|
Critical Mass (book)
''Critical Mass: How One Thing Leads to Another'' is a non-fiction book by English chemist and physicist Philip Ball, originally published in 2004, discusses the concept of a "physics of society". Ball examines past thinkers, such as Thomas Hobbes, Lewis Mumford, Emyr Hughes, and Gottfried Achenwall, who have attempted to apply (or argue against) the use of physics, chemistry, or mathematics in the study of mass social phenomena. He also discusses how the concept relates to recent research, including his own.Ball, Philip. (2004). Critical Mass- How One Thing Leads to Another'' ("particles become people", pg. 110). New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. Physics of society The outlines of Ball's ''Critical Mass'', the most popular of his many noted books, beginning in various circa 2001 lectures, talks, and articles focused on what he calls a 'physics of society', similar to the social physics in the Auguste Comte sense, a subject Ball approaches using statistical mechanics viewing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Ball
Philip Ball (born 1962) is a British science writer. For over twenty years he has been an editor of the journal ''Nature'' for which he continues to write regularly. He now writes a regular column in '' Chemistry World''. He has contributed to publications ranging from ''New Scientist'' to the ''New York Times'', ''The Guardian'', the ''Financial Times'' and ''New Statesman''. He is the regular contributor to '' Prospect'' magazine, and also a columnist for ''Chemistry World'', ''Nature Materials'' and BBC Future. He has broadcast on many occasions on radio and TV, and in June 2004 he presented a three-part serial on nanotechnology, ''Small Worlds'', on BBC Radio 4. Work Ball's 2004 book '' Critical Mass: How One Thing Leads to Another'' was the winner of the 2005 Aventis Prize for Science Books. It examines a wide range of topics including the business cycle, random walks, phase transitions, bifurcation theory, traffic flow, Zipf's law, Small world phenomenon, catastrophe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Will
Free will is the capacity of agents to choose between different possible courses of action unimpeded. Free will is closely linked to the concepts of moral responsibility, praise, culpability, sin, and other judgements which apply only to actions that are freely chosen. It is also connected with the concepts of advice, persuasion, deliberation, and prohibition. Traditionally, only actions that are freely willed are seen as deserving credit or blame. Whether free will exists, what it is and the implications of whether it exists or not are some of the longest running debates of philosophy and religion. Some conceive of free will as the right to act outside of external influences or wishes. Some conceive free will to be the capacity to make choices undetermined by past events. Determinism suggests that only one course of events is possible, which is inconsistent with a libertarian model of free will. Ancient Greek philosophy identified this issue, which remains a major focus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Mass (sociodynamics)
In social dynamics, critical mass is a sufficient number of adopters of a new idea, technology or innovation in a social system so that the rate of adoption becomes self-sustaining and creates further growth. The point at which critical mass is achieved is sometimes referred to as a threshold within the threshold model of statistical modeling. The term critical mass is borrowed from nuclear physics and in that field, it refers to the amount of a substance needed to sustain a chain reaction. Within social sciences, critical mass has its roots in sociology and is often used to explain the conditions under which reciprocal behavior is started within collective groups, and how it becomes self-sustaining. Recent technology research in platform ecosystems shows that apart from the quantitative notion of a “sufficient number” critical mass is also influenced by qualitative properties such as reputation, interests, commitments, capabilities, goals, consensuses, and decisions, all of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Winton Prize For Science Books
The Royal Society Science Books Prize is an annual £25,000 prize awarded by the Royal Society to celebrate outstanding popular science books from around the world. It is open to authors of science books written for a non-specialist audience, and since it was established in 1988 has championed writers such as Stephen Hawking, Jared Diamond, Stephen Jay Gould and Bill Bryson. In 2015 ''The Guardian'' described the prize as "the most prestigious science book prize in Britain". History The Royal Society established the Science Books Prize in 1988 with the aim of encouraging the writing, publishing and reading of good and accessible popular science books. Its name has varied according to sponsorship agreements. Judging process A panel of judges decides the shortlist and the winner of the Prize each year. The panel is chaired by a fellow of the Royal Society and includes authors, scientists and media personalities. The judges for the 2016 prize included author Bill Bryson, theoretic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aventis Prize For Science Books
The Royal Society Science Books Prize is an annual £25,000 prize awarded by the Royal Society to celebrate outstanding popular science books from around the world. It is open to authors of science books written for a non-specialist audience, and since it was established in 1988 has championed writers such as Stephen Hawking, Jared Diamond, Stephen Jay Gould and Bill Bryson. In 2015 ''The Guardian'' described the prize as "the most prestigious science book prize in Britain". History The Royal Society established the Science Books Prize in 1988 with the aim of encouraging the writing, publishing and reading of good and accessible popular science books. Its name has varied according to sponsorship agreements. Judging process A panel of judges decides the shortlist and the winner of the Prize each year. The panel is chaired by a fellow of the Royal Society and includes authors, scientists and media personalities. The judges for the 2016 prize included author Bill Bryson, theoreti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Models
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in the natural sciences (such as physics, biology, earth science, chemistry) and engineering disciplines (such as computer science, electrical engineering), as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences (such as economics, psychology, sociology, political science). The use of mathematical models to solve problems in business or military operations is a large part of the field of operations research. Mathematical models are also used in music, linguistics, and philosophy (for example, intensively in analytic philosophy). A model may help to explain a system and to study the effects of different components, and to make predictions about behavior. Elements of a mathematical model Mathematical models can take many forms, including dynamical systems, statistical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner's Dilemma
The Prisoner's Dilemma is an example of a game analyzed in game theory. It is also a thought experiment that challenges two completely rational agents to a dilemma: cooperate with their partner for mutual reward, or betray their partner ("defect") for individual reward. This dilemma was originally framed by Merrill Flood and Melvin Dresher while working at RAND in 1950. Albert W. Tucker appropriated the game and formalized it by structuring the rewards in terms of prison sentences and named it "prisoner's dilemma". William Poundstone in his 1993 book ''Prisoner's Dilemma'' writes the following version:Two members of a criminal gang are arrested and imprisoned. Each prisoner is in solitary confinement with no means of speaking to or exchanging messages with the other. The police admit they don't have enough evidence to convict the pair on the principal charge. They plan to sentence both to two years in prison on a lesser charge. Simultaneously, the police offer each prisoner a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catastrophe Theory
In mathematics, catastrophe theory is a branch of bifurcation theory in the study of dynamical systems; it is also a particular special case of more general singularity theory in geometry. Bifurcation theory studies and classifies phenomena characterized by sudden shifts in behavior arising from small changes in circumstances, analysing how the qualitative nature of equation solutions depends on the parameters that appear in the equation. This may lead to sudden and dramatic changes, for example the unpredictable timing and magnitude of a landslide. Catastrophe theory originated with the work of the French mathematician René Thom in the 1960s, and became very popular due to the efforts of Christopher Zeeman in the 1970s. It considers the special case where the long-run stable equilibrium can be identified as the minimum of a smooth, well-defined potential function (Lyapunov function). In the late 1970s, applications of catastrophe theory to areas outside its scope began to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small World Phenomenon
The small-world experiment comprised several experiments conducted by Stanley Milgram and other researchers examining the average path length for social networks of people in the United States. The research was groundbreaking in that it suggested that human society is a small-world-type network characterized by short path-lengths. The experiments are often associated with the phrase "six degrees of separation", although Milgram did not use this term himself. Historical context of the small-world problem Guglielmo Marconi's conjectures based on his radio work in the early 20th century, which were articulated in his 1909 Nobel Prize address, may have inspired Hungarian author Frigyes Karinthy to write a challenge to find another person to whom he could not be connected through at most five people.Barabási, Albert-László . 2003. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Flow
In mathematics and transportation engineering, traffic flow is the study of interactions between travellers (including pedestrians, cyclists, drivers, and their vehicles) and infrastructure (including highways, signage, and traffic control devices), with the aim of understanding and developing an optimal transport network with efficient movement of traffic and minimal traffic congestion problems. History Attempts to produce a mathematical theory of traffic flow date back to the 1920s, when Frank Knight first produced an analysis of traffic equilibrium, which was refined into John Glen Wardrop, Wardrop's first and second principles of equilibrium in 1952. Nonetheless, even with the advent of significant computer processing power, to date there has been no satisfactory general theory that can be consistently applied to real flow conditions. Current traffic models use a mixture of empirical and Deductive reasoning, theoretical techniques. These models are then developed into Trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
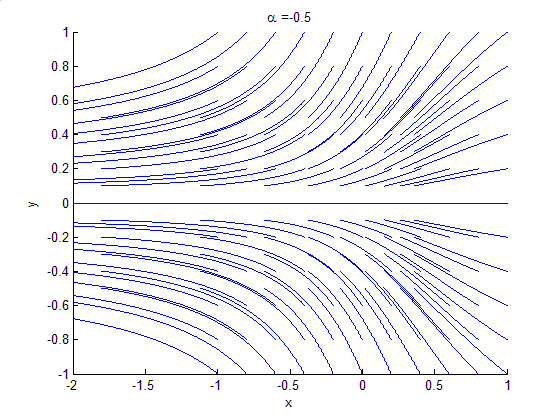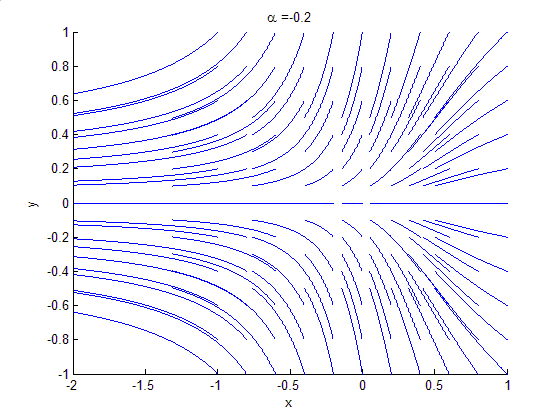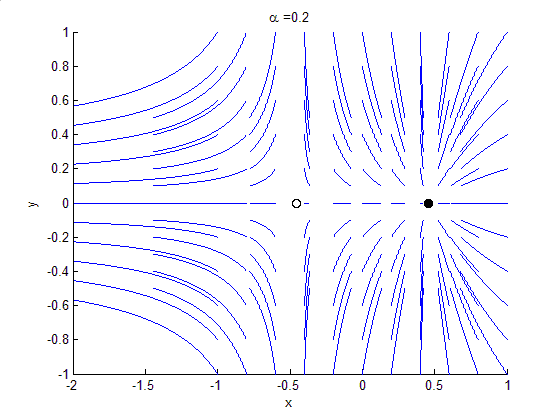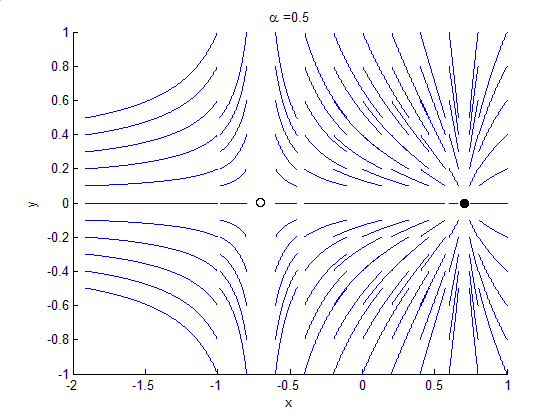
Bifurcation Theory
Bifurcation theory is the mathematical study of changes in the qualitative or topological structure of a given family of curves, such as the integral curves of a family of vector fields, and the solutions of a family of differential equations. Most commonly applied to the mathematical study of dynamical systems, a bifurcation occurs when a small smooth change made to the parameter values (the bifurcation parameters) of a system causes a sudden 'qualitative' or topological change in its behavior. Bifurcations occur in both continuous systems (described by ordinary, delay or partial differential equations) and discrete systems (described by maps). The name "bifurcation" was first introduced by Henri Poincaré in 1885 in the first paper in mathematics showing such a behavior. Henri Poincaré also later named various types of stationary points and classified them . Bifurcation types It is useful to divide bifurcations into two principal classes: * Local bifurcations, which can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |