|
Creinch
Creinch ( gd, Craobh-Innis, Tree Island) is an island on the Highland Boundary Fault in Loch Lomond. History Formerly Inchcroin (not to be confused with Inchcruin), Creinch lies a little north of Inchmurrin.Wilson, Rev. John ''The Gazetteer of Scotland'' (Edinburgh, 1882) Published by W. & A.K. Johnstone Inchcailloch, Torrinch, Creinch and Inchmurrin form part of the Highland boundary fault.Worsley, Harry ''Loch Lomond: The Loch, the Lairds and the Legends'' Lindsay Publications (Glasgow) 1988 In 1800 Garnett referred to the island as 'Grange'. Wildlife As the Gaelic name implies, it is completely covered in ivy draped trees, including some wych elms. In summer it can be difficult to penetrate the interior and in spring, it is carpeted in wild garlic, wild hyacinths and wood anemone The phrase wood anemone is used in common names for several closely related species of flowering plants in genus ''Anemonoides'', including: * ''Anemonoides nemorosa ''Anemonoides nemorosa'' (sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torrinch
Torrinch or Inchtore ( gd, Torr-Innis) is a wooded island in Loch Lomond in Scotland. The name Torremach is also recorded for it.Wilson, Rev. John ''The Gazetteer of Scotland'' (Edinburgh, 1882) Published by W. & A.K. Johnstone Geography It is one of the smaller islands in the loch. Torrinch, along with Inchmurrin, Creinch, and Inchcailloch, forms part of the Highland Boundary Fault.Worsley, Harry ''Loch Lomond: The Loch, the Lairds and the Legends'' Lindsay Publications (Glasgow) 1988 In the 1800s it was covered with oaks.Garnett, T. (1800). ''Observations on a Tour of the Highlands'' ... London. V.1. p. 40. It lies just to the south-west of the larger island of Inchcailloch, and north-east of Creinch Creinch ( gd, Craobh-Innis, Tree Island) is an island on the Highland Boundary Fault in Loch Lomond. History Formerly Inchcroin (not to be confused with Inchcruin), Creinch lies a little north of Inchmurrin.Wilson, Rev. John ''The Gazetteer of S .... Footnotes External l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Boundary Fault
The Highland Boundary Fault is a major fault zone that traverses Scotland from Arran and Helensburgh on the west coast to Stonehaven in the east. It separates two different geological terranes which give rise to two distinct physiographic terrains: the Highlands and the Lowlands, and in most places it is recognisable as a change in topography. Where rivers cross the fault, they often pass through gorges, and the associated waterfalls can be a barrier to salmon migration. The fault is believed to have formed in conjunction with the Strathmore syncline to the south-east during the Acadian orogeny in a transpressive regime that caused the uplift of the Grampian block and a small sinistral movement on the Highland Boundary Fault. Discovery One of the earliest and most prominent references to the Highland Boundary Fault was by George Barrow in 1912 ʻOn the Geology of Lower Dee-side and the Southern Highland Borderʼ, which highlights the nature of the rocks accompanying the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Lomond
Loch Lomond (; gd, Loch Laomainn - 'Lake of the Elms'Richens, R. J. (1984) ''Elm'', Cambridge University Press.) is a freshwater Scottish loch which crosses the Highland Boundary Fault, often considered the boundary between the lowlands of Central Scotland and the Highlands.Tom Weir. ''The Scottish Lochs''. pp. 33-43. Published by Constable and Company, 1980. Traditionally forming part of the boundary between the counties of Stirlingshire and Dunbartonshire, Loch Lomond is split between the council areas of Stirling, Argyll and Bute and West Dunbartonshire. Its southern shores are about northwest of the centre of Glasgow, Scotland's largest city. The Loch forms part of the Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park which was established in 2002. Loch Lomond is long and between wide, with a surface area of . It is the largest lake in Great Britain by surface area; in the United Kingdom, it is surpassed only by Lough Neagh and Lough Erne in Northern Ireland. In the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inchmurrin
Inchmurrin ( gd, Innis Mhearain) is an island in Loch Lomond in Scotland. It is the largest fresh water island in the British Isles. Geography and geology Inchmurrin is the largest and most southerly of the islands in Loch Lomond. It reaches a height of towards the north and is largely wooded. There is an excellent view of the north end of the loch. Along with Creinch, Torrinch, and Inchcailloch, Inchmurrin forms part of the Highland boundary fault. History Inchmurrin was the site of a 7th-century monastery, with a chapel dedicated to Saint Mirin, after whom it was named. The island was formerly a deer park of the Dukes of Montrose, who had a hunting lodge built in 1793 and maintained a gamekeeper and his family there. 200 deer are recorded in 1800. There are ruins of a castle, probably built for Duncan, 8th Earl of Lennox whose seat was Balloch Castle at the south end of Loch Lomond. The castle was probably a hunting lodge for the deer park established on the island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Boundary Fault
The Highland Boundary Fault is a major fault zone that traverses Scotland from Arran and Helensburgh on the west coast to Stonehaven in the east. It separates two different geological terranes which give rise to two distinct physiographic terrains: the Highlands and the Lowlands, and in most places it is recognisable as a change in topography. Where rivers cross the fault, they often pass through gorges, and the associated waterfalls can be a barrier to salmon migration. The fault is believed to have formed in conjunction with the Strathmore syncline to the south-east during the Acadian orogeny in a transpressive regime that caused the uplift of the Grampian block and a small sinistral movement on the Highland Boundary Fault. Discovery One of the earliest and most prominent references to the Highland Boundary Fault was by George Barrow in 1912 ʻOn the Geology of Lower Dee-side and the Southern Highland Borderʼ, which highlights the nature of the rocks accompanying the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inchcruin
Inchcruin is an island in Loch Lomond in Scotland. It is not to be confused with Creinch, which has occasionally been referred to as "Inchcroin". Geography Inchcruin is one of an island group just south of Luss. It is long, and in elevation at its highest point. Its name means "round island" in the Scottish Gaelic language, although it is not round, but a rather jagged shape. It has a couple of beaches, and is wooded, with some open fields. Only a very narrow channel, called the Geggles separates Inchcruin from Inchmoan. At only deep, it is sometimes possible to wade between the islands.Worsley, Harry ''Loch Lomond: The Loch, the Lairds and the Legends'' Lindsay Publications (Glasgow) 1988 History The travel writer, H.V. Morton visited Loch Lomond in the 1930s, and mentions Inchcruin briefly and wrongly as "Inchcruim". In the 18th century it was used as an asylum for the insane. It contains one house, around 200 years old, which was inhabited in the past by people who f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inchcailloch
Inchcailloch ( gd, Innis na Cailleach) is an islet on Loch Lomond in Scotland. It is at its highest point. It is also known to some as Inchebroida. The name Inchcailloch means "Isle of the old woman" or "Isle of the Cowled (Hooded) Woman" in the Scottish Gaelic language. Saint Kentigerna went to Scotland from Ireland to preach and spread Christianity and the island is thought to be named after her. Geography and geology Inchmurrin, Creinch, Torrinch, and Inchcailloch all form part of the Highland boundary fault. There is a burial ground in the north of the island, and a bay, Port Bawn ( gd, Port Bàn; en, White Port), in the south. Like many of the Loch Lomond islands, it is quite heavily wooded. Transport There is a passenger ferry across the short channel separating it from Balmaha on the mainland. As a result, it receives more visitors than most of the Loch Lomond islands, currently 20,000 visitors per year. There is a camp site in the south at Port Bawn and a nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wych Elm
''Ulmus glabra'' Hudson, the wych elm or Scots elm, has the widest range of the European elm species, from Ireland eastwards to the Urals, and from the Arctic Circle south to the mountains of the Peloponnese and Sicily, where the species reaches its southern limit in Europe; it is also found in Iran. A large deciduous tree, it is essentially a montane species, growing at elevations up to , preferring sites with moist soils and high humidity.Heybroek, H. M., Goudzwaard, L, Kaljee, H. (2009). ''Iep of olm, karakterboom van de Lage Landen'' (:Elm, a tree with character of the Low Countries). KNNV, Uitgeverij. The tree can form pure forests in Scandinavia and occurs as far north as latitude 67°N at Beiarn in Norway. It has been successfully introduced as far north as Tromsø, Norway and Alta, Norway (70°N). It has also been successfully introduced to Narsarsuaq, near the southern tip of Greenland ( 61°N). The tree was by far the most common elm in the north and west of the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
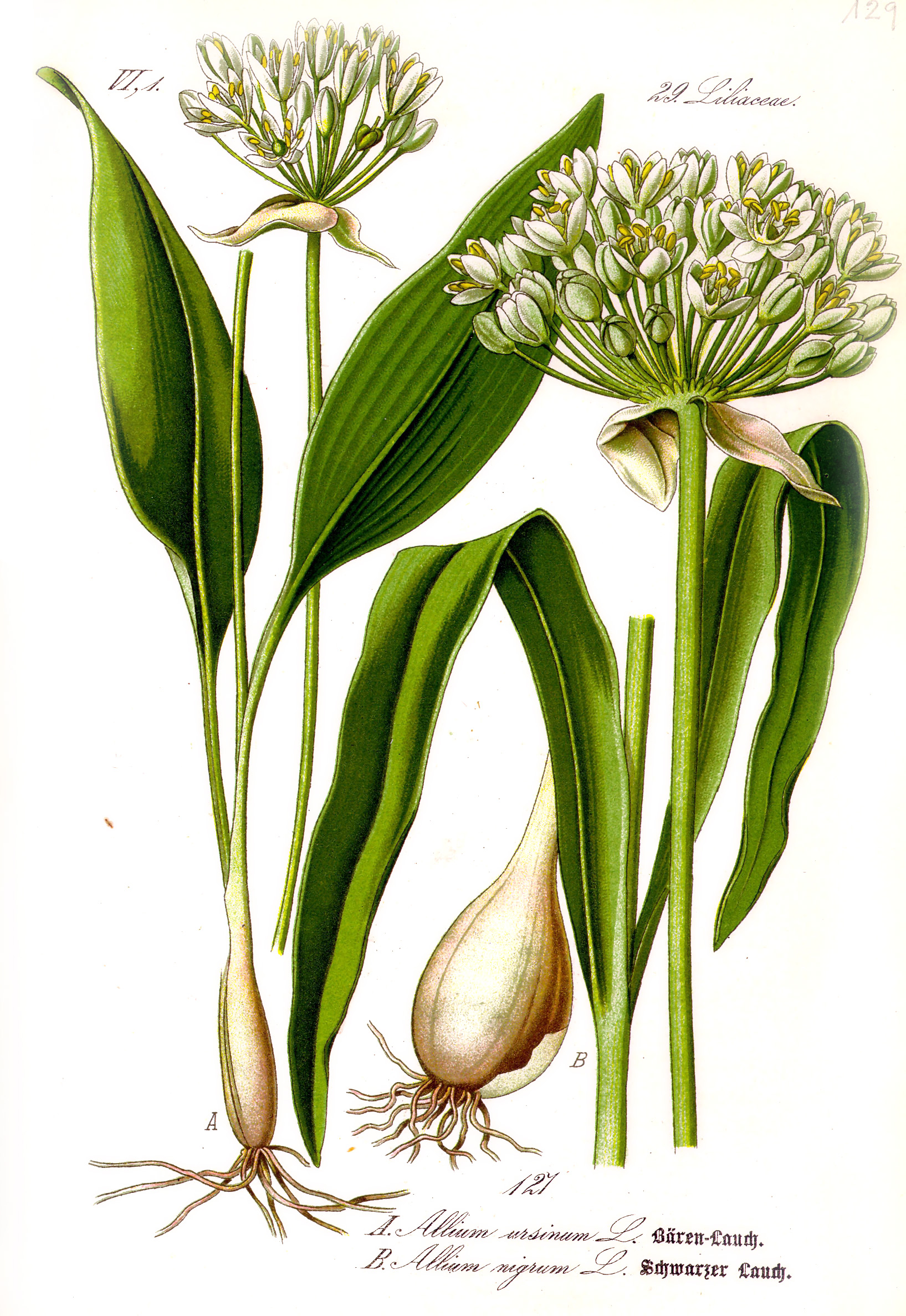
Allium Ursinum
''Allium ursinum'', known as wild garlic, ramsons, cowleekes, cows's leek, cowleek, buckrams, broad-leaved garlic, wood garlic, bear leek, Eurasian wild garlic or bear's garlic, is a bulbous perennial flowering plant in the amaryllis family Amaryllidaceae. It is native to Europe and Asia, where it grows in moist woodland. It is a wild relative of onion and garlic, all belonging to the same genus, ''Allium''. There are two recognized subspecies: ''A. ursinum'' subsp. ''ursinum'' and ''A. ursinum'' subsp. ''ucrainicum''. Etymology The Latin specific name ''ursinum'' translates to 'bear' and refers to the supposed fondness of the brown bear for the bulbs; folk tales describe the bears consuming them after awakening from hibernation. Another theory is that the "''ursinum''" may refer to Ursa Major, as ''A. ursinum'' was perhaps one of the most northerly distributed ''Allium'' species known to the ancient Greeks, though this hypothesis is disputed. Common names for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Hyacinth '', from western North America
{{Plant common name ...
Wild hyacinth may refer to: *''Hyacinthoides non-scripta'', a European species also called the common bluebell *''Camassia'', a genus of six North American species *''Dipterostemon capitatus'', a species from North America, the only species in the genus ''Dipterostemon'' *''Dichelostemma multiflorum'', a species from California and Oregon *''Lachenalia contaminata'', a species from South Africa *various species of ''Brodiaea ''Brodiaea'' , also known by the common name cluster-lilies, is a monocot genus of flowering plants. One school of thought places the genus in the family , while another school of thought places it in the subfamily Brodiaeoideae of the family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemone Nemorosa
''Anemonoides nemorosa'' (syn. ''Anemone nemorosa''), the wood anemone, is an early-spring flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, native to Europe. Other common names include windflower, European thimbleweed, and smell fox, an allusion to the musky smell of the leaves. It is a perennial herbaceous plant growing tall. Description ''Anemonoides nemorosa'' is a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial plant less than in height. The compound basal leaves are palmate or ternate (divided into three lobes). They grow from underground root-like stems called rhizomes and die back down by mid summer (summer dormant). The plants start blooming in spring, March to May in the British Isles soon after the foliage emerges from the ground. The flowers are solitary, held above the foliage on short stems, with a whorl of three palmate or palmately-lobed leaflike bracts beneath. The flowers are diameter, with six or seven (and on rare occasions eight to ten) tepals (petal-like segments) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_(d.j.b.).jpg)