|
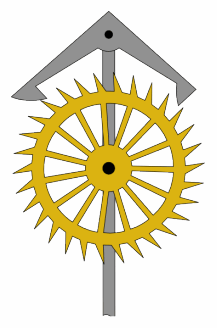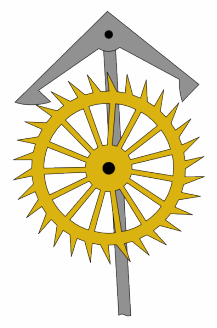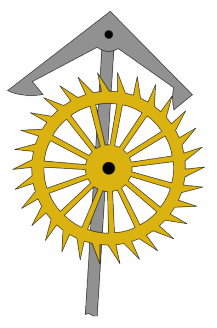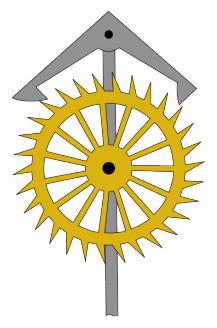
Cross-beat Escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to the clock's timekeeping element (usually a pendulum or balance wheel) to replace the energy lost to friction during its cycle and keep the timekeeper oscillating. The escapement is driven by force from a coiled spring or a suspended weight, transmitted through the timepiece's gear train. Each swing of the pendulum or balance wheel releases a tooth of the escapement's ''escape wheel'', allowing the clock's gear train to advance or "escape" by a fixed amount. This regular periodic advancement moves the clock's hands forward at a steady rate. At the same time, the tooth gives the timekeeping element a push, before another tooth catches on the escapement's pallet, returning the escapement to its "locked" state. The sudden stopping of the esc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchor Escapement Animation 217x328px
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal , used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ''ancora'', which itself comes from the Greek ἄγκυρα (ankȳra). Anchors can either be temporary or permanent. Permanent anchors are used in the creation of a mooring, and are rarely moved; a specialist service is normally needed to move or maintain them. Vessels carry one or more temporary anchors, which may be of different designs and weights. A sea anchor is a drag device, not in contact with the seabed, used to minimise drift of a vessel relative to the water. A drogue is a drag device used to slow or help steer a vessel running before a storm in a following or overtaking sea, or when crossing a bar in a breaking sea.. Overview Anchors achieve holding power either by "hooking" into the seabed, or mass, or a combination of the two. Permanent moorings use large masses (common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Clock
A water clock or clepsydra (; ; ) is a timepiece by which time is measured by the regulated flow of liquid into (inflow type) or out from (outflow type) a vessel, and where the amount is then measured. Water clocks are one of the oldest time-measuring instruments. The bowl-shaped outflow is the simplest form of a water clock and is known to have existed in Babylon, Egypt, and Persia around the 16th century BC. Other regions of the world, including India and China, also have early evidence of water clocks, but the earliest dates are less certain. Some authors, however, claim that water clocks appeared in China as early as 4000 BC. Water clocks were also used in ancient Greece and ancient Rome, described by technical writers such as Ctesibius and Vitruvius. Designs A water clock uses the flow of water to measure time. If viscosity is neglected, the physical principle required to study such clocks is Torricelli's law. There are two types of water clocks: inflow and outflo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Clock
An astronomical clock, horologium, or orloj is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets. Definition The term is loosely used to refer to any clock that shows, in addition to the time of day, astronomical information. This could include the location of the Sun and Moon in the sky, the age and Lunar phases, the position of the Sun on the ecliptic and the current zodiac sign, the sidereal time, and other astronomical data such as the Moon's nodes (for indicating eclipses) or a rotating star map. The term should not be confused with ''astronomical regulator'', a high precision but otherwise ordinary pendulum clock used in observatories. Astronomical clocks usually represent the Solar System using the geocentric model. The center of the dial is often marked with a disc or sphere representing the Earth, located at the center of the Solar Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Su Song
Su Song (, 1020–1101), courtesy name Zirong (), was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman. Excelling in a variety of fields, he was accomplished in mathematics, Chinese astronomy, astronomy, History of cartography#China, cartography, geography, horology, pharmacology, mineralogy, metallurgy, zoology, botany, mechanical engineering, hydraulic engineering, civil engineering, invention, art, Chinese poetry, poetry, Chinese philosophy, philosophy, antiquities, and Foreign relations of Imperial China, statesmanship during the Song dynasty (960–1279). Su Song was the engineer for a Hydraulics, hydro-mechanical Astronomical clock, astronomical clock tower in medieval Kaifeng, which employed an early escapement mechanism.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 445.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 448.Bodde, 140.Fry, 10. The escapement mechanism of Su's clock tower had been invented by Tang dynasty Buddhist monk Yi Xing and government official Liang Lingzan in 725 AD to operate a water-powered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Sixun
Zhang Sixun (, fl. 10th century) was a Chinese astronomer and mechanical engineer from Bazhong, Sichuan during the early Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD).Liu, 577. He is credited with creating an armillary sphere for his astronomical clock tower that employed the use of liquid mercury (dripped periodically from a clepsydra clock).Needham, Volume 4, 469-471. The liquid mercury filled scoops of the waterwheel would rotate and thus provide the effect of an escapement mechanism in clockworks and allow the astronomical armillary sphere to rotate as needed. Life and works According to the '' History of Song'', Zhang Sixun passed the state examinations in astronomy and mathematics, for this he was appointed to service in the national astronomical observatory (Si Tian Jian), within two years of taking office he had finished construction of an armillary sphere either in 977 or 979. As a result, he was rewarded as assistant to the Astronomical Bureau. Zhang Sixun, although innovative, built u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drive Wheel
A drive wheel is a wheel of a motor vehicle that transmits force, transforming torque into tractive force from the tires to the road, causing the vehicle to move. The powertrain delivers enough torque to the wheel to overcome stationary forces, resulting in the vehicle moving forwards or backwards. A two-wheel drive vehicle has two driven wheels, typically both at the front or back, while a four-wheel drive has four. A steering wheel is a wheel that turns to change the direction of a vehicle. A trailer wheel is one that is neither a drive wheel, nor a steer wheel. Front-wheel drive vehicles typically have the rear wheels as trailer wheels. Drive wheel configurations Front-wheel drive Front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles' engines drive the front wheels. Using the front wheels for delivery of power as well as steering allows the driving force to act in the same direction as the wheel is pointing. This layout is commonly used in modern passenger cars. A rare example of front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armillary Sphere
An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (on the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centered on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features, such as the ecliptic. As such, it differs from a celestial globe, which is a smooth sphere whose principal purpose is to map the constellations. It was invented separately first in ancient China during the 4th century BC and ancient Greece during the 3rd century BC, with later uses in the Islamic world and Medieval Europe. With the Earth as center, an armillary sphere is known as ''Ptolemaic''. With the Sun as center, it is known as '' Copernican''. The flag of Portugal features an armillary sphere. The armillary sphere is also featured in Portuguese heraldry, associated with the Portuguese discoveries during the Age of Exploration. Manuel I of Portugal, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang Lingzan
Liang Lingzan () was a Chinese artist, astronomer, inventor, mechanical engineer and politician of the Kaiyuan era during the Tang Dynasty. He invented a mechanized water clock with the Tantric monk and mathematician Yi Xing (). It was actually an astronomical instrument that served as a clock, made of bronze in the capital of Chang'an in the 720s. It was described by a contemporary text this way: twas made in the image of the round heavens and on it were shown the lunar mansions in their order, the equator and the degrees of the heavenly circumference. Water, flowing into scoops, turned a wheel automatically, rotating it one complete revolution in one day and night. Besides this, there were two rings fitted around the celestial sphere outside, having the sun and moon threaded on them, and these were made to move in circling orbit ... And they made a wooden casing the surface of which represented the horizon, since the instrument was half sunk in it. It permitted the exact d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi Xing
Yi Xing (, 683–727), born Zhang Sui (), was a Chinese astronomer, Buddhist monk, inventor, mathematician, mechanical engineer, and philosopher during the Tang dynasty. His astronomical celestial globe featured a liquid-driven escapement, the first in a long tradition of Chinese astronomical clockworks. Science and technology Astrogeodetic survey In the early 8th century, the Tang court put Yi Xing in charge of an astrogeodetic survey.Hsu, 98. This survey had many purposes. It was established in order to obtain new astronomical data that would aid in the prediction of solar eclipses. The survey was also initiated so that flaws in the calendar system could be corrected and a new, updated calendar installed in its place. The survey was also essential in determining the arc measurement, i.e., the length of meridian arc-although Yi Xing, who did not know the Earth was spherical, did not conceptualize his measurements in these terms. This would resolve the confusion created by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular volcanic rock that differs from pumice in having larger vesicles, thicker vesicle walls, and being dark colored and denser.Jackson, J.A., J. Mehl, and K. Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' American Geological Institute, Alexandria, Virginia. 800 pp. McPhie, J., M. Doyle, and R. Allen (1993) ''Volcanic Textures A guide to the interpretation of textures in volcanic rocks'' Centre for Ore Deposit and Exploration Studies, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Tasmania..198 pp. Pumice is created when super-heated, highly pressurized rock is violently ejected from a volcano. The unusual foamy configuration of pumice happens because of simultaneous rapid cooling and rapid depressurization. The depressurization creates bubbles by lowering the solubi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washstand
A washstand or basin stand is a piece of furniture consisting of a small table or cabinet, usually supported on three or four legs, and most commonly made of mahogany, walnut, or rosewood, and made for holding a wash basin and water pitcher. The smaller varieties were used for rose-water ablutions, or for hair-powdering. The larger ones, which possessed receptacles for soap-dishes, were the predecessors of the modern bathroom wash basin, or sink. Both varieties, often of very elegant form, were in extensive use throughout a large part of the 18th century and early-19th century, eventually disappearing with the advent of modern indoor plumbing. Ancient Greece In his ''Pneumatics'', (chapter 31) Philo of Byzantium, a Greek engineer and writer on mechanics, describes an escapement mechanism, the earliest known, as part of a washstand. A counterweighted spoon, supplied by a water tank, tips over in a basin when full releasing a pumice in the process. Once the spoon has emptied, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


