|
Cray XT4
The Cray XT4 (codenamed ''Hood'' during development) is an updated version of the Cray XT3 supercomputer. It was released on November 18, 2006. It includes an updated version of the SeaStar interconnect router called SeaStar2, processor sockets for Socket AM2 Opteron processors, and 240-pin unbuffered DDR2 memory. The XT4 also includes support for FPGA coprocessors that plug into riser cards in the Service and IO blades. The interconnect, cabinet, system software and programming environment remain unchanged from the Cray XT3. It was superseded in 2007 by the Cray XT5 The Cray XT5 is an updated version of the Cray XT4 supercomputer, launched on November 6, 2007. It includes a faster version of the XT4's SeaStar2 interconnect router called SeaStar2+, and can be configured either with XT4 compute blades, which .... External links News release regarding ''Hood''on HPCwireCray XT4 at top500.org References Xt4 X86 supercomputers {{super-compu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Museum Of America (42)
The Computer Museum of America was established in Roswell, Georgia and opened in July 2019 to coincide with the fiftieth anniversary of the Moon landing. It is the largest technology museum on the East Coast with the opening of Phase I and when completed will be among the largest in the world. The museum was founded by Lonnie Mimms, who originally operated an Apple pop up museum, and includes original technologies including the Cray-1 The Cray-1 was a supercomputer designed, manufactured and marketed by Cray Research. Announced in 1975, the first Cray-1 system was installed at Los Alamos National Laboratory in 1976. Eventually, over 100 Cray-1s were sold, making it one of the ..., one of a kind developments, and more, including the contents of the former Bugbook Historical Computer Museum, yet only a fraction of his 300,000 item collection are on display. References External links * * Museums in Fulton County, Georgia Computer museums in the United States Museums ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray XT3
The Cray XT3 is a distributed memory massively parallel MIMD supercomputer designed by Cray Inc. with Sandia National Laboratories under the codename '' Red Storm''. Cray turned the design into a commercial product in 2004. The XT3 derives much of its architecture from the previous Cray T3E system, and also from the Intel ASCI Red supercomputer. XT3 The XT3 consists of between 192 and 32,768 ''processing elements'' (PEs), where each PE comprises a 2.4 or 2.6 GHz AMD Opteron processor with up to two cores, a custom "SeaStar" communications chip, and between 1 and 8 GB of RAM. The PowerPC 440 based SeaStar device provides a 6.4 gigabyte per second connection to the processor across HyperTransport, as well as six 8-gigabyte per second links to neighboring PEs. The PEs are arranged in a 3-dimensional torus topology, with 96 PEs in each cabinet. The XT3 runs an operating system called UNICOS/lc that partitions the machine into three sections, the largest comprising the ''Compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second ( FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, there have existed supercomputers which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers. Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computational science, and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerPC 400
The PowerPC 400 family is a line of 32-bit embedded RISC processor cores based on the PowerPC or Power ISA instruction set architectures. The cores are designed to fit inside specialized applications ranging from system-on-a-chip (SoC) microcontrollers, network appliances, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) to set-top boxes, storage devices and supercomputers. Applied Micro Circuits Corporation (AMCC) bought assets concerning the 400 family cores from IBM in April 2004 for $227 million, and they now market the processors under their own name. IBM continues evolving the cores while supplying design and foundry services around the cores. Several cores are also available for licensing by OEMs from IBM and Synopsys. Variants PowerPC 403 Introduced in 1994, the PowerPC 403 was one of the first PowerPC processors. It was the first one targeted strictly to the embedded market. Compared to the other PowerPC processors of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
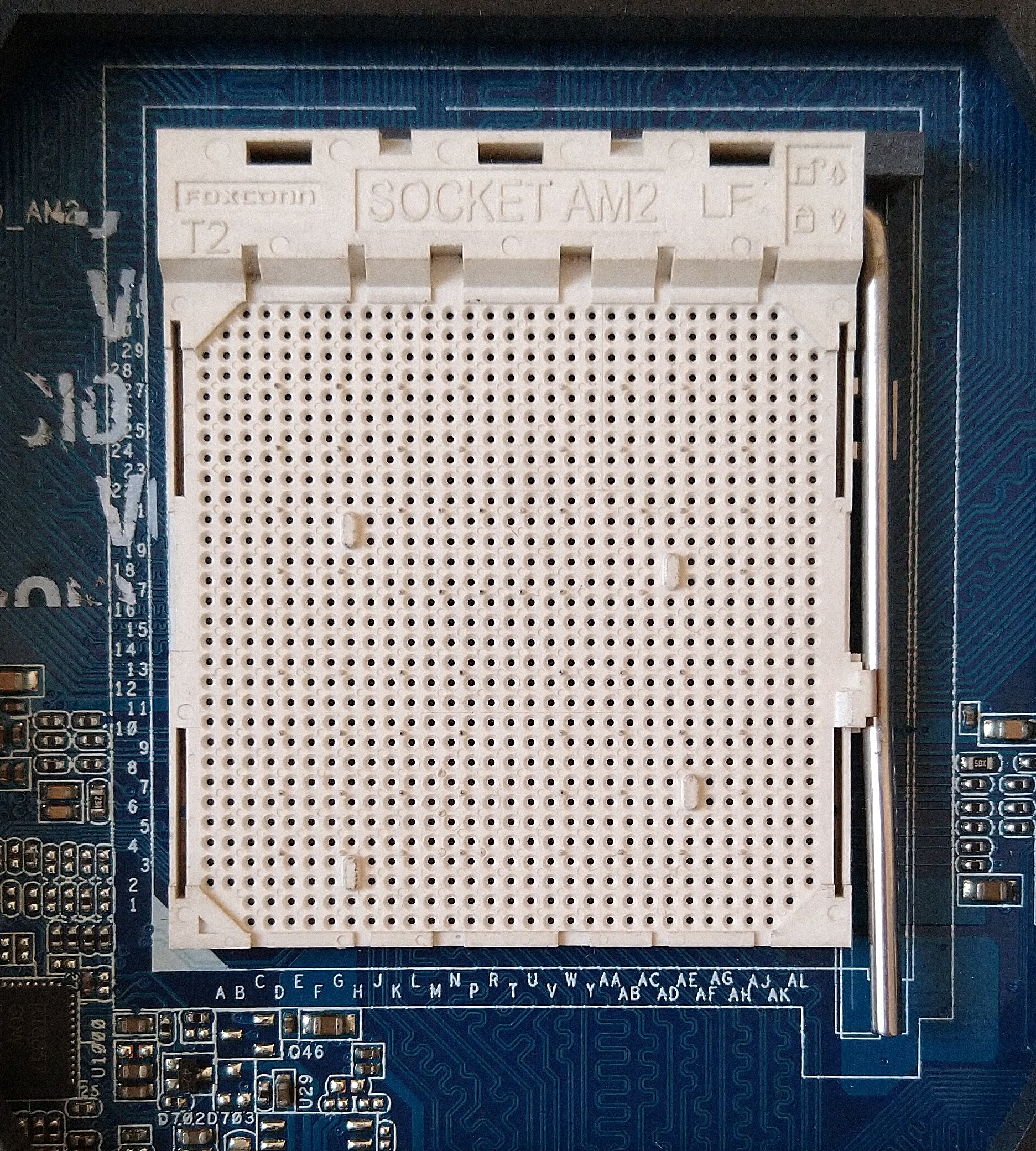
Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 (to prevent using the same name as Cyrix MII processors), is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments. It was released on May 23, 2006, as a replacement for Socket 939. Technical specifications AM2 processors are incompatible with 939 motherboards and vice versa, and although it has 940 pins, it is incompatible with Socket 940. Socket AM2 supports DDR2 SDRAM memory but not DDR memory, which the previous Socket 939 supported. '' AnandTech'' reported that Socket AM2 system performance was only about 7% faster than Socket 939 equivalents, with most applications about 2% faster, despite having over 30% greater memory bandwidth due to DDR2 support. The first processor cores to support socket AM2 were the single-core Orleans ( Athlon 64) and Manila (Sempron), and the dual-core Windsor (Athlon 64 X2 and Athlon 64 FX). Most processors on Socket AM2 include SSE3 instructions and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opteron
Opteron is AMD's x86 former server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture (known generically as x86-64 or AMD64). It was released on April 22, 2003, with the ''SledgeHammer'' core (K8) and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same segment as the Intel Xeon processor. Processors based on the AMD K10 microarchitecture (codenamed ''Barcelona'') were announced on September 10, 2007, featuring a new quad-core configuration. The most-recently released Opteron CPUs are the Piledriver-based Opteron 4300 and 6300 series processors, codenamed "Seoul" and "Abu Dhabi" respectively. In January 2016, the first ARMv8-A based Opteron-branded SoC was released, though it is unclear what, if any, heritage this Opteron-branded product line shares with the original Opteron technology other than intended use in the server space. Technical description Two key capabilities Opt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
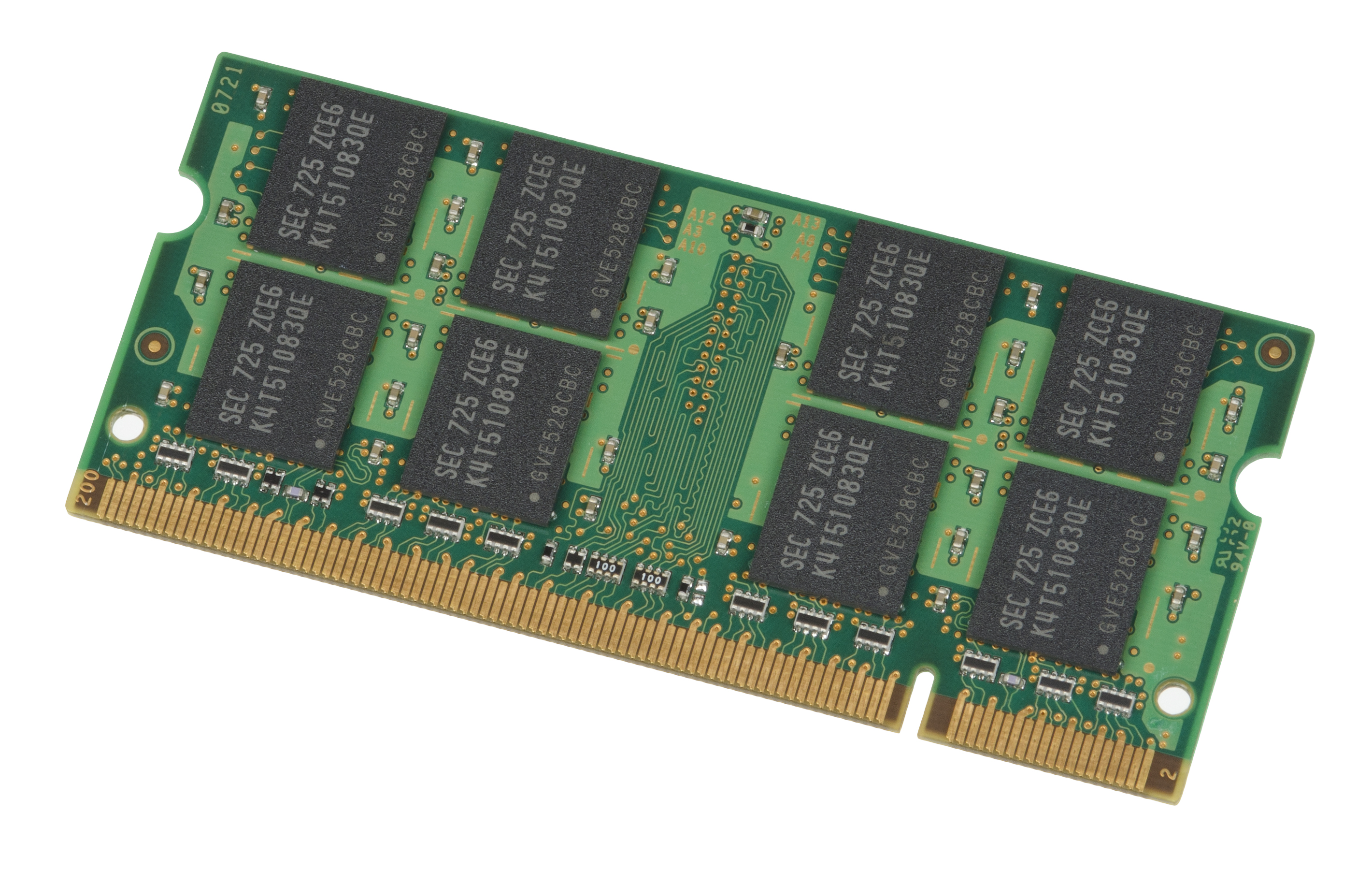
DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR3 SDRAM (launched in 2007). DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better latency. Alternatively, DDR2 memory operating at twice the external data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools. FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic blocks, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects allowing blocks to be wired together. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory. Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfigurabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray XT5
The Cray XT5 is an updated version of the Cray XT4 supercomputer, launched on November 6, 2007. It includes a faster version of the XT4's SeaStar2 interconnect router called SeaStar2+, and can be configured either with XT4 compute blades, which have four dual-core AMD Opteron processor sockets, or XT5 blades, with eight sockets supporting dual or quad-core Opterons. The XT5 uses a 3-dimensional torus network topology. XT5 family The XT5 family run the Cray Linux Environment, formerly known as UNICOS/lc. This incorporates SUSE Linux Enterprise Server and Cray's Compute Node Linux. The XT5h (''hybrid'') variant also includes support for Cray X2 vector processor blades, and Cray XR1 blades which combine Opterons with FPGA-based Reconfigurable Processor Units (RPUs) provided by DRC Computer Corporation. The XT5m variant is a mid-ranged supercomputer with most of the features of the XT5, but having a 2-dimensional torus network topology and scalable to 6 cabinets. In the fall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray Products
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world. Cray manufactures its products in part in Chippewa Falls, Wisconsin, where its founder, Seymour Cray, was born and raised. The company also has offices in Bloomington, Minnesota (which have been converted to Hewlett Packard Enterprise offices), and numerous other sales, service, engineering, and R&D locations around the world. The company's predecessor, Cray Research, Inc. (CRI), was founded in 1972 by computer designer Seymour Cray. Seymour Cray later formed Cray Computer Corporation (CCC) in 1989, which went bankrupt in 1995. Cray Research was acquired by Silicon Graphics (SGI) in 1996. Cray Inc. was formed in 2000 when Tera Computer Company purchased the Cray R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)