Traffic Flow on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In

 Traffic behaves in a complex and nonlinear way, depending on the interactions of a large number of
Traffic behaves in a complex and nonlinear way, depending on the interactions of a large number of


 The density (''k'') within a length of roadway (''L'') at a given time (''t''1) is equal to the inverse of the average spacing of the ''n'' vehicles.
In a time-space diagram, the density may be evaluated in the region A.
where ''tt'' is the total travel time in ''A''.
The density (''k'') within a length of roadway (''L'') at a given time (''t''1) is equal to the inverse of the average spacing of the ''n'' vehicles.
In a time-space diagram, the density may be evaluated in the region A.
where ''tt'' is the total travel time in ''A''.

 If vehicles experience no delay as they travel from ''X''1 to ''X''2, then the arrivals of vehicles at location ''X''1 is represented by curve ''N''1 and the arrivals of the vehicles at location ''X''2 is represented by ''N''2 in figure 8. More commonly, curve ''N''1 is known as the ''arrival curve'' of vehicles at location ''X''1 and curve ''N''2 is known as the ''arrival curve'' of vehicles at location ''X''2. Using a one-lane signalized approach to an intersection as an example, where ''X''1 is the location of the stop bar at the approach and ''X''2 is an arbitrary line on the receiving lane just across of the intersection, when the traffic signal is green, vehicles can travel through both points with no delay and the time it takes to travel that distance is equal to the free-flow travel time. Graphically, this is shown as the two separate curves in figure 8.
However, when the traffic signal is red, vehicles arrive at the stop bar (''X''1) and are delayed by the red light before crossing ''X''2 some time after the signal turns green. As a result, a queue builds at the stop bar as more vehicles are arriving at the intersection while the traffic signal is still red. Therefore, for as long as vehicles arriving at the intersection are still hindered by the queue, the curve ''N''2 no longer represents the vehicles’ arrival at location ''X''2; it now represents the vehicles’ ''virtual arrival'' at location ''X''2, or in other words, it represents the vehicles' arrival at ''X''2 if they did not experience any delay. The vehicles' arrival at location ''X''2, taking into account the delay from the traffic signal, is now represented by the curve ''N′''2 in figure 9.
However, the concept of the ''virtual arrival curve'' is flawed. This curve does not correctly show the queue length resulting from the interruption in traffic (i.e. red signal). It assumes that all vehicles are still reaching the stop bar before being delayed by the red light. In other words, the ''virtual arrival curve'' portrays the stacking of vehicles vertically at the stop bar. When the traffic signal turns green, these vehicles are served in a first-in-first-out (FIFO) order. For a multi-lane approach, however, the service order is not necessarily FIFO. Nonetheless, the interpretation is still useful because of the concern with average total delay instead of total delays for individual vehicles.Pitstick, Mark E. "Measuring Delay and Simulating Performance at Isolated Signalized Intersections Using Cumulative Curves." ''Transportation Research Record 1287'' (1990)
If vehicles experience no delay as they travel from ''X''1 to ''X''2, then the arrivals of vehicles at location ''X''1 is represented by curve ''N''1 and the arrivals of the vehicles at location ''X''2 is represented by ''N''2 in figure 8. More commonly, curve ''N''1 is known as the ''arrival curve'' of vehicles at location ''X''1 and curve ''N''2 is known as the ''arrival curve'' of vehicles at location ''X''2. Using a one-lane signalized approach to an intersection as an example, where ''X''1 is the location of the stop bar at the approach and ''X''2 is an arbitrary line on the receiving lane just across of the intersection, when the traffic signal is green, vehicles can travel through both points with no delay and the time it takes to travel that distance is equal to the free-flow travel time. Graphically, this is shown as the two separate curves in figure 8.
However, when the traffic signal is red, vehicles arrive at the stop bar (''X''1) and are delayed by the red light before crossing ''X''2 some time after the signal turns green. As a result, a queue builds at the stop bar as more vehicles are arriving at the intersection while the traffic signal is still red. Therefore, for as long as vehicles arriving at the intersection are still hindered by the queue, the curve ''N''2 no longer represents the vehicles’ arrival at location ''X''2; it now represents the vehicles’ ''virtual arrival'' at location ''X''2, or in other words, it represents the vehicles' arrival at ''X''2 if they did not experience any delay. The vehicles' arrival at location ''X''2, taking into account the delay from the traffic signal, is now represented by the curve ''N′''2 in figure 9.
However, the concept of the ''virtual arrival curve'' is flawed. This curve does not correctly show the queue length resulting from the interruption in traffic (i.e. red signal). It assumes that all vehicles are still reaching the stop bar before being delayed by the red light. In other words, the ''virtual arrival curve'' portrays the stacking of vehicles vertically at the stop bar. When the traffic signal turns green, these vehicles are served in a first-in-first-out (FIFO) order. For a multi-lane approach, however, the service order is not necessarily FIFO. Nonetheless, the interpretation is still useful because of the concern with average total delay instead of total delays for individual vehicles.Pitstick, Mark E. "Measuring Delay and Simulating Performance at Isolated Signalized Intersections Using Cumulative Curves." ''Transportation Research Record 1287'' (1990)
 The traffic light example depicts ''N''-curves as smooth functions. Theoretically, however, plotting ''N''-curves from collected data should result in a step-function (figure 10). Each step represents the arrival or departure of one vehicle at that point in time. When the ''N''-curve is drawn on larger scale reflecting a period of time that covers several cycles, then the steps for individual vehicles can be ignored, and the curve will then look like a smooth function (figure 8).
The traffic light example depicts ''N''-curves as smooth functions. Theoretically, however, plotting ''N''-curves from collected data should result in a step-function (figure 10). Each step represents the arrival or departure of one vehicle at that point in time. When the ''N''-curve is drawn on larger scale reflecting a period of time that covers several cycles, then the steps for individual vehicles can be ignored, and the curve will then look like a smooth function (figure 8).
 The aim of traffic flow analysis is to create and implement a model which would enable vehicles to reach their destination in the shortest possible time using the maximum roadway capacity. This is a four-step process:
* Generation – the program estimates how many trips would be generated. For this, the program needs the statistical data of residence areas by population, location of workplaces etc.;
* Distribution – after generation it makes the different Origin-Destination (OD) pairs between the location found in step 1;
* Modal Split/Mode Choice – the system has to decide how much percentage of the population would be split between the difference modes of available transport, e.g. cars, buses, rails, etc.;
* Route Assignment – finally, routes are assigned to the vehicles based on minimum criterion rules.
This cycle is repeated until the solution converges.
There are two main approaches to tackle this problem with the end objectives:
* System optimum
* User equilibrium
The aim of traffic flow analysis is to create and implement a model which would enable vehicles to reach their destination in the shortest possible time using the maximum roadway capacity. This is a four-step process:
* Generation – the program estimates how many trips would be generated. For this, the program needs the statistical data of residence areas by population, location of workplaces etc.;
* Distribution – after generation it makes the different Origin-Destination (OD) pairs between the location found in step 1;
* Modal Split/Mode Choice – the system has to decide how much percentage of the population would be split between the difference modes of available transport, e.g. cars, buses, rails, etc.;
* Route Assignment – finally, routes are assigned to the vehicles based on minimum criterion rules.
This cycle is repeated until the solution converges.
There are two main approaches to tackle this problem with the end objectives:
* System optimum
* User equilibrium
 The core principle of User Equilibrium is that all used routes between a given OD pair have the same travel time. An alternative route option is enabled to use when the actual travel time in the system has reached the free-flow travel time on that route.
For a highway user optimum model considering one alternative route, a typical process of traffic assignment is shown in figure 15. When the traffic demand stays below the highway capacity, the delay time on highway stays zero. When the traffic demand exceeds the capacity, the queue of vehicle will appear on the highway and the delay time will increase. Some of users will turn to the city streets when the delay time reaches the difference between the free-flow travel time on highway and the free-flow travel time on city streets. It indicates that the users staying on the highway will spend as much travel time as the ones who turn to the city streets. At this stage, the travel time on both the highway and the alternative route stays the same. This situation may be ended when the demand falls below the road capacity, that is the travel time on highway begins to decrease and all the users will stay on the highway. The total of part area 1 and 3 represents the benefits by providing an alternative route. The total of area 4 and area 2 shows the total delay cost in the system, in which area 4 is the total delay occurs on the highway and area 2 is the extra delay by shifting traffic to city streets.
Navigation function i
The core principle of User Equilibrium is that all used routes between a given OD pair have the same travel time. An alternative route option is enabled to use when the actual travel time in the system has reached the free-flow travel time on that route.
For a highway user optimum model considering one alternative route, a typical process of traffic assignment is shown in figure 15. When the traffic demand stays below the highway capacity, the delay time on highway stays zero. When the traffic demand exceeds the capacity, the queue of vehicle will appear on the highway and the delay time will increase. Some of users will turn to the city streets when the delay time reaches the difference between the free-flow travel time on highway and the free-flow travel time on city streets. It indicates that the users staying on the highway will spend as much travel time as the ones who turn to the city streets. At this stage, the travel time on both the highway and the alternative route stays the same. This situation may be ended when the demand falls below the road capacity, that is the travel time on highway begins to decrease and all the users will stay on the highway. The total of part area 1 and 3 represents the benefits by providing an alternative route. The total of area 4 and area 2 shows the total delay cost in the system, in which area 4 is the total delay occurs on the highway and area 2 is the extra delay by shifting traffic to city streets.
Navigation function i
Google Maps
can be referred as a typical industrial application of dynamic traffic assignment based on User Equilibrium since it provides every user the routing option in lowest cost (travel time).
 Reactive time delay is when the user has no knowledge of the traffic conditions ahead. The user waits to experience the point where the delay is observed and the decision to reroute is in reaction to that experience at the moment. Predictive delay gives significantly better results than the reactive delay method. In the vehicle counts-time diagram, predictive delay at time t is horizontal line segment on the ''left'' side of time t, between the arrival and departure curve, shown in Figure 16. the corresponding y coordinate is the number nth vehicle that enters the system at time t.
Reactive time delay is when the user has no knowledge of the traffic conditions ahead. The user waits to experience the point where the delay is observed and the decision to reroute is in reaction to that experience at the moment. Predictive delay gives significantly better results than the reactive delay method. In the vehicle counts-time diagram, predictive delay at time t is horizontal line segment on the ''left'' side of time t, between the arrival and departure curve, shown in Figure 16. the corresponding y coordinate is the number nth vehicle that enters the system at time t.
 In this figure ("Flow-Speed Diagram for a Typical Roadway"), the point of the curve represents optimal traffic movement in both flow and speed. However, beyond this point the speed of travel quickly reaches a threshold and starts to decline rapidly. In order to reduce the potential risk of this rapid speed decline, variable speed limits reduce the speed at a more gradual rate (5-mph increments), allowing drivers to have more time to prepare and acclimate to the slowdown due to congestion/weather. The development of a uniform travel speed reduces the probability of erratic driver behavior and therefore crashes.
Through historical data obtained at VSL sites, it has been determined that implementation of this practice reduces accident numbers by 20-30%.
In addition to safety and efficiency concerns, VSL's can also garner environmental benefits such as decreased emissions, noise, and fuel consumption. This is due to the fact that vehicles are more fuel-efficient when at a constant rate of travel, rather than in a state of constant acceleration and deacceleration like that usually found in congested conditions.
In this figure ("Flow-Speed Diagram for a Typical Roadway"), the point of the curve represents optimal traffic movement in both flow and speed. However, beyond this point the speed of travel quickly reaches a threshold and starts to decline rapidly. In order to reduce the potential risk of this rapid speed decline, variable speed limits reduce the speed at a more gradual rate (5-mph increments), allowing drivers to have more time to prepare and acclimate to the slowdown due to congestion/weather. The development of a uniform travel speed reduces the probability of erratic driver behavior and therefore crashes.
Through historical data obtained at VSL sites, it has been determined that implementation of this practice reduces accident numbers by 20-30%.
In addition to safety and efficiency concerns, VSL's can also garner environmental benefits such as decreased emissions, noise, and fuel consumption. This is due to the fact that vehicles are more fuel-efficient when at a constant rate of travel, rather than in a state of constant acceleration and deacceleration like that usually found in congested conditions.
 The general cause of stationary bottlenecks are lane drops which occurs when the a multilane roadway loses one or more its lane. This causes the vehicular traffic in the ending lanes to merge onto the other lanes.
The general cause of stationary bottlenecks are lane drops which occurs when the a multilane roadway loses one or more its lane. This causes the vehicular traffic in the ending lanes to merge onto the other lanes.
/ref> Daganzo introduced a cell-transmission model (CTM) that is consistent with the LWR model. # A traffic flow instability that causes a growing wave of a local reduction of the vehicle speed. This classical traffic flow instability was introduced in 1959–61 in the General Motors (GM) car-following model by Herman, Gazis, Montroll, Potts, and Rothery.R. Herman, E.W. Montroll, R.B. Potts, and R.W. Rothery, "Traffic dynamics: analysis of stability in car following". Oper. Res., 7, 86-106 (1959)
/ref>D.C. Gazis, R. Herman, and R.W. Rothery. "Nonlinear follow-the-leader models of traffic flow". Oper. Res., 9, 545-567 (1961)
/ref> The classical traffic flow instability of the GM model has been incorporated in a huge number of traffic flow models like Gipps's model, Payne's model, Newell's optimal velocity (OV) model, Wiedemann's model, Whitham's model, the Nagel-Schreckenberg (NaSch) cellular automaton (CA) model, Bando et al. OV model, Treiber's IDM, Krauß model, the Aw-Rascle model and many other well-known microscopic and macroscopic traffic-flow models, which are the basis of
/ref>). Currently, it is assumed that highway capacity of free flow at a highway bottleneck is a stochastic value. However, in accordance with the classical understanding of highway capacity, it is assumed that at a given time instant there can be only one particular value of this stochastic highway capacity (see references in the book). # Wardrop's user equilibrium (UE) and system optimum (SO) principles for traffic and transportation network optimization and control.J.G. Wardrop, "Some theoretical aspects of road traffic research", in Proc. of Inst. of Civil Eng. II., 1, 325—362 (1952)
/ref>
/ref>Boris S. Kerner, "Congested Traffic Flow: Observations and Theory" Transportation Research Record, 1678, 160-167 (1999). doi: 10.3141/1678-20
/ref>Boris S. Kerner, "The Physics of Traffic" Physics World 12, No. 8, 25-30 (August 1999). doi: 10.1088/2058-7058/12/8/30
/ref> Three-phase theory states that at any time instance there is a range of highway capacities of free flow at a bottleneck. The capacity range is between some maximum and minimum capacities. The range of highway capacities of free flow at the bottleneck in three-phase traffic theory contradicts fundamentally classical traffic theories as well as methods for traffic management and traffic control which at any time instant assume the existence of a particular deterministic or stochastic highway capacity of free flow at the bottleneck.
 In the condition of traffic flows leaving two branch roadways and merging into a single flow through a single roadway, determining the flows that pass through the merging process and the state of each branch of roadways becomes an important task for traffic engineers. The Newell-Daganzo merge model is a good approach to solve these problems. This simple model is the output of the result of both Gordon Newell's description of the merging process and the Daganzo's cell transmission model. In order to apply the model to determine the flows which exiting two branch of roadways and the stat of each branch of roadways, one needs to know the capacities of the two input branches of roadways, the exiting capacity, the demands for each branch of roadways, and the number of lanes of the single roadway. The merge ratio will be calculated in order to determine the proportion of the two input flows when both of branches of roadway are operating in congested conditions.
As can be seen in a simplified model of the process of merging, the exiting capacity of the system is defined to be μ, the capacities of the two input branches of roadways are defined as μ1 and μ2, and the demands for each branch of roadways are defined as q1D and q2D. The q1 and q2 are the output of the model which are the flows that pass through the merging process. The process of the model is based on the assumption that the sum of capacities of the two input branches of roadways is less than the exiting capacity of the system, μ1+μ2 ≤ μ.
In the condition of traffic flows leaving two branch roadways and merging into a single flow through a single roadway, determining the flows that pass through the merging process and the state of each branch of roadways becomes an important task for traffic engineers. The Newell-Daganzo merge model is a good approach to solve these problems. This simple model is the output of the result of both Gordon Newell's description of the merging process and the Daganzo's cell transmission model. In order to apply the model to determine the flows which exiting two branch of roadways and the stat of each branch of roadways, one needs to know the capacities of the two input branches of roadways, the exiting capacity, the demands for each branch of roadways, and the number of lanes of the single roadway. The merge ratio will be calculated in order to determine the proportion of the two input flows when both of branches of roadway are operating in congested conditions.
As can be seen in a simplified model of the process of merging, the exiting capacity of the system is defined to be μ, the capacities of the two input branches of roadways are defined as μ1 and μ2, and the demands for each branch of roadways are defined as q1D and q2D. The q1 and q2 are the output of the model which are the flows that pass through the merging process. The process of the model is based on the assumption that the sum of capacities of the two input branches of roadways is less than the exiting capacity of the system, μ1+μ2 ≤ μ.
Modelling Traffic on Motorways: State-of-the-Art, Numerical Data Analysis, and Dynamic Traffic Assignment
', Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, 2006 *M. Garavello and B. Piccoli, Traffic Flow on Networks, American Institute of Mathematical Sciences (AIMS), Springfield, MO, 2006. pp. xvi+243 *Carlos F.Daganzo, "Fundamentals of Transportation and Traffic Operations.", Pergamon-Elsevier, Oxford, U.K. (1997)
B.S. Kerner, ''Introduction to Modern Traffic Flow Theory and Control: The Long Road to Three-Phase Traffic Theory'', Springer, Berlin, New York 2009
*Cassidy, M.J. and R.L. Bertini. "Observations at a Freeway Bottleneck." ''Transportation and Traffic Theory'' (1999). *Daganzo, Carlos F. "A Simple Traffic Analysis Procedure." ''Networks and Spatial Economics'' 1.i (2001): 77–101. *Lindgren, Roger V.F. "Analysis of Flow Features in Queued Traffic on a German Freeway." ''Portland State University'' (2005). *Ni, B. and J.D. Leonard. "Direct Methods of Determining Traffic Stream Characteristics by Definition." ''Transportation Research Record'' (2006). Useful books from the physical point of view:
M. Treiber and A. Kesting, "Traffic Flow Dynamics", Springer, 2013B.S. Kerner, ''The Physics of Traffic'', Springer, Berlin, New York 2004Traffic flow on arxiv.org
*May, Adolf. ''Traffic Flow Fundamentals''. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1990. *Taylor, Nicholas.
The Contram dynamic traffic assignment model
' TRL 2003
The Transportation Research Board's (TRB) fifth edition of the Highway Capacity Manual (HCM 2010)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Traffic Flow Road transport Mathematical physics Conservation equations Road traffic management
transportation engineering
Transportation engineering or transport engineering is the application of technology and scientific principles to the planning, functional design, operation and management of facilities for any mode of transportation to provide for the safe, ...
, traffic flow is the study of interactions between travellers (including pedestrians, cyclists, drivers, and their vehicles) and infrastructure (including highways, signage, and traffic control devices), with the aim of understanding and developing an optimal transport network with efficient movement of traffic
Traffic is the movement of vehicles and pedestrians along land routes.
Traffic laws govern and regulate traffic, while rules of the road include traffic laws and informal rules that may have developed over time to facilitate the orderly an ...
and minimal traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition in transport that is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. Traffic congestion on urban road networks has increased substantially since the 1950s, resulting in m ...
problems.
The foundation for modern traffic flow analysis dates back to the 1920s with Frank Knight
Frank Hyneman Knight (November 7, 1885 – April 15, 1972) was an American economist who spent most of his career at the University of Chicago, where he became one of the founders of the Chicago School.
Nobel laureates Milton Friedman, George S ...
's analysis of traffic equilibrium, further developed by Wardrop in 1952. Despite advances in computing, a universally satisfactory theory applicable to real-world conditions remains elusive. Current models blend empirical and theoretical techniques to forecast traffic and identify congestion areas, considering variables like vehicle use and land changes.
Traffic flow is influenced by the complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
interactions of vehicles, displaying behaviors such as cluster formation and shock wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
propagation. Key traffic stream variables include speed, flow, and density, which are interconnected. Free-flowing traffic is characterized by fewer than 12 vehicles per mile per lane, whereas higher densities can lead to unstable conditions and persistent stop-and-go traffic. Models and diagrams, such as time-space diagrams, help visualize and analyze these dynamics. Traffic flow analysis can be approached at different scales: microscopic (individual vehicle behavior), macroscopic (fluid dynamics-like models), and mesoscopic
Mesoscopic physics is a subdiscipline of condensed matter physics that deals with materials of an intermediate size. These materials range in size between the nanoscale for a quantity of atoms (such as a molecule) and of materials measuring mic ...
(probability functions for vehicle distributions). Empirical approaches, such as those outlined in the Highway Capacity Manual, are commonly used by engineers to model and forecast traffic flow, incorporating factors like fuel consumption and emissions.
The kinematic wave model, introduced by Lighthill and Whitham in 1955, is a cornerstone of traffic flow theory, describing the propagation of traffic waves and impact of bottlenecks. Bottlenecks, whether stationary or moving, significantly disrupt flow and reduce roadway capacity. The Federal Highway Authority attributes 40% of congestion to bottlenecks. Classical traffic flow theories include the Lighthill-Whitham-Richards model and various car-following models that describe how vehicles interact in traffic streams. An alternative theory, Kerner's three-phase traffic theory
Three-phase traffic theory is a theory of traffic flow developed by Boris Kerner between 1996 and 2002. It focuses mainly on the explanation of the physics of traffic breakdown and resulting congested traffic on highways. Kerner describes three pha ...
, suggests a range of capacities at bottlenecks rather than a single value. The Newell-Daganzo merge model and car-following models further refine our understanding of traffic dynamics and are instrumental in modern traffic engineering and simulation.
History
Attempts to produce a mathematical theory of traffic flow date back to the 1920s, when American EconomistFrank Knight
Frank Hyneman Knight (November 7, 1885 – April 15, 1972) was an American economist who spent most of his career at the University of Chicago, where he became one of the founders of the Chicago School.
Nobel laureates Milton Friedman, George S ...
first produced an analysis of traffic equilibrium, which was refined into Wardrop's first and second principles of equilibrium in 1952.
Nonetheless, even with the advent of significant computer processing power, to date there has been no satisfactory general theory that can be consistently applied to real flow conditions. Current traffic models use a mixture of empirical
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law.
There is no general agreement on how t ...
and theoretical techniques. These models are then developed into traffic forecasts, and take account of proposed local or major changes, such as increased vehicle use, changes in land use
Land use is an umbrella term to describe what happens on a parcel of land. It concerns the benefits derived from using the land, and also the land management actions that humans carry out there. The following categories are used for land use: fo ...
or changes in mode of transport
A mode of transport is a method or way of travelling, or of transporting people or cargo. The different modes of transport include air, water, and land transport, which includes rails or railways, road and off-road transport. Other modes of t ...
(with people moving from bus to train or car, for example), and to identify areas of congestion where the network needs to be adjusted.
Overview

 Traffic behaves in a complex and nonlinear way, depending on the interactions of a large number of
Traffic behaves in a complex and nonlinear way, depending on the interactions of a large number of vehicle
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered land vehicle, human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velo ...
s. Due to the individual reactions of human drivers, vehicles do not interact simply following the laws of mechanics, but rather display cluster formation and shock wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
propagation, both forward and backward, depending on vehicle density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
. Some mathematical models of traffic flow use a vertical queue assumption, in which the vehicles along a congested link do not spill back along the length of the link.
In a free-flowing network, ''traffic flow theory'' refers to the traffic stream variables of speed, flow, and concentration. These relationships are mainly concerned with uninterrupted traffic flow, primarily found on freeways or expressways.
Flow conditions are considered "free" when less than 12 vehicles per mile per lane are on a road. "Stable" is sometimes described as 12–30 vehicles per mile per lane. As the density reaches the maximum mass flow rate
In physics and engineering, mass flow rate is the Temporal rate, rate at which mass of a substance changes over time. Its unit of measurement, unit is kilogram per second (kg/s) in SI units, and Slug (unit), slug per second or pound (mass), pou ...
(or flux
Flux describes any effect that appears to pass or travel (whether it actually moves or not) through a surface or substance. Flux is a concept in applied mathematics and vector calculus which has many applications in physics. For transport phe ...
) and exceeds the optimum density (above 30 vehicles per mile per lane), traffic flow becomes unstable, and even a minor incident can result in persistent stop-and-go driving conditions. A "breakdown" condition occurs when traffic becomes unstable and exceeds 67 vehicles per mile per lane. "Jam density" refers to extreme traffic density when traffic flow stops completely, usually in the range of 185–250 vehicles per mile per lane.
However, calculations about congested networks are more complex and rely more on empirical studies and extrapolations from actual road counts. Because these are often urban or suburban in nature, other factors (such as road-user safety and environmental considerations) also influence the optimum conditions.
Traffic stream properties
Traffic flow is generally constrained along a one-dimensional pathway (e.g. a travel lane). A time-space diagram shows graphically the flow of vehicles along a pathway over time. Time is displayed along the horizontal axis, and distance is shown along the vertical axis. Traffic flow in a time-space diagram is represented by the individual trajectory lines of individual vehicles. Vehicles following each other along a given travel lane will have parallel trajectories, and trajectories will cross when one vehicle passes another. Time-space diagrams are useful tools for displaying and analyzing the traffic flow characteristics of a given roadway segment over time (e.g. analyzing traffic flow congestion). There are three main variables to visualize a traffic stream: speed (v), density (indicated k; the number of vehicles per unit of space), and flow (indicated q; the number of vehicles per unit of time).Speed
Speed is the distance covered per unit of time. One cannot track the speed of every vehicle; so, in practice, average speed is measured by sampling vehicles in a given area over a period of time. Two definitions of average speed are identified: "time mean speed" and "space mean speed". The "space mean speed" is thus theharmonic mean
In mathematics, the harmonic mean is a kind of average, one of the Pythagorean means.
It is the most appropriate average for ratios and rate (mathematics), rates such as speeds, and is normally only used for positive arguments.
The harmonic mean ...
of the speeds. The time mean speed is never less than space mean speed: , where is the variance of the space mean speed
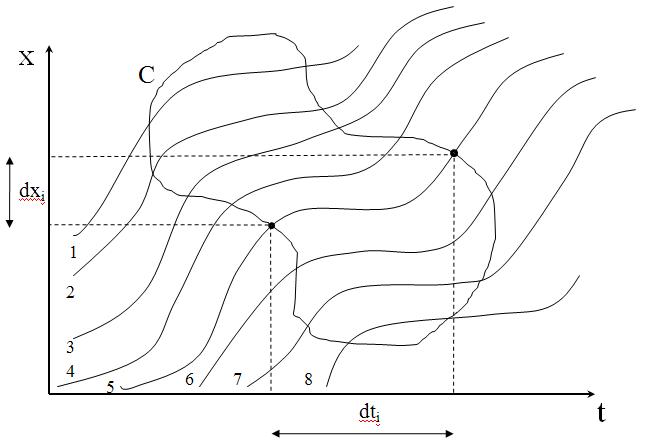
In a time-space diagram, the instantaneous velocity, v = dx/dt, of a vehicle is equal to the slope along the vehicle's trajectory. The average velocity of a vehicle is equal to the slope of the line connecting the trajectory endpoints where a vehicle enters and leaves the roadway segment. The vertical separation (distance) between parallel trajectories is the vehicle spacing (s) between a leading and following vehicle. Similarly, the horizontal separation (time) represents the vehicle headway (h). A time-space diagram is useful for relating headway and spacing to traffic flow and density, respectively.
Density
Density (k) is defined as the number of vehicles per unit length of the roadway. In traffic flow, the two most important densities are the critical density (''k''''c'') and jam density (''k''''j''). The maximum density achievable under free flow is ''k''''c'', while ''k''''j'' is the maximum density achieved under congestion. In general, jam density is five times the critical density. Inverse of density is spacing (s), which is the center-to-center distance between two vehicles.
 The density (''k'') within a length of roadway (''L'') at a given time (''t''1) is equal to the inverse of the average spacing of the ''n'' vehicles.
In a time-space diagram, the density may be evaluated in the region A.
where ''tt'' is the total travel time in ''A''.
The density (''k'') within a length of roadway (''L'') at a given time (''t''1) is equal to the inverse of the average spacing of the ''n'' vehicles.
In a time-space diagram, the density may be evaluated in the region A.
where ''tt'' is the total travel time in ''A''.
Flow
Flow (''q'') is the number of vehicles passing a reference point per unit of time, vehicles per hour. The inverse of flow is headway (''h''), which is the time that elapses between the ''i''th vehicle passing a reference point in space and the (''i'' + 1)th vehicle. In congestion, ''h'' remains constant. As a traffic jam forms, ''h'' approaches infinity. The flow (''q'') passing a fixed point (''x''1) during an interval (''T'') is equal to the inverse of the average headway of the ''m'' vehicles. In a time-space diagram, the flow may be evaluated in the region ''B''. where ''td'' is the total distance traveled in ''B''.Methods of analysis
Analysts approach the problem in three main ways, corresponding to the three main scales of observation in physics: *Microscopic scale
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens (optics), lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as ...
: At the most basic level, every vehicle is considered as an individual. An equation can be written for each, usually an ordinary differential equation
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation (ODE) is a differential equation (DE) dependent on only a single independent variable (mathematics), variable. As with any other DE, its unknown(s) consists of one (or more) Function (mathematic ...
(ODE). Cellular automation models can also be used, where the road is divided into cells, each of which contains a moving car, or is empty. The Nagel–Schreckenberg model is a simple example of such a model. As the cars interact it can model collective phenomena such as traffic jams.
* Macroscopic scale
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenom ...
: Similar to models of fluid dynamics
In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids – liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including (the study of air and other gases in motion ...
, it is considered useful to employ a system of partial differential equations
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which involves a multivariable function and one or more of its partial derivatives.
The function is often thought of as an "unknown" that solves the equation, similar to how ...
, which balance laws for some gross quantities of interest; e.g., the density of vehicles or their mean velocity.
* Mesoscopic (kinetic) scale: A third, intermediate possibility, is to define a function which expresses the probability of having a vehicle at time in position which runs with velocity . This function, following methods of statistical mechanics
In physics, statistical mechanics is a mathematical framework that applies statistical methods and probability theory to large assemblies of microscopic entities. Sometimes called statistical physics or statistical thermodynamics, its applicati ...
, can be computed using an integro-differential equation such as the Boltzmann equation
The Boltzmann equation or Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) describes the statistical behaviour of a thermodynamic system not in a state of equilibrium; it was devised by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872.Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd Edition), R. G ...
.
The engineering approach to analysis of highway traffic flow problems is primarily based on empirical analysis (i.e., observation and mathematical curve fitting). One major reference used by American planners is the ''Highway Capacity Manual'', published by the Transportation Research Board
The Transportation Research Board (TRB) is a division of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. TRB's mission is to mobilize expertise, experience, and knowledge to anticipate and solve complex transportation-related challe ...
, which is part of the United States National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nati ...
. This recommends modelling traffic flows using the whole travel time across a link using a delay/flow function, including the effects of queuing. This technique is used in many US traffic models and in the SATURN model in Europe.
In many parts of Europe, a hybrid empirical approach to traffic design is used, combining macro-, micro-, and mesoscopic features. Rather than simulating a steady state
In systems theory, a system or a process is in a steady state if the variables (called state variables) which define the behavior of the system or the process are unchanging in time. In continuous time, this means that for those properties ''p' ...
of flow for a journey, transient "demand peaks" of congestion are simulated. These are modeled by using small "time slices" across the network throughout the working day or weekend. Typically, the origins and destinations for trips are first estimated and a traffic model is generated before being calibrated by comparing the mathematical model with observed counts of actual traffic flows, classified by type of vehicle. "Matrix estimation" is then applied to the model to achieve a better match to observed link counts before any changes, and the revised model is used to generate a more realistic traffic forecast for any proposed scheme. The model would be run several times (including a current baseline, an "average day" forecast based on a range of economic parameters and supported by sensitivity analysis) in order to understand the implications of temporary blockages or incidents around the network. From the models, it is possible to total the time taken for all drivers of different types of vehicle on the network and thus deduce average fuel consumption and emissions.
Much of UK, Scandinavian, and Dutch authority practice is to use the modelling program CONTRAM for large schemes, which has been developed over several decades under the auspices of the UK's Transport Research Laboratory
TRL Limited, trading as TRL (formerly Transport Research Laboratory) is an independent private company offering a transport consultancy and research service to the public and private sector. Originally established in 1933 by the UK Government ...
, and more recently with the support of the Swedish Road Administration. By modelling forecasts of the road network for several decades into the future, the economic benefits of changes to the road network can be calculated, using estimates for value of time and other parameters. The output of these models can then be fed into a cost-benefit analysis program.
Cumulative vehicle count curves (''N''-curves)
A cumulative vehicle count curve, the ''N''-curve, shows the cumulative number of vehicles that pass a certain location ''x'' by time ''t'', measured from the passage of some reference vehicle. This curve can be plotted if the arrival times are known for individual vehicles approaching a location ''x'', and the departure times are also known as they leave location ''x''. Obtaining these arrival and departure times could involve data collection: for example, one could set two point sensors at locations ''X''1 and ''X''2, and count the number of vehicles that pass this segment while also recording the time each vehicle arrives at ''X''1 and departs from ''X''2. The resulting plot is a pair of cumulative curves where the vertical axis (''N'') represents the cumulative number of vehicles that pass the two points: ''X''1 and ''X''2, and the horizontal axis (''t'') represents the elapsed time from ''X''1 and ''X''2. If vehicles experience no delay as they travel from ''X''1 to ''X''2, then the arrivals of vehicles at location ''X''1 is represented by curve ''N''1 and the arrivals of the vehicles at location ''X''2 is represented by ''N''2 in figure 8. More commonly, curve ''N''1 is known as the ''arrival curve'' of vehicles at location ''X''1 and curve ''N''2 is known as the ''arrival curve'' of vehicles at location ''X''2. Using a one-lane signalized approach to an intersection as an example, where ''X''1 is the location of the stop bar at the approach and ''X''2 is an arbitrary line on the receiving lane just across of the intersection, when the traffic signal is green, vehicles can travel through both points with no delay and the time it takes to travel that distance is equal to the free-flow travel time. Graphically, this is shown as the two separate curves in figure 8.
However, when the traffic signal is red, vehicles arrive at the stop bar (''X''1) and are delayed by the red light before crossing ''X''2 some time after the signal turns green. As a result, a queue builds at the stop bar as more vehicles are arriving at the intersection while the traffic signal is still red. Therefore, for as long as vehicles arriving at the intersection are still hindered by the queue, the curve ''N''2 no longer represents the vehicles’ arrival at location ''X''2; it now represents the vehicles’ ''virtual arrival'' at location ''X''2, or in other words, it represents the vehicles' arrival at ''X''2 if they did not experience any delay. The vehicles' arrival at location ''X''2, taking into account the delay from the traffic signal, is now represented by the curve ''N′''2 in figure 9.
However, the concept of the ''virtual arrival curve'' is flawed. This curve does not correctly show the queue length resulting from the interruption in traffic (i.e. red signal). It assumes that all vehicles are still reaching the stop bar before being delayed by the red light. In other words, the ''virtual arrival curve'' portrays the stacking of vehicles vertically at the stop bar. When the traffic signal turns green, these vehicles are served in a first-in-first-out (FIFO) order. For a multi-lane approach, however, the service order is not necessarily FIFO. Nonetheless, the interpretation is still useful because of the concern with average total delay instead of total delays for individual vehicles.Pitstick, Mark E. "Measuring Delay and Simulating Performance at Isolated Signalized Intersections Using Cumulative Curves." ''Transportation Research Record 1287'' (1990)
If vehicles experience no delay as they travel from ''X''1 to ''X''2, then the arrivals of vehicles at location ''X''1 is represented by curve ''N''1 and the arrivals of the vehicles at location ''X''2 is represented by ''N''2 in figure 8. More commonly, curve ''N''1 is known as the ''arrival curve'' of vehicles at location ''X''1 and curve ''N''2 is known as the ''arrival curve'' of vehicles at location ''X''2. Using a one-lane signalized approach to an intersection as an example, where ''X''1 is the location of the stop bar at the approach and ''X''2 is an arbitrary line on the receiving lane just across of the intersection, when the traffic signal is green, vehicles can travel through both points with no delay and the time it takes to travel that distance is equal to the free-flow travel time. Graphically, this is shown as the two separate curves in figure 8.
However, when the traffic signal is red, vehicles arrive at the stop bar (''X''1) and are delayed by the red light before crossing ''X''2 some time after the signal turns green. As a result, a queue builds at the stop bar as more vehicles are arriving at the intersection while the traffic signal is still red. Therefore, for as long as vehicles arriving at the intersection are still hindered by the queue, the curve ''N''2 no longer represents the vehicles’ arrival at location ''X''2; it now represents the vehicles’ ''virtual arrival'' at location ''X''2, or in other words, it represents the vehicles' arrival at ''X''2 if they did not experience any delay. The vehicles' arrival at location ''X''2, taking into account the delay from the traffic signal, is now represented by the curve ''N′''2 in figure 9.
However, the concept of the ''virtual arrival curve'' is flawed. This curve does not correctly show the queue length resulting from the interruption in traffic (i.e. red signal). It assumes that all vehicles are still reaching the stop bar before being delayed by the red light. In other words, the ''virtual arrival curve'' portrays the stacking of vehicles vertically at the stop bar. When the traffic signal turns green, these vehicles are served in a first-in-first-out (FIFO) order. For a multi-lane approach, however, the service order is not necessarily FIFO. Nonetheless, the interpretation is still useful because of the concern with average total delay instead of total delays for individual vehicles.Pitstick, Mark E. "Measuring Delay and Simulating Performance at Isolated Signalized Intersections Using Cumulative Curves." ''Transportation Research Record 1287'' (1990)
Step function vs. smooth function
 The traffic light example depicts ''N''-curves as smooth functions. Theoretically, however, plotting ''N''-curves from collected data should result in a step-function (figure 10). Each step represents the arrival or departure of one vehicle at that point in time. When the ''N''-curve is drawn on larger scale reflecting a period of time that covers several cycles, then the steps for individual vehicles can be ignored, and the curve will then look like a smooth function (figure 8).
The traffic light example depicts ''N''-curves as smooth functions. Theoretically, however, plotting ''N''-curves from collected data should result in a step-function (figure 10). Each step represents the arrival or departure of one vehicle at that point in time. When the ''N''-curve is drawn on larger scale reflecting a period of time that covers several cycles, then the steps for individual vehicles can be ignored, and the curve will then look like a smooth function (figure 8).
Traffic assignment
 The aim of traffic flow analysis is to create and implement a model which would enable vehicles to reach their destination in the shortest possible time using the maximum roadway capacity. This is a four-step process:
* Generation – the program estimates how many trips would be generated. For this, the program needs the statistical data of residence areas by population, location of workplaces etc.;
* Distribution – after generation it makes the different Origin-Destination (OD) pairs between the location found in step 1;
* Modal Split/Mode Choice – the system has to decide how much percentage of the population would be split between the difference modes of available transport, e.g. cars, buses, rails, etc.;
* Route Assignment – finally, routes are assigned to the vehicles based on minimum criterion rules.
This cycle is repeated until the solution converges.
There are two main approaches to tackle this problem with the end objectives:
* System optimum
* User equilibrium
The aim of traffic flow analysis is to create and implement a model which would enable vehicles to reach their destination in the shortest possible time using the maximum roadway capacity. This is a four-step process:
* Generation – the program estimates how many trips would be generated. For this, the program needs the statistical data of residence areas by population, location of workplaces etc.;
* Distribution – after generation it makes the different Origin-Destination (OD) pairs between the location found in step 1;
* Modal Split/Mode Choice – the system has to decide how much percentage of the population would be split between the difference modes of available transport, e.g. cars, buses, rails, etc.;
* Route Assignment – finally, routes are assigned to the vehicles based on minimum criterion rules.
This cycle is repeated until the solution converges.
There are two main approaches to tackle this problem with the end objectives:
* System optimum
* User equilibrium
System optimum
In short, a network is in system optimum (SO) when the total system cost is the minimum among all possible assignments. System Optimum is based on the assumption that routes of all vehicles would be controlled by the system, and that rerouting would be based on maximum utilization of resources and minimum total system cost. (Cost can be interpreted as travel time.) Hence, in a System Optimum routing algorithm, all routes between a given OD pair have the same marginal cost. In traditional transportation economics, System Optimum is determined by equilibrium of demand function and marginal cost function. In this approach, marginal cost is roughly depicted as increasing function in traffic congestion. In traffic flow approach, the marginal cost of the trip can be expressed as sum of the cost (delay time, ''w'') experienced by the driver and the externality (''e'') that a driver imposes on the rest of the users. Suppose there is a freeway (0) and an alternative route (1), which users can be diverted onto off-ramp. Operator knows total arrival rate (''A''(''t'')), the capacity of the freeway (''μ''0), and the capacity of the alternative route (''μ''1). From the time 't0', when freeway is congested, some of the users start moving to alternative route. However, when ''t''1, alternative route is also full of capacity. Now operator decides the number of vehicles(N), which use alternative route. The optimal number of vehicles (''N'') can be obtained by calculus of variation, to make marginal cost of each route equal. Thus, optimal condition is ''T''0 = T1 + ''∆''1. In this graph, we can see that the queue on the alternative route should clear ''∆''1 time units before it clears from the freeway. This solution does not define how we should allocates vehicles arriving between ''t''1 and ''T''1, we just can conclude that the optimal solution is not unique. If operator wants freeway not to be congested, operator can impose the congestion toll, ''e''0 ― ''e''1, which is the difference between the externality of freeway and alternative route. In this situation, freeway will maintain free flow speed, however alternative route will be extremely congested.User equilibrium
In brief, A network is in user equilibrium (UE) when every driver chooses the routes in its lowest cost between origin and destination regardless whether total system cost is minimized. The user optimum equilibrium assumes that all users choose their own route towards their destination based on the travel time that will be consumed in different route options. The users will choose the route which requires the least travel time. The user optimum model is often used in simulating the impact on traffic assignment by highway bottlenecks. When the congestion occurs on highway, it will extend the delay time in travelling through the highway and create a longer travel time. Under the user optimum assumption, the users would choose to wait until the travel time using a certain freeway is equal to the travel time using city streets, and hence equilibrium is reached. This equilibrium is called User Equilibrium, Wardrop Equilibrium or Nash Equilibrium. The core principle of User Equilibrium is that all used routes between a given OD pair have the same travel time. An alternative route option is enabled to use when the actual travel time in the system has reached the free-flow travel time on that route.
For a highway user optimum model considering one alternative route, a typical process of traffic assignment is shown in figure 15. When the traffic demand stays below the highway capacity, the delay time on highway stays zero. When the traffic demand exceeds the capacity, the queue of vehicle will appear on the highway and the delay time will increase. Some of users will turn to the city streets when the delay time reaches the difference between the free-flow travel time on highway and the free-flow travel time on city streets. It indicates that the users staying on the highway will spend as much travel time as the ones who turn to the city streets. At this stage, the travel time on both the highway and the alternative route stays the same. This situation may be ended when the demand falls below the road capacity, that is the travel time on highway begins to decrease and all the users will stay on the highway. The total of part area 1 and 3 represents the benefits by providing an alternative route. The total of area 4 and area 2 shows the total delay cost in the system, in which area 4 is the total delay occurs on the highway and area 2 is the extra delay by shifting traffic to city streets.
Navigation function i
The core principle of User Equilibrium is that all used routes between a given OD pair have the same travel time. An alternative route option is enabled to use when the actual travel time in the system has reached the free-flow travel time on that route.
For a highway user optimum model considering one alternative route, a typical process of traffic assignment is shown in figure 15. When the traffic demand stays below the highway capacity, the delay time on highway stays zero. When the traffic demand exceeds the capacity, the queue of vehicle will appear on the highway and the delay time will increase. Some of users will turn to the city streets when the delay time reaches the difference between the free-flow travel time on highway and the free-flow travel time on city streets. It indicates that the users staying on the highway will spend as much travel time as the ones who turn to the city streets. At this stage, the travel time on both the highway and the alternative route stays the same. This situation may be ended when the demand falls below the road capacity, that is the travel time on highway begins to decrease and all the users will stay on the highway. The total of part area 1 and 3 represents the benefits by providing an alternative route. The total of area 4 and area 2 shows the total delay cost in the system, in which area 4 is the total delay occurs on the highway and area 2 is the extra delay by shifting traffic to city streets.
Navigation function iGoogle Maps
can be referred as a typical industrial application of dynamic traffic assignment based on User Equilibrium since it provides every user the routing option in lowest cost (travel time).
Time delay
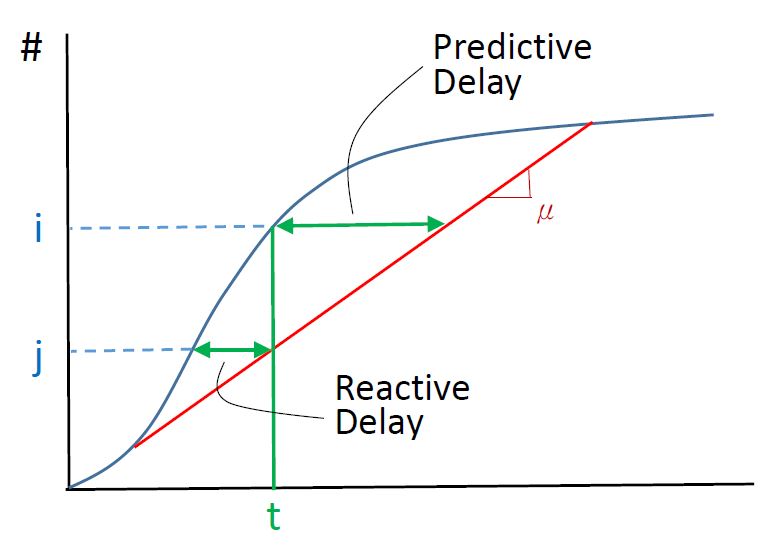
Both User Optimum and System Optimum can be subdivided into two categories on the basis of the approach of time delay taken for their solution:Predictive Time Delay
Predictive time delay assumes that the user of the system knows exactly how long the delay is going to be right ahead. Predictive delay knows when a certain congestion level will be reached and when the delay of that system would be more than taking the other system, so the decision for reroute can be made in time. In the vehicle counts-time diagram, predictive delay at time t is horizontal line segment on the ''right'' side of time t, between the arrival and departure curve, shown in Figure 16. the corresponding y coordinate is the number nth vehicle that leaves the system at time t.Reactive Time Delay
 Reactive time delay is when the user has no knowledge of the traffic conditions ahead. The user waits to experience the point where the delay is observed and the decision to reroute is in reaction to that experience at the moment. Predictive delay gives significantly better results than the reactive delay method. In the vehicle counts-time diagram, predictive delay at time t is horizontal line segment on the ''left'' side of time t, between the arrival and departure curve, shown in Figure 16. the corresponding y coordinate is the number nth vehicle that enters the system at time t.
Reactive time delay is when the user has no knowledge of the traffic conditions ahead. The user waits to experience the point where the delay is observed and the decision to reroute is in reaction to that experience at the moment. Predictive delay gives significantly better results than the reactive delay method. In the vehicle counts-time diagram, predictive delay at time t is horizontal line segment on the ''left'' side of time t, between the arrival and departure curve, shown in Figure 16. the corresponding y coordinate is the number nth vehicle that enters the system at time t.
Variable speed limit assignment
This is an upcoming approach of eliminating shockwave and increasing safety for the vehicles. The concept is based on the fact that the risk of accident on a roadway increases with speed differential between the upstream and downstream vehicles. The two types of crash risk which can be reduced from VSL implementation are the rear-end crash and the lane-change crash. Variable speed limits seek to homogenize speed, leading to a more constant flow. Different approaches have been implemented by researchers to build a suitable VSL algorithm. Variable speed limits are usually enacted when sensors along the roadway detect that congestion or weather events have exceeded thresholds. The roadway speed limit will then be reduced in 5-mph increments through the use of signs above the roadway (Dynamic Message Signs) controlled by the Department of Transportation. The goal of this process is the both increase safety through accident reduction and to avoid or postpone the onset of congestion on the roadway. The ideal resulting traffic flow is slower overall, but less stop-and-go, resulting in fewer instances of rear-end and lane-change crashes. The use of VSL's also regularly employs shoulder-lanes permitted for transportation only under congested states which this process aims to combat. The need for a variable speed limit is shown by Flow-Density diagram to the right. In this figure ("Flow-Speed Diagram for a Typical Roadway"), the point of the curve represents optimal traffic movement in both flow and speed. However, beyond this point the speed of travel quickly reaches a threshold and starts to decline rapidly. In order to reduce the potential risk of this rapid speed decline, variable speed limits reduce the speed at a more gradual rate (5-mph increments), allowing drivers to have more time to prepare and acclimate to the slowdown due to congestion/weather. The development of a uniform travel speed reduces the probability of erratic driver behavior and therefore crashes.
Through historical data obtained at VSL sites, it has been determined that implementation of this practice reduces accident numbers by 20-30%.
In addition to safety and efficiency concerns, VSL's can also garner environmental benefits such as decreased emissions, noise, and fuel consumption. This is due to the fact that vehicles are more fuel-efficient when at a constant rate of travel, rather than in a state of constant acceleration and deacceleration like that usually found in congested conditions.
In this figure ("Flow-Speed Diagram for a Typical Roadway"), the point of the curve represents optimal traffic movement in both flow and speed. However, beyond this point the speed of travel quickly reaches a threshold and starts to decline rapidly. In order to reduce the potential risk of this rapid speed decline, variable speed limits reduce the speed at a more gradual rate (5-mph increments), allowing drivers to have more time to prepare and acclimate to the slowdown due to congestion/weather. The development of a uniform travel speed reduces the probability of erratic driver behavior and therefore crashes.
Through historical data obtained at VSL sites, it has been determined that implementation of this practice reduces accident numbers by 20-30%.
In addition to safety and efficiency concerns, VSL's can also garner environmental benefits such as decreased emissions, noise, and fuel consumption. This is due to the fact that vehicles are more fuel-efficient when at a constant rate of travel, rather than in a state of constant acceleration and deacceleration like that usually found in congested conditions.
Road junctions
A major consideration in road capacity relates to the design of junctions. By allowing long "weaving sections" on gently curving roads at graded intersections, vehicles can often move across lanes without causing significant interference to the flow. However, this is expensive and takes up a large amount of land, so other patterns are often used, particularly in urban or very rural areas. Most large models use crude simulations for intersections, but computer simulations are available to model specific sets of traffic lights, roundabouts, and other scenarios where flow is interrupted or shared with other types of road users or pedestrians. A well-designed junction can enable significantly more traffic flow at a range of traffic densities during the day. By matching such a model to an "Intelligent Transport System", traffic can be sent in uninterrupted "packets" of vehicles at predetermined speeds through a series of phased traffic lights. The UK's TRL has developed junction modelling programs for small-scale local schemes that can take account of detailed geometry and sight lines; ARCADY for roundabouts, PICADY for priority intersections, and OSCADY and TRANSYT for signals. Many other junction analysis software packages exist such as Sidra and LinSig and Synchro.Kinematic wave model
The kinematic wave model was first applied to traffic flow by Lighthill and Whitham in 1955. Their two-part paper first developed the theory of kinematic waves using the motion of water as an example. In the second half, they extended the theory to traffic on “crowded arterial roads.” This paper was primarily concerned with developing the idea of traffic “humps” (increases in flow) and their effects on speed, especially through bottlenecks. The authors began by discussing previous approaches to traffic flow theory. They note that at the time there had been some experimental work, but that “theoretical approaches to the subjectere
Ere or ERE may refer to:
* ''Environmental and Resource Economics'', a peer-reviewed academic journal
* ERE Informatique, one of the first French video game companies
* Ere language, an Austronesian language
* Ebi Ere (born 1981), American-Nigeria ...
in their infancy.” One researcher in particular, John Glen Wardrop, was primarily concerned with statistical methods of examination, such as space mean speed, time mean speed, and “the effect of increase of flow on overtaking” and the resulting decrease in speed it would cause. Other previous research had focused on two separate models: one related traffic speed to traffic flow and another related speed to the headway between vehicles.
The goal of Lighthill and Whitham, on the other hand, was to propose a new method of study “suggested by theories of the flow about supersonic projectiles and of flood movement in rivers.” The resulting model would capture both of the aforementioned relationships, speed-flow and speed-headway, into a single curve, which would “ umup all the properties of a stretch of road which are relevant to its ability to handle the flow of congested traffic.” The model they presented related traffic flow to concentration (now typically known as density). They wrote, “The fundamental hypothesis of the theory is that at any point of the road the flow q (vehicles per hour) is a function of the concentration k (vehicles per mile).” According to this model, traffic flow resembled the flow of water in that “Slight changes in flow are propagated back through the stream of vehicles along ‘kinematic waves,’ whose velocity relative to the road is the slope of the graph of flow against concentration.” The authors included an example of such a graph; this flow-versus-concentration (density) plot is still used today (see figure 3 above).
The authors used this flow-concentration model to illustrate the concept of shock waves, which slow down vehicles which enter them, and the conditions that surround them. They also discussed bottlenecks and intersections, relating both to their new model. For each of these topics, flow-concentration and time-space diagrams were included. Finally, the authors noted that no agreed-upon definition for capacity existed, and argued that it should be defined as the “maximum flow of which the road is capable.” Lighthill and Whitham also recognized that their model had a significant limitation: it was only appropriate for use on long, crowded roadways, as the “continuous flow” approach only works with a large number of vehicles.
Components of the kinematic wave model of traffic flow theory
The kinematic wave model of traffic flow theory is the simplest dynamic traffic flow model that reproduces the propagation oftraffic wave
Traffic waves, which are also called stop waves, ghost jams, traffic snakes or traffic shocks, are traveling disturbances in the distribution of cars on a highway. Traffic waves travel backwards relative to the cars themselves. Relative to a fixed ...
s. It is made up of three components: the fundamental diagram, the conservation equation, and initial conditions. The law of conservation is the fundamental law governing the kinematic wave model:
The fundamental diagram of the kinematic wave model relates traffic flow with density, as seen in figure 3 above. It can be written as:
Finally, initial conditions must be defined to solve a problem using the model. A boundary is defined to be , representing density as a function of time and position. These boundaries typically take two different forms, resulting in initial value problems (IVPs) and boundary value problems (BVPs). Initial value problems give the traffic density at time , such that , where is the given density function. Boundary value problems give some function that represents the density at the position, such that .
The model has many uses in traffic flow. One of the primary uses is in modeling traffic bottlenecks, as described in the following section.
Traffic bottleneck
Traffic bottlenecks are disruptions of traffic on a roadway caused either due to road design, traffic lights, or accidents. There are two general types of bottlenecks, stationary and moving bottlenecks. Stationary bottlenecks are those that arise due to a disturbance that occurs due to a stationary situation like narrowing of a roadway, an accident. Moving bottlenecks on the other hand are those vehicles or vehicle behavior that causes the disruption in the vehicles which are upstream of the vehicle. Generally, moving bottlenecks are caused by heavy trucks as they are slow moving vehicles with less acceleration and also may make lane changes.7 Bottlenecks are important considerations because they impact the flow in traffic, the average speeds of the vehicles. The main consequence of a bottleneck is an immediate reduction in capacity of the roadway. The Federal Highway Authority has stated that 40% of all congestion is from bottlenecks.Stationary bottleneck
Moving bottleneck
As explained above, moving bottlenecks are caused due to slow moving vehicles that cause disruption in traffic. Moving bottlenecks can be active or inactive bottlenecks. If the reduced capacity(qu) caused due to a moving bottleneck is greater than the actual capacity(μ) downstream of the vehicle, then this bottleneck is said to be an active bottleneck.Classical traffic flow theories
The generally accepted classical fundamentals and methodologies of traffic and transportation theory are as follows: # The Lighthill-Whitham-Richards (LWR) model introduced in 1955–56.P.I. Richards, "Shockwaves on the highway". Oper. Res., 4, 42-51 (1956)/ref> Daganzo introduced a cell-transmission model (CTM) that is consistent with the LWR model. # A traffic flow instability that causes a growing wave of a local reduction of the vehicle speed. This classical traffic flow instability was introduced in 1959–61 in the General Motors (GM) car-following model by Herman, Gazis, Montroll, Potts, and Rothery.R. Herman, E.W. Montroll, R.B. Potts, and R.W. Rothery, "Traffic dynamics: analysis of stability in car following". Oper. Res., 7, 86-106 (1959)
/ref>D.C. Gazis, R. Herman, and R.W. Rothery. "Nonlinear follow-the-leader models of traffic flow". Oper. Res., 9, 545-567 (1961)
/ref> The classical traffic flow instability of the GM model has been incorporated in a huge number of traffic flow models like Gipps's model, Payne's model, Newell's optimal velocity (OV) model, Wiedemann's model, Whitham's model, the Nagel-Schreckenberg (NaSch) cellular automaton (CA) model, Bando et al. OV model, Treiber's IDM, Krauß model, the Aw-Rascle model and many other well-known microscopic and macroscopic traffic-flow models, which are the basis of
traffic simulation Traffic simulation or the simulation of transportation systems is the computer simulation, mathematical modeling of transportation systems (e.g., freeway junctions, arterial routes, roundabouts, downtown grid systems, etc.) through the application o ...
tools widely used by traffic engineers and researchers (see, e.g., references in review).
# The understanding of highway capacity as a ''particular'' value. This understanding of road capacity was probably introduced in 1920–35 (see Greenshields, B.D. "A study of traffic capacity". Highway Research Board Proceedings, 14, 448–477 (1935) )/ref>). Currently, it is assumed that highway capacity of free flow at a highway bottleneck is a stochastic value. However, in accordance with the classical understanding of highway capacity, it is assumed that at a given time instant there can be only one particular value of this stochastic highway capacity (see references in the book). # Wardrop's user equilibrium (UE) and system optimum (SO) principles for traffic and transportation network optimization and control.J.G. Wardrop, "Some theoretical aspects of road traffic research", in Proc. of Inst. of Civil Eng. II., 1, 325—362 (1952)
/ref>
Alternatives: Three phase traffic theory
Three-phase traffic theory
Three-phase traffic theory is a theory of traffic flow developed by Boris Kerner between 1996 and 2002. It focuses mainly on the explanation of the physics of traffic breakdown and resulting congested traffic on highways. Kerner describes three pha ...
is an alternative theory of traffic flow created by Boris Kerner at the end of 1990s.Boris S. Kerner, "Experimental Properties of Self-Organization in Traffic Flow" Physical Review Letters 81, 3797-3800 (1998). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.3797/ref>Boris S. Kerner, "Congested Traffic Flow: Observations and Theory" Transportation Research Record, 1678, 160-167 (1999). doi: 10.3141/1678-20
/ref>Boris S. Kerner, "The Physics of Traffic" Physics World 12, No. 8, 25-30 (August 1999). doi: 10.1088/2058-7058/12/8/30
/ref> Three-phase theory states that at any time instance there is a range of highway capacities of free flow at a bottleneck. The capacity range is between some maximum and minimum capacities. The range of highway capacities of free flow at the bottleneck in three-phase traffic theory contradicts fundamentally classical traffic theories as well as methods for traffic management and traffic control which at any time instant assume the existence of a particular deterministic or stochastic highway capacity of free flow at the bottleneck.
Newell-Daganzo Merge Models
 In the condition of traffic flows leaving two branch roadways and merging into a single flow through a single roadway, determining the flows that pass through the merging process and the state of each branch of roadways becomes an important task for traffic engineers. The Newell-Daganzo merge model is a good approach to solve these problems. This simple model is the output of the result of both Gordon Newell's description of the merging process and the Daganzo's cell transmission model. In order to apply the model to determine the flows which exiting two branch of roadways and the stat of each branch of roadways, one needs to know the capacities of the two input branches of roadways, the exiting capacity, the demands for each branch of roadways, and the number of lanes of the single roadway. The merge ratio will be calculated in order to determine the proportion of the two input flows when both of branches of roadway are operating in congested conditions.
As can be seen in a simplified model of the process of merging, the exiting capacity of the system is defined to be μ, the capacities of the two input branches of roadways are defined as μ1 and μ2, and the demands for each branch of roadways are defined as q1D and q2D. The q1 and q2 are the output of the model which are the flows that pass through the merging process. The process of the model is based on the assumption that the sum of capacities of the two input branches of roadways is less than the exiting capacity of the system, μ1+μ2 ≤ μ.
In the condition of traffic flows leaving two branch roadways and merging into a single flow through a single roadway, determining the flows that pass through the merging process and the state of each branch of roadways becomes an important task for traffic engineers. The Newell-Daganzo merge model is a good approach to solve these problems. This simple model is the output of the result of both Gordon Newell's description of the merging process and the Daganzo's cell transmission model. In order to apply the model to determine the flows which exiting two branch of roadways and the stat of each branch of roadways, one needs to know the capacities of the two input branches of roadways, the exiting capacity, the demands for each branch of roadways, and the number of lanes of the single roadway. The merge ratio will be calculated in order to determine the proportion of the two input flows when both of branches of roadway are operating in congested conditions.
As can be seen in a simplified model of the process of merging, the exiting capacity of the system is defined to be μ, the capacities of the two input branches of roadways are defined as μ1 and μ2, and the demands for each branch of roadways are defined as q1D and q2D. The q1 and q2 are the output of the model which are the flows that pass through the merging process. The process of the model is based on the assumption that the sum of capacities of the two input branches of roadways is less than the exiting capacity of the system, μ1+μ2 ≤ μ.Car-following models
Car-following models describe how one vehicle follows another vehicle in an uninterrupted traffic flow. They are a type of microscopic traffic flow model.Examples of car-following models
* Newell's car-following model *Louis A. Pipes started researching and gaining acknowledgment from the public in the early 1950s. Pipes car-following model is based on a safe driving rule in the California Motor Vehicle Code, and this model utilized an assumption of safe distance: a good rule for following another vehicle is to allocate an inter-vehicle distance of at least the length of a car for every ten miles per hour of vehicle speed. M *To capture the potential nonlinear effects in the dynamics of car following, G. F. Newell proposed a nonlinear car-following model based on empirical data. Unlike Pipes model which is solely relying on rules of safe driving, Newell nonlinear model aims at capturing the correct shape of fundamental diagrams (e.g., density-speed, flow-speed, density-flow, spacing-speed, pace-headway, etc.). *The Optimal Velocity Model (OVM) was introduced by Bando et al. in 1995 based on the assumption that each driver tries to reach to the optimal velocity according to the inter-vehicle difference and velocity difference between preceding vehicles. * Intelligent driver model is widely adopted in the research of Connected Vehicle (CV) and Connected and Autonomous Vehicle (CAV).See also
* Braess's paradox *Data flow
In computing, dataflow is a broad concept, which has various meanings depending on the application and context. In the context of software architecture, data flow relates to stream processing or reactive programming.
Software architecture
Dat ...
* Dijkstra's algorithm
* Epidemiology of motor vehicle collisions
* Floating car data
* Green transport hierarchy
* Infrared traffic logger
* Truck lane restriction
* Road traffic control
: ''For the road traffic science, see various articles under :Road traffic management, Road traffic management.''
Road traffic control involves directing vehicular and pedestrian traffic around a construction zone, accident or other road disruptio ...
* Road traffic safety#Statistics
* Rule 184
* Traffic counter
A traffic count is a count of vehicular or pedestrian traffic, which is conducted along a particular road, path, or Intersection (road), intersection. A traffic count is commonly undertaken either automatically (with the installation of a tempor ...
* Traffic engineering
* Turning movement counters
References
Further reading
A survey about the state of art in traffic flow modeling: *N. Bellomo, V. Coscia, M. Delitala, On the Mathematical Theory of Vehicular Traffic Flow I. Fluid Dynamic and Kinetic Modelling, ''Math. Mod. Meth. App. Sc.'', Vol. 12, No. 12 (2002) 1801–1843 *S. Maerivoet,Modelling Traffic on Motorways: State-of-the-Art, Numerical Data Analysis, and Dynamic Traffic Assignment
', Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, 2006 *M. Garavello and B. Piccoli, Traffic Flow on Networks, American Institute of Mathematical Sciences (AIMS), Springfield, MO, 2006. pp. xvi+243 *Carlos F.Daganzo, "Fundamentals of Transportation and Traffic Operations.", Pergamon-Elsevier, Oxford, U.K. (1997)
B.S. Kerner, ''Introduction to Modern Traffic Flow Theory and Control: The Long Road to Three-Phase Traffic Theory'', Springer, Berlin, New York 2009
*Cassidy, M.J. and R.L. Bertini. "Observations at a Freeway Bottleneck." ''Transportation and Traffic Theory'' (1999). *Daganzo, Carlos F. "A Simple Traffic Analysis Procedure." ''Networks and Spatial Economics'' 1.i (2001): 77–101. *Lindgren, Roger V.F. "Analysis of Flow Features in Queued Traffic on a German Freeway." ''Portland State University'' (2005). *Ni, B. and J.D. Leonard. "Direct Methods of Determining Traffic Stream Characteristics by Definition." ''Transportation Research Record'' (2006). Useful books from the physical point of view:
M. Treiber and A. Kesting, "Traffic Flow Dynamics", Springer, 2013
*May, Adolf. ''Traffic Flow Fundamentals''. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1990. *Taylor, Nicholas.
The Contram dynamic traffic assignment model
' TRL 2003
External links
The Transportation Research Board's (TRB) fifth edition of the Highway Capacity Manual (HCM 2010)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Traffic Flow Road transport Mathematical physics Conservation equations Road traffic management