralini affair was the controversy surrounding the publication, retraction, and republication of a journal article by French molecular biologist Gilles-Éric Séralini. First published by ''Food and Chemical Toxicology '' in September 2012, the article presented a two-year feeding study in rats, and reported an increase in tumors among rats fed genetically modified corn and the herbicide RoundUp. Scientists and regulatory agencies subsequently concluded that the study's design was flawed and its findings unsubstantiated. A chief criticism was that each part of the study had too few rats to obtain statistically useful data, particularly because the strain of rat used, Sprague Dawley, develops tumors at a high rate over its lifetime. The publicity surrounding publication of the article also attracted criticism, with science writer Declan Butler calling it "a tightly orchestrated media offensive". As part of a news embargo, Séralini required journalists to sign an unusu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoxin
Toxication, toxification or toxicity exaltation is the conversion of a chemical compound into a more toxic form in living organisms or in substrates such as soil or water. The conversion can be caused by enzymatic metabolism in the organisms, as well as by abiotic chemical reactions. While the parent drug are usually less active, both the parent drug and its metabolite can be chemically active and cause toxicity, leading to mutagenesis, teratogenesis, and carcinogenesis. Different classes of enzymes, such as P450-monooxygenases, epoxide hydrolase, or acetyltransferases can catalyze the process in the cell, mostly in the liver. Parent non-toxic chemicals are generally referred to as ''protoxins''. While toxication is generally undesirable, in certain cases it is required for the ''in vivo'' conversion of a prodrug to a metabolite with desired pharmacological or toxicological activity. Codeine is an example of a prodrug, metabolized in the body to the active compounds morphine and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |