|
Crosswell Glacier
Crosswell Glacier () is a glacier long, flowing north-northeast from Mount Shinn between Sullivan Heights and Bearskin Ridge, in the central part of the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. Together with Patton and Pulpudeva Glaciers, it enters Ellen Glacier northwest of Mamarchev Peak and southeast of Mount Jumper. The glacier was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1957–59, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Colonel Horace A. Crosswell, United States Air Force, leader of C-124 Globemaster air drops in establishing the scientific station at the South Pole in the 1956–57 season. Tributary glaciers * Ramorino Glacier * Cervellati Glacier See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamarchev Peak
Mamarchev Peak ( bg, Мамарчев връх, Mamarchev vrah, ) is the peak with tween heights both rising to Reference Elevation Model of Antarctica. Polar Geospatial Center. University of Minnesota, 2019 in the north part of Sullivan Heights in central in , , and surmounting [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glaciers In The Antarctic
There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include ice sheets, ice caps or ice fields, such as the Antarctic ice sheet, but includes glacial features that are defined by their flow, rather than general bodies of ice. The lists include outlet glaciers, valley glaciers, cirque glaciers, tidewater glaciers and ice streams. Ice streams are a type of glacier and many of them have "glacier" in their name, e.g. Pine Island Glacier. Ice shelves are listed separately in the List of Antarctic ice shelves. For the purposes of these lists, the Antarctic is defined as any latitude further south than 60° (the continental limit according to the Antarctic Treaty System). List by letters * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: A–H * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: I–Z See also * List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands * List of Antarctic ice rises * List of Antarctic ice shelves * List of Antarctic ice streams * List of glaciers * List of subantar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervellati Glacier
Cervellati Glacier () is the long glacier situated southeast of Patton Glacier and northwest of Ramorino Glacier on the east slope of Sentinel Range in the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It flows northeastwards between Tyree Ridge and Epperly Ridge, and enters Crosswell Glacier southeast of Mount Bearskin. The feature was named by US-ACAN in 2006 after Roberto Cervellati, Italian representative to the SCAR Expert Group on Geographic Information, 1992–2006, and director of the SCAR Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica in the same period. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, climato ... Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramorino Glacier
Ramorino Glacier () is the long glacier situated northwest of upper Crosswell Glacier and southeast of Cervellati Glacier on the east slope of Sentinel Range in the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It flows northeastwards between Epperly Ridge and Shinn Ridge, and enters Crosswell Glacier northwest of Mount Segers. The feature was named by US-ACAN in 2006 after Maria Chiara Ramorino, manager of the Italian team that compiled and promulgated the SCAR Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica, 1998–2006. Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly updated. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
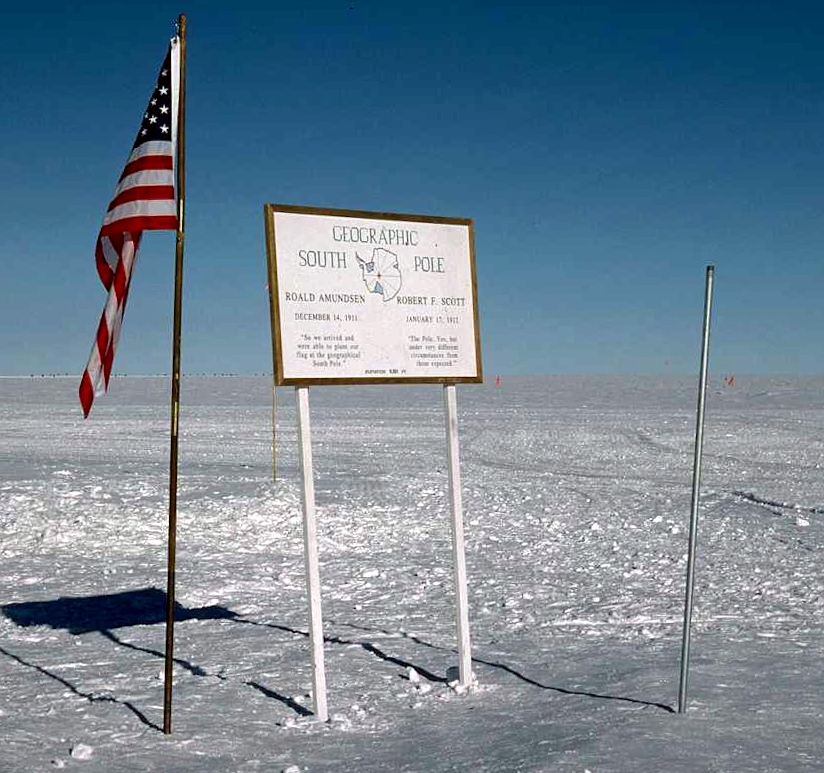
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipodally on the opposite side of Earth from the North Pole, at a distance of 12,430 miles (20,004 km) in all directions. Situated on the continent of Antarctica, it is the site of the United States Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station, which was established in 1956 and has been permanently staffed since that year. The Geographic South Pole is distinct from the South Magnetic Pole, the position of which is defined based on Earth's magnetic field. The South Pole is at the centre of the Southern Hemisphere. Geography For most purposes, the Geographic South Pole is defined as the southern point of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface (the other being the Geographic North Pole). However, Earth's axis of rotat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-124 Globemaster
The Douglas C-124 Globemaster II, nicknamed "Old Shaky", is an American heavy-lift cargo aircraft built by the Douglas Aircraft Company in Long Beach, California. The C-124 was the primary heavy-lift transport for United States Air Force (USAF) Military Air Transport Service (MATS) during the 1950s and early 1960s, until the Lockheed C-141 Starlifter entered service. It served in MATS, later Military Airlift Command (MAC), units of the Air Force Reserve and Air National Guard until retired in 1974. Design and development Douglas Aircraft developed the C-124 from 1947 to 1949, from a prototype they created from a World War II–design Douglas C-74 Globemaster, and based on lessons learned during the Berlin Airlift. The aircraft was powered by four large Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major piston engines producing each. The C-124's design featured two large clamshell doors and a hydraulically actuated ramp in the nose as well as a cargo elevator under the aft fuselage. The C-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control. The United States Air Force is a military service branch organized within the Department of the Air Force, one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The Air Force through the Department of the Air Force is headed by the civilian Secretary of the Air Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horace A
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 – 27 November 8 BC), known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his ''Odes'' as just about the only Latin lyrics worth reading: "He can be lofty sometimes, yet he is also full of charm and grace, versatile in his figures, and felicitously daring in his choice of words."Quintilian 10.1.96. The only other lyrical poet Quintilian thought comparable with Horace was the now obscure poet/metrical theorist, Caesius Bassus (R. Tarrant, ''Ancient Receptions of Horace'', 280) Horace also crafted elegant hexameter verses (''Satires'' and '' Epistles'') and caustic iambic poetry ('' Epodes''). The hexameters are amusing yet serious works, friendly in tone, leading the ancient satirist Persius to comment: "as his friend laughs, Horace slyly puts his finger on his every fault; once let in, he plays about the heartstring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Jumper
Mount Jumper () is a mountain high located east of Mount Viets in the central part of the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. Debren Pass separates it from the side ridge descending via Evans Peak. The mountain overlooks Ellen Glacier to the north and east, and its tributaries Patton Glacier and Rumyana Glacier to the south and northwest respectively. Mount Jumper was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos from 1957 to 1959, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Major Jesse T. Jumper of the United States Air Force who participated in establishing the South Pole Station in the 1956–57 season. See also * Mountains in Antarctica This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica South Atl ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |