|
Criechingen
The County of Kriechingen was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. It was originally a part of the Duchy of Lorraine, and was raised to an imperial estate in 1617. It belonged to the Upper Rhenish Circle. In 1697, Kriechingen was inherited by the Principality of East Frisia, and later by the County of Wied-Runkel. In 1793 Kriechingen was occupied by France; this was recognized by the Holy Roman Empire in the Treaty of Lunéville of 1801. The county was named after its capital, Kriechingen, today Créhange Créhange (; Lorraine Franconian and German ''Krischingen'') is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. The writer Joël Egloff (born 1970) was born in Créhange. It had a population of 3,868 in 2017. Until .... At the end of its existence, it had an area of approximately 100 km2 and a population of 4000. Between 1766, when Lorraine became a part of France, and 1793, Kriechingen formed two exclaves of the Holy Roman Empire surrounded b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kriechingen
The County of Kriechingen was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. It was originally a part of the Duchy of Lorraine, and was raised to an imperial estate in 1617. It belonged to the Upper Rhenish Circle. In 1697, Kriechingen was inherited by the Principality of East Frisia, and later by the County of Wied-Runkel. In 1793 Kriechingen was occupied by France; this was recognized by the Holy Roman Empire in the Treaty of Lunéville of 1801. The county was named after its capital, Kriechingen, today Créhange Créhange (; Lorraine Franconian and German ''Krischingen'') is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. The writer Joël Egloff (born 1970) was born in Créhange. It had a population of 3,868 in 2017. Until .... At the end of its existence, it had an area of approximately 100 km2 and a population of 4000. Between 1766, when Lorraine became a part of France, and 1793, Kriechingen formed two exclaves of the Holy Roman Empire surrounded b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
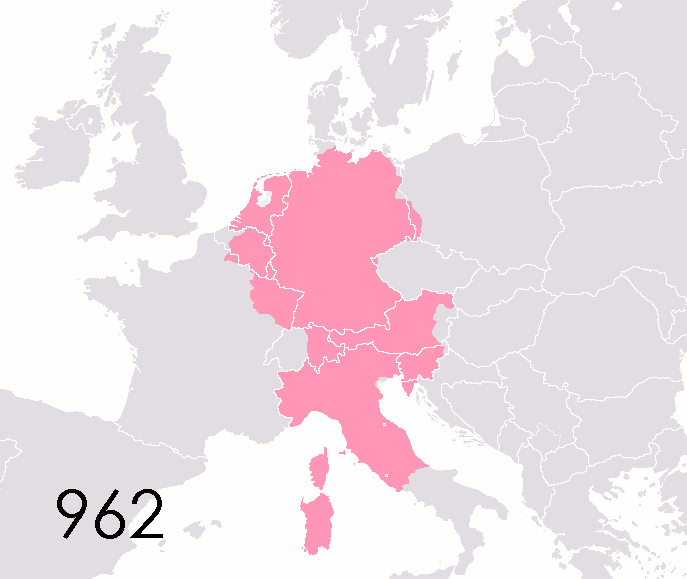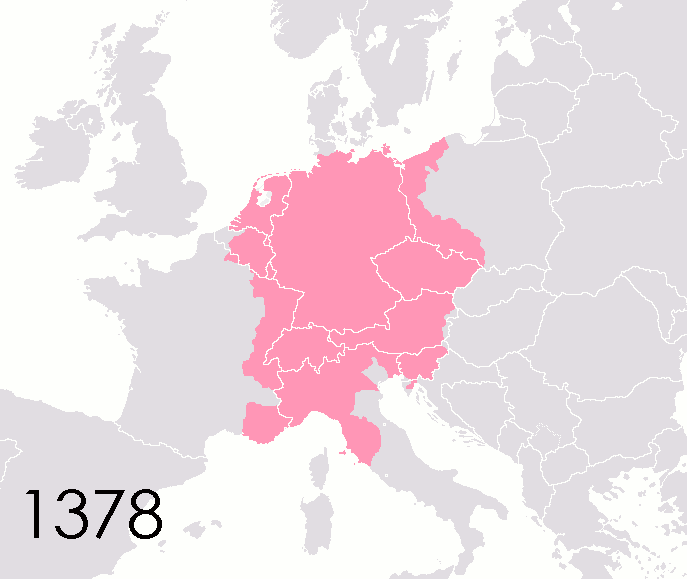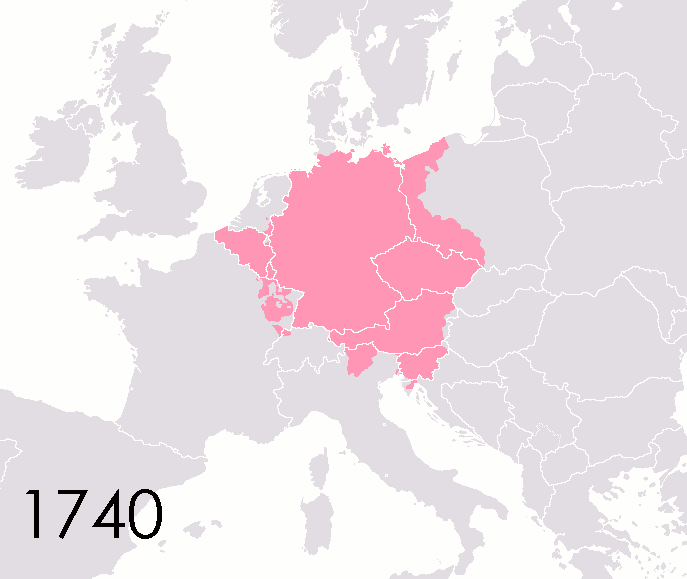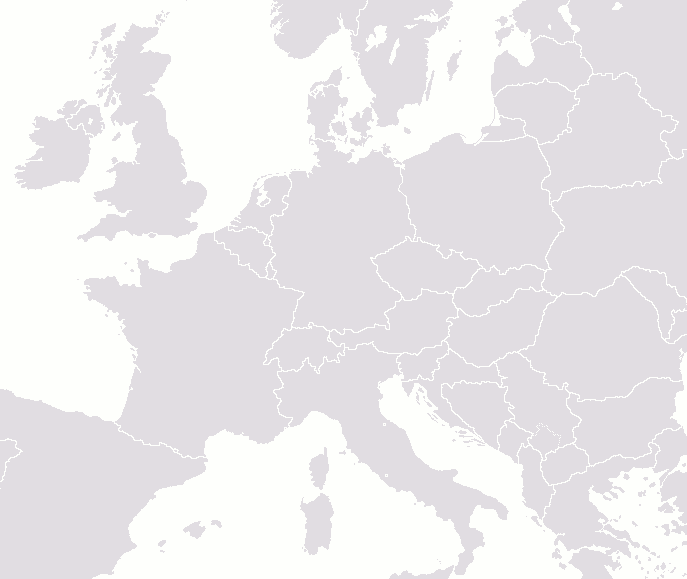
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd Schneidmüller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian Dynasty, Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the List of Frankish kings, Frankish king Charlemagne as Carolingi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Lorraine
The Duchy of Lorraine (french: Lorraine ; german: Lothringen ), originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy. It was founded in 959 following the division of Lotharingia into two separate duchies: Upper and Lower Lorraine, the westernmost parts of the Holy Roman Empire. The Lower duchy was quickly dismantled, while Upper Lorraine came to be known as simply the Duchy of Lorraine. The Duchy of Lorraine was coveted and briefly occupied by the dukes of Burgundy and the kings of France. In 1737, the duchy was given to Stanisław Leszczyński, the former king of Poland, who had lost his throne as a result of the War of the Polish Succession, with the understanding that it would fall to the French crown on his death. When Stanisław died on 23 February 1766, Lorraine was annexed by France and reorganized as a province. History Lotharingia Lorraine's predecessor, Lotharingia, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Rhenish Circle
The Upper Rhenish Circle (german: Oberrheinischer Reichskreis) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1500 on the territory of the former Duchy of Upper Lorraine and large parts of Rhenish Franconia including the Swabian Alsace region and the Burgundian duchy of Savoy. Many of the circle's states west of the Rhine river were annexed by France under King Louis XIV during the 17th century, sealed by the 1678/79 Treaties of Nijmegen. Composition The circle was made up of the following states: Sources *The list of states making up the Upper Rhenish Circle is based in part on that in the German German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) ** Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Ge ... Wikipedia article Oberrheinischer Reichskreis. External links Historicalmaps.com: Historical Maps of Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia and to the west of Landkreis Friesland. Administratively, East Frisia consists of the districts Aurich, Leer and Wittmund and the city of Emden. It has a population of approximately 469,000 people and an area of . There is a chain of islands off the coast, called the East Frisian Islands (''Ostfriesische Inseln''). From west to east, these islands are: Borkum, Juist, Norderney, Baltrum, Langeoog and Spiekeroog. History The geographical region of East Frisia was inhabited in Paleolithic times by reindeer hunters of the Hamburg culture. Later there were Mesolithic and Neolithic settlements of various cultures. The period after prehistory can only be reconstructed from archaeological evidence. Access to the early history of East Fris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wied-Runkel
Wied-Runkel was a small German sovereign state. Wied-Runkel was located around the town and castle of Runkel, located on the Lahn River. It extended from the town of Runkel to further north of Schupbach, but also held an exclave east of Villmar. Wied-Runkel was a partition of Wied, and was raised from a County to a Principality in 1791. Wied-Runkel was mediatised to Nassau Nassau may refer to: Places Bahamas *Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence Canada *Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792 *Nassau Street (Winnipeg), .... Counts of Wied-Runkel (1698–1791) * 1698–1699: Johann Friederich Wilhelm von Wied-Runkel († 1698) * 1692–1706: Maximilian Heinrich von Wied-Runkel († 1706), his grandson * 1706–1762: Johann Ludwig Adolph von Wied-Runkel († 1762), his son * 1762–1791: Christian Ludwig von Wied-Runkel († 1791), his son Princes of Wied-Runkel (1791–1806) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Lunéville
The Treaty of Lunéville (or Peace of Lunéville) was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville on 9 February 1801. The signatory parties were the French Republic and Emperor Francis II, who signed on his own behalf as ruler of the hereditary domains of the House of Austria and on behalf of the Holy Roman Empire. The signatories were Joseph Bonaparte and Count Ludwig von Cobenzl, the Austrian foreign minister. The treaty formally ended Austrian and Imperial participation in the War of the Second Coalition and the French Revolutionary Wars. The Austrian army had been defeated by Napoleon Bonaparte at the Battle of Marengo on 14 June 1800 and then by Jean Victor Moreau at the Battle of Hohenlinden on 3 December. Forced to sue for peace, the Austrians signed the treaty of Lunéville, which largely confirmed the treaty of Campo Formio (17 October 1797), which itself had confirmed the treaty of Leoben (April 1797). The United Kingdom was the sole nation still at war with France for anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Créhange
Créhange (; Lorraine Franconian and German ''Krischingen'') is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. The writer Joël Egloff (born 1970) was born in Créhange. It had a population of 3,868 in 2017. Until 1793, Créhange was the capital of the County of Kriechingen, a state of the Holy Roman Empire. See also * Communes of the Moselle department The following is a list of the 725 communes of the Moselle department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Moselle (department) {{ForbachBoulayMoselle-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of The Holy Roman Empire
This list of states in the Holy Roman Empire includes any territory ruled by an authority that had been granted imperial immediacy, as well as many other feudal entities such as lordships, sous-fiefs and allodial fiefs. The Holy Roman Empire was a complex political entity that existed in central Europe for most of the medieval and early modern periods and was generally ruled by a German-speaking Emperor. The states that composed the Empire, while enjoying a unique form of territorial authority (called '' Landeshoheit'') that granted them many attributes of sovereignty, were never fully sovereign states in the sense that term is understood today. In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 such territories, the majority being tiny estates owned by the families of Imperial Knights. This page does not directly contain the list but discusses the format of the various lists and offers some background to understand the complex organisation of the Holy R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |