|
Coronary CT Calcium Scan
A coronary CT calcium scan is a computed tomography (CT) scan of the heart for the assessment of severity of coronary artery disease. Specifically, it looks for calcium deposits in atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary arteries that can narrow arteries and increase the risk of heart attack. These plaques are the cause of most heart attacks, and become calcified as they mature. These calcifications can then be detected by CT because of their high attenuation. This severity can be presented as Agatston score or coronary artery calcium (CAC) score. The CAC score is an independent marker of risk for cardiac events, cardiac mortality, and all-cause mortality. In addition, it provides additional prognostic information to other cardiovascular risk markers. Obstructions may be present even with an Agatston score of zero, especially in younger patients. A typical coronary CT calcium scan is done without the use of radiocontrast, but it can possibly be done from contrast-enhanced images as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
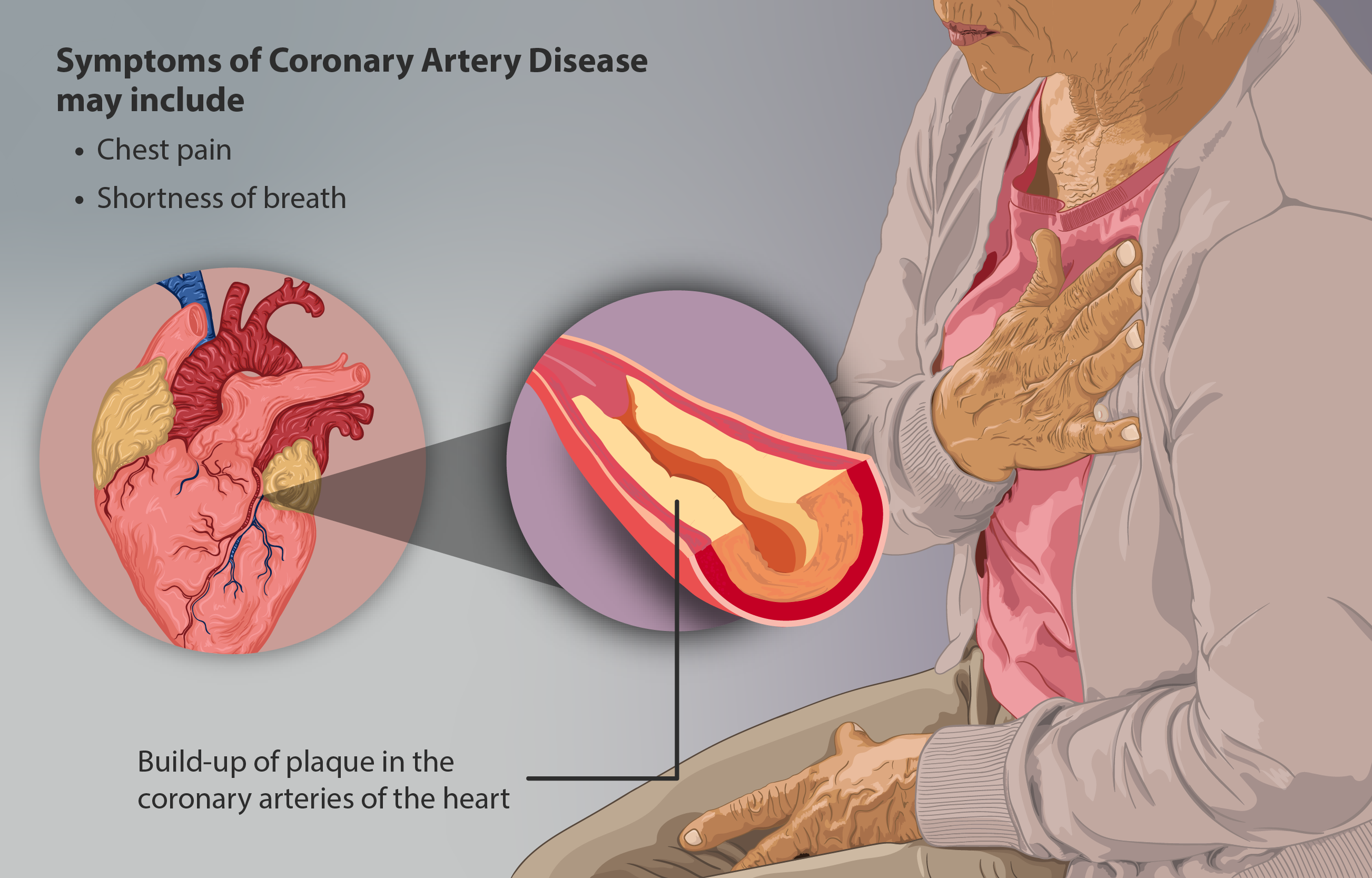 |
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the myocardium, heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the Coronary arteries, arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Stress (psychological), stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a Myocardial infarction, heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Radiocontrast
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus MRI contrast agents have a different mode of action. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei. Types and uses Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped in positive (iodinated agents, barium sulfate), and negative agents (air, carbon dioxide, methylcellulose). Iodine (circulatory system) Iodinated contrast contains iodine. It is the main type of radiocontrast used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Coronary CT Angiography
Coronary CT angiography (CTA or CCTA) is the use of computed tomography (CT) angiography to assess the coronary arteries of the heart. The patient receives an intravenous injection of radiocontrast and then the heart is scanned using a high speed CT scanner, allowing physicians to assess the extent of occlusion in the coronary arteries, usually in order to diagnose coronary artery disease. CTA is superior to coronary CT calcium scan in determining the risk of Major Adverse Cardiac Events (MACE). Medical uses Faster CT machines, due to multidetector capabilities, have made imaging of the heart and circulatory system very practical in a number of clinical settings. The faster capability has allowed the imaging of the heart with minimal involuntary motion, which creates motion blur on the image, and has a number of practical applications. It may be useful in the diagnosis of suspected coronary heart disease, for follow-up of a coronary artery bypass, for the evaluation of valvula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Arthur Agatston
Arthur Agatston (born January 22, 1947) is an American cardiologist and celebrity doctor best known as the developer of the South Beach Diet, but also as the author of many published scholarly papers in the field of noninvasive cardiac diagnostics. His scientific research led to the Agatston score for measuring coronary artery calcium. Education Agatston earned an MD at New York University School of Medicine in 1973, studied internal medicine at Montefiore Medical Center at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine and completed his cardiology fellowship at NYU. Career Agatston started his medical career on staff at New York University Medical Center. After a year, he took a position at the Mount Sinai Medical Center & Miami Heart Institute in Miami Beach Miami Beach is a coastal resort city in Miami-Dade County, Florida. It was incorporated on March 26, 1915. The municipality is located on natural and man-made barrier islands between the Atlantic Ocean and Biscayne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Electron Beam Tomography
Electron beam computed tomography (EBCT) is a specific form of computed tomography (CT) in which the X-ray tube is not mechanically spun in order to rotate the source of X-ray photons. This different design was explicitly developed to better image heart structures that never stop moving, performing a complete cycle of movement with each heartbeat. As in conventional CT technology, the X-ray source-point moves along a circle in space around an object to be imaged. In EBCT, the X-ray tube itself is large and stationary, and partially surrounds the imaging circle. Rather than moving the tube itself, electron-beam focal point (and hence the X-ray source point) is swept electronically along a tungsten anode in the tube, tracing a large circular arc on its inner surface. This motion can be very fast. Advantages and disadvantages The principal application advantage of EBT machines, and the reason for the invention, is that because the X-ray source-point is swept electronically, not m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Hounsfield Scale
The Hounsfield scale , named after Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, is a quantitative scale for describing radiodensity. It is frequently used in CT scans, where its value is also termed CT number. Definition The Hounsfield unit (HU) scale is a linear transformation of the original linear attenuation coefficient measurement into one in which the radiodensity of distilled water at standard pressure and temperature ( STP) is defined as 0 Hounsfield units (HU), while the radiodensity of air at STP is defined as −1000 HU. In a voxel with average linear attenuation coefficient \mu, the corresponding HU value is therefore given by: HU = 1000\times\frac where \mu_ and \mu_ are respectively the linear attenuation coefficients of water and air. Thus, a change of one Hounsfield unit (HU) represents a change of 0.1% of the attenuation coefficient of water since the attenuation coefficient of air is nearly zero. Calibration tests of HU with reference to water and other materials may be done to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Agatston Score
A coronary CT calcium scan is a computed tomography (CT) scan of the heart for the assessment of severity of coronary artery disease. Specifically, it looks for calcium deposits in atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary arteries that can narrow arteries and increase the risk of heart attack. These plaques are the cause of most heart attacks, and become calcified as they mature. These calcifications can then be detected by CT because of their high attenuation. This severity can be presented as Agatston score or coronary artery calcium (CAC) score. The CAC score is an independent marker of risk for cardiac events, cardiac mortality, and all-cause mortality. In addition, it provides additional prognostic information to other cardiovascular risk markers. Obstructions may be present even with an Agatston score of zero, especially in younger patients. A typical coronary CT calcium scan is done without the use of radiocontrast, but it can possibly be done from contrast-enhanced images as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Cardiac Imaging
Cardiac imaging refers to non-invasive imaging of the heart using ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), or nuclear medicine (NM) imaging with PET or SPECT. These cardiac techniques are otherwise referred to as echocardiography, Cardiac MRI, Cardiac CT, Cardiac PET and Cardiac SPECT including myocardial perfusion imaging. Indications A physician may recommend cardiac imaging to support a diagnosis of a heart condition. Medical specialty professional organizations discourage the use of routine cardiac imaging during pre-operative assessment for patients about to undergo low or mid-risk non-cardiac surgery because the procedure carries risks and is unlikely to result in the change of a patient's management., citing * * Stress cardiac imaging is discouraged in the evaluation of patients without cardiac symptoms or in routine follow-ups. Echocardiography '' Transthoracic echocardiography'' uses ultrasonic waves for continuous heart chamber a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |