|
Councilman Body
In pathology, a Councilman body, also known as a Councilman hyaline body or apoptotic body, is an eosinophilic globule of apoptotic hepatocyte cell fragments. Ultimately, the fragments are taken up by macrophages or adjacent parenchymal cells.Ivan Damjanov, MD, PhD: Pathology for the Health Professions, 4th ed, St. Louis, Saunders Elsevier, 2012, p 19, Fig. 1-26.) They are found in the liver of individuals suffering from acute viral hepatitis, yellow fever, and other viral syndromes. Associated conditions Councilman bodies were first identified in Yellow fever, which characteristically shows a midzonal hepatic necrosis on biopsy. Similar inclusions are observed in other viral hemorrhagic fevers and all of the viral hepatitides. Liver biopsy of acute viral hepatitis shows panlobular lymphocytic infiltrates with ballooning hepatocytes. Eponym Councilman bodies are named after American pathologist William Thomas Councilman (1854–1933), who discovered them. See also * Ballooning de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballooning Degeneration High Mag Cropped
Ballooning may refer to: * Hot air ballooning * Balloon (aeronautics) * Ballooning (spider) * Ballooning degeneration, a disease * Memory ballooning See also * Balloon (other) {{Disambiguation Ballooning, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
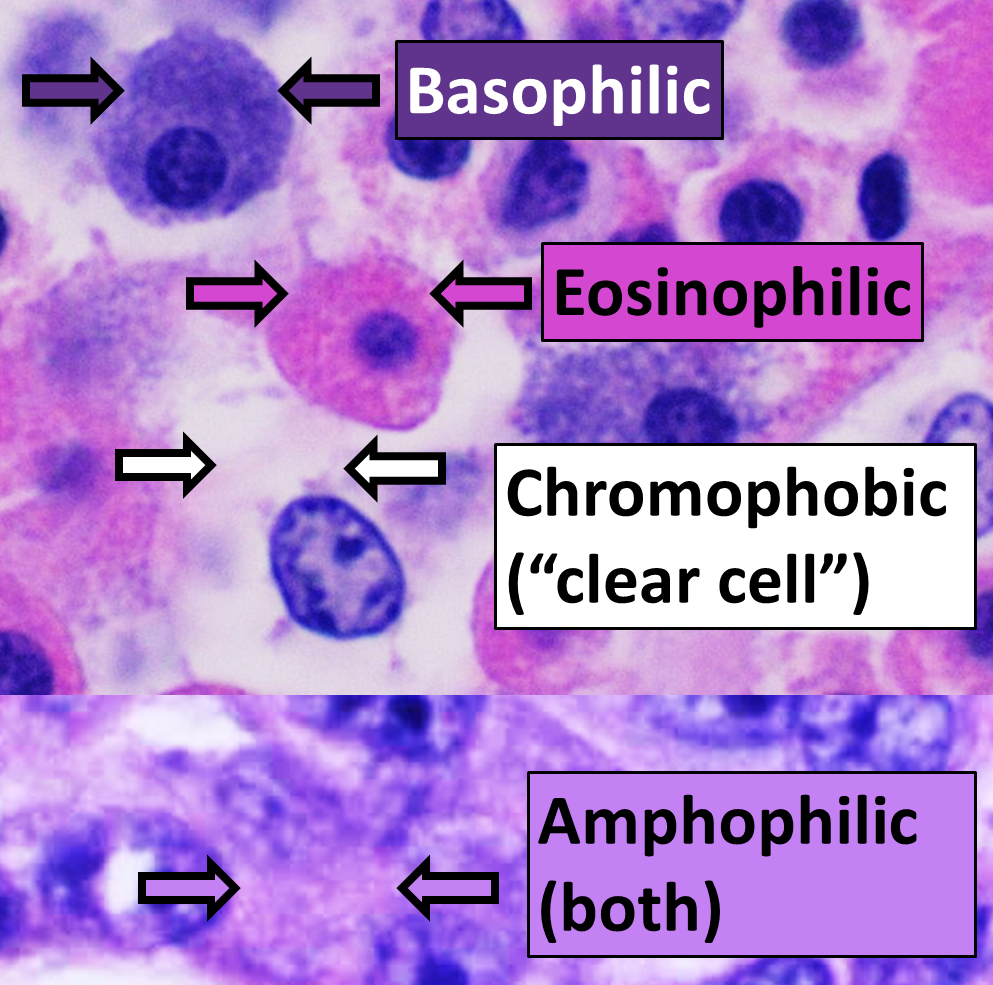
Eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix -phil-, meaning ''loves eosin'') is the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye. Eosin is an acidic dye for staining cell cytoplasm, collagen, and muscle fibers. ''Eosinophilic'' describes the appearance of cells and structures seen in histological sections that take up the staining dye eosin. Such eosinophilic structures are, in general, composed of protein. Eosin is usually combined with a stain called hematoxylin to produce a hematoxylin- and eosin-stained section (also called an H&E stain, HE or H+E section). It is the most widely used histological stain for a medical diagnosis. When a pathologist examines a biopsy of a suspected cancer, they will stain the biopsy with H&E. Some structures seen inside cells are described as being eosinophilic; for example, Lewy and Mallory bodies. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In about 15% of people, within a day of improving the fever comes back, abdominal pain occurs, and liver damage begins causing yellow skin. If this occurs, the risk of bleeding and kidney problems is increased. The disease is caused by the yellow fever virus and is spread by the bite of an infected mosquito. It infects humans, other primates, and several types of mosquitoes. In cities, it is spread primarily by ''Aedes aegypti'', a type of mosquito found throughout the tropics and subtropics. The virus is an RNA virus of the genus ''Flavivirus''. The disease may be difficult to tell apart from other illnesses, especially in the early stages. To confirm a suspected case, blood-sample testing with polymerase chain reaction is required. A saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the ruptu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using values between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle tone, muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes Flushing (physiology), flushed, and may begin to Perspiration, sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral infection, viral, bacterial infection, bacterial, and parasitic infect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathologist
Pathology is the study of the causal, causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue (biology), tissue, human cell, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be "Pathophysiology, pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thomas Councilman
William Thomas Councilman (January 1, 1854 in Pikesville, Maryland – May 26, 1933 in York Village, Maine) was an American pathologist. He is remembered for his contribution in a monograph on amoebic dysentery (1891) which described detailed observations of it and its parasite. He is even better known for his work on Yellow Fever. William Thomas Councilman served as the first pathologist-in-chief at Peter Bent Brigham Hospital (PBBH). Councilman had arrived in Harvard Medical School earlier in 1892 and was an expert in the study of amebiasis, diphtheria, smallpox, and yellow fever. His vivid morphologic description of changes seen in the liver of yellow fever lives on today as "Councilman body". In 1916, he went with the Rice Expedition, led by Alexander H. Rice, Jr., to the Amazon and Brazil. With Robert Archibald Lambert, he wrote a report and book on the expedition which was published in 1918. By invitation, two years after his retirement at Harvard, he temporarily joine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballooning Degeneration
In histopathology, ballooning degeneration, formally ballooning degeneration of hepatocytes, is a form of liver parenchymal cell (i.e. hepatocyte) death. The name is derived from the fact that the cells undergoing this form of cell death increase in size (balloon). It is generally considered a form of apoptosis, and is a descriptor used in the context of inflamed fatty liver (steatohepatitis) (which may be due to obesity or alcohol), as well as viral hepatitis. The histomorphological appearance of ballooning degeneration is not pathognomonic for steatohepatitis, but usage of the term is generally confined to the condition, i.e. in the context of other histopathological findings the label ''ballooning degeneration'' is not used for cell death with cytoplasmic clearing and cell swelling. Appearance Ballooned cells are typically two to three times the size of adjacent hepatocytes and are characterized by a wispy cleared cytoplasm on H&E stained sections. They can be differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)