|
Coroico
Coroico is a town in Nor Yungas Province, in the La Paz Department, Bolivia, La Paz Department of western Bolivia. History Coroico Viejo (Old Coroico) was founded above the river Quri Wayq'u (Quechua language, Quechua ''quri'' gold, ''wayq'u'' valley, hispanicized spellings ''Coriguayco'', ''Kori Huayco''). The town lived from mining gold, but the massive attacks by Native populations left the first Spanish colonial settlers in search of protection. Looking for a defendable position in the early 18th century, the settlers arrived at the current location of Coroico only to be chased into a cave by one of Mount Uchumachi's powerful lightning storms. The cave still exists below the church on the main plaza of Coroico. In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, Coroico survived a couple of Indian attacks - the biggest one was at the time of the Bolivian War of Independence. 5000 Aymaras attacked the town, which in those days only had 500 inhabitants. The town stood strong, forcing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Coroico
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Coroico ( la, Dioecesis Coroicensis) is a diocese located in the city of Coroico in the Ecclesiastical province of La Paz in Bolivia. History * November 7, 1958: Established as Territorial Prelature of Coroico from the Metropolitan Archdiocese of La Paz * July 28, 1983: Promoted as Diocese of Coroico Bishops Ordinaries (in reverse chronological order) * Bishops of Coroico (Roman rite) ** Bishop Juan Carlos Huaygua Oropeza, O.P. (2022.12.03 – present) ** Bishop Juan Vargas Aruquipa (1997.08.20 – 2022.12.03) ** Bishop Tomás Roberto Manning, O.F.M. (1983.07.28 – 1996.10.09) * Prelates of Coroico (Roman rite) ** Bishop Tomás Roberto Manning, O.F.M. (1959.04.21 – 1983.07.28) Auxiliary bishop * Juan Vargas Aruquipa (1992-1997), appointed Bishop here See also *Roman Catholicism in Bolivia The Catholic Church in Bolivia is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome. Catholicism was introduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nor Yungas Province
Nor Yungas is a province in the Yungas area of the Bolivian department of La Paz. During the presidency of José Manuel Pando the Yungas Province was divided into two parts, the Nor Yungas and the Sud Yungas Province, by law of January 12, 1899. Its administrative seat is the town of Coroico. Subdivision The province is divided into two municipalities. Places of interest * Cotapata National Park and Integrated Management Natural Area See also * Kimsa Warmini * P'iqi Q'ara * P'iqi Q'ara P'iqi Q'ara (Aymara language, Aymara ''p'iqi, p'iq'iña, phiq'i, phiq'iña'' head, ''q'ara'' bald, bare, "bald-headed", also spelled ''Pekhe Khara'') is a mountain in the Andes of Bolivia. It is located in the La Paz Department (Bolivia), La P ... (in Coroico) References Provinces of La Paz Department (Bolivia) Yungas {{LaPazBO-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
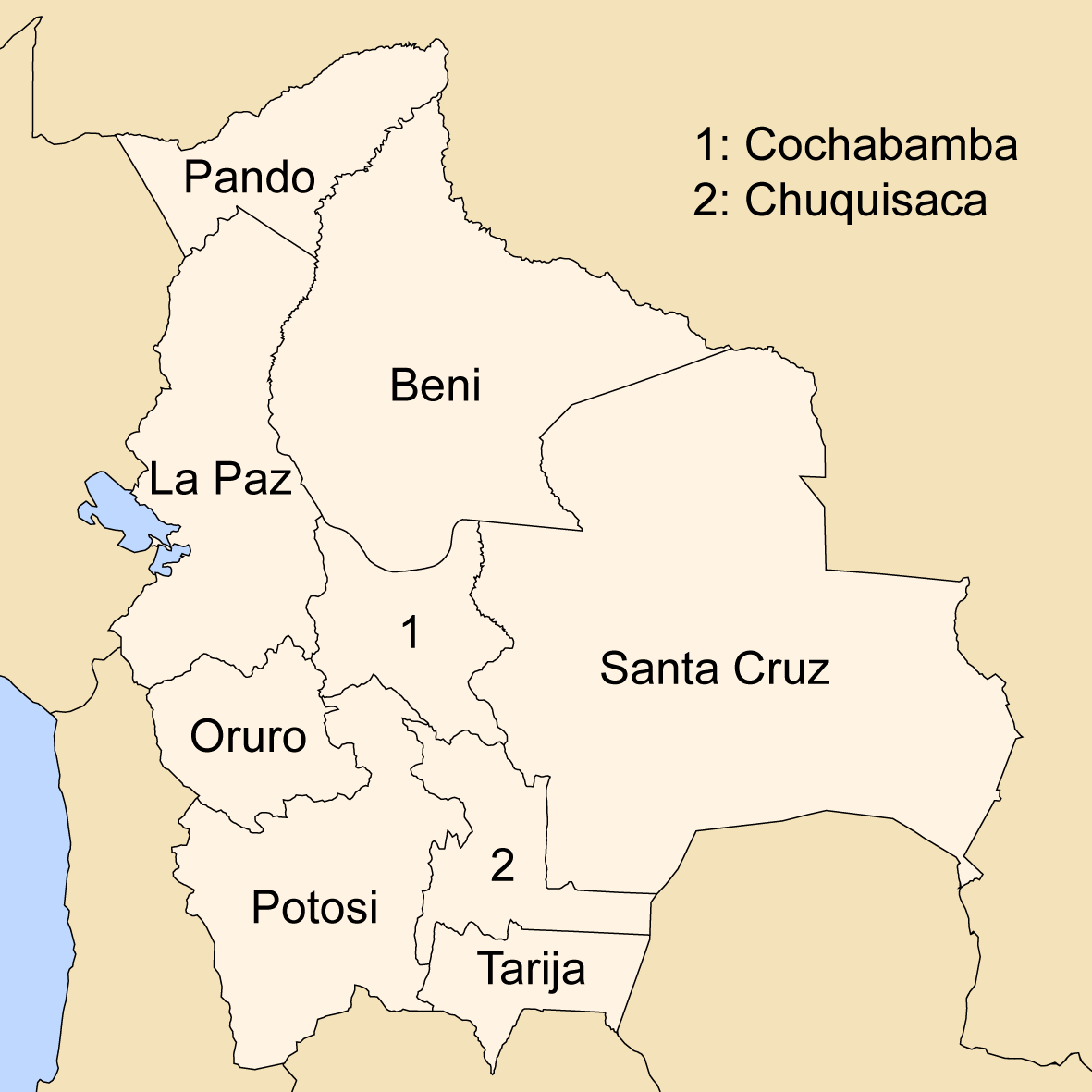
Provinces Of Bolivia
A province is the second largest administrative division in Bolivia, after a department. Each department is divided into provinces. There are 112 provinces. The country's provinces are further divided into 337 municipalities which are administered by an alcalde and municipal council. List of provinces Beni Department Chuquisaca Department Cochabamba Department La Paz Department Oruro Department Pando Department Potosí Department Santa Cruz Department Tarija Department See also * Departments of Bolivia Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine departments ( es, departamentos). Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinatio ... * Municipalities of Bolivia Sources Instituto Nacional de Estadística - Bolivia(Spanish) {{Articles on second-level administrative divisions of South American countries S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unidad Académica Campesina-Carmen Pampa
The Unidad Académica Campesina-Carmen Pampa (UAC-Carmen Pampa) is a satellite campus of the Catholic University of Bolivia founded in 1993 to serve the rural poor of Bolivia.Carmen Pampa Fund. n.d. History and Mission of the College. Available at http://carmenpampafund.org/uac_history.htm. Accessed 2010-08-17. It is located in Carmen Pampa, a small farming community 12 km. from the town of Coroico. History The UAC-Carmen Pampa was founded on October 3, 1993, by Sister Damon Nolan, a nun of the Missionary Franciscan Sisters of the Immaculate Conception of the Third Order of Saint Francis. It started as part of a consortium of rural campuses of the Catholic University of Bolivia called UACs (Unidades Académicas Campesinas), created to educate the rural poor, and in 2010 became an independent satellite campus of the Catholic University of Bolivia. The university first offered technical degrees in agronomy, veterinary/animal science and nursing. In 1998 the UAC-Carmen Pampa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square patchwork with the (top left to bottom right) diagonals forming colored stripes (green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, white, green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, from top right to bottom left) , other_symbol = , other_symbol_type = Dual flag: , image_coat = Escudo de Bolivia.svg , national_anthem = " National Anthem of Bolivia" , image_map = BOL orthographic.svg , map_width = 220px , alt_map = , image_map2 = , alt_map2 = , map_caption = , capital = La Paz Sucre , largest_city = , official_languages = Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Paz Department, Bolivia
The La Paz Department of Bolivia comprises with a 2012 census population of 2,706,359 inhabitants. It is situated at the western border of Bolivia, sharing Lake Titicaca with adjacent Peru. It contains the '' Cordillera Real'', which reaches altitudes of . Northeast of the Cordillera Real are the '' Yungas'', the steep eastern slopes of the Andes Mountains that make the transition to the Amazon River basin to the northeast. The capital of the department is the city of La Paz and is the administrative city and seat of government/national capital of Bolivia. Provinces The Department of La Paz is divided into 20 provinces (''provincias'') which are further subdivided into 85 municipalities (''municipios'') and - on the fourth level - into cantons. The provinces with their capitals are: Government The chief executive office of Bolivia's departments (since May 2010) is the Governor; before then, the office was called the Prefect, and until 2006 the prefect was app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Bolivia
The flag of Bolivia is the national flag of the Plurinational State of Bolivia. It was originally adopted in 1851. The state and war flag is a horizontal tricolor of red, yellow and green with the Bolivian coat of arms in the center. According to one source, the red stands for Bolivia's brave soldiers, while the green symbolizes fertility and yellow the nation's mineral deposits. Since 2009 the Wiphala also holds the status of ''dual flag'' in the country. According to the revised Constitution of Bolivia of 2009, the Wiphala is considered a national symbol of Bolivia (along with the flag, national anthem, coat of arms, the cockade; kantuta flower and patujú flower). Despite its landlocked status, Bolivia has a naval ensign used by navy vessels on rivers and lakes. It consists of a blue field with the state flag in the canton bordered by nine small yellow five-pointed stars, with a larger yellow five-pointed star in the fly. The nine small stars represent the nine de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of Bolivia
Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine departments ( es, departamentos). Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly—a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Each department is represented by four Senators, while Deputies are awarded to each department in proportion to their total population. Out of the nine departments, La Paz was originally the most populous, with 2,706,351 inhabitants as of 2012 but the far eastern department of Santa Cruz has since surpassed it by 2020; Santa Cruz also claims the title as the largest, encompassing . Pando is the least populated, with a population of 110,436. The smallest in area is Tarija, encompassing . Departments Former Departments By population Notes See also * ISO 3166-2:BO, the ISO codes for the departments of Bolivia. * Boliv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua Language
Quechua (, ; ), usually called ("people's language") in Quechuan languages, is an indigenous language family spoken by the Quechua peoples, primarily living in the Peruvian Andes. Derived from a common ancestral language, it is the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with an estimated 8–10 million speakers as of 2004.Adelaar 2004, pp. 167–168, 255. Approximately 25% (7.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechuan language. It is perhaps most widely known for being the main language family of the Inca Empire. The Spanish encouraged its use until the Peruvian struggle for independence of the 1780s. As a result, Quechua variants are still widely spoken today, being the co-official language of many regions and the second most spoken language family in Peru. History Quechua had already expanded across wide ranges of the central Andes long before the expansion of the Inca Empire. The Inca were one among many peoples in present-day Peru who alread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coca
Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known worldwide for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine. The plant is grown as a cash crop in the Argentine Northwest, Bolivia, Alto Rio Negro Territory in Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Peru, even in areas where its cultivation is unlawful. There are some reports that the plant is being cultivated in the south of Mexico, by using seeds imported from South America, as an alternative to smuggling its recreational product cocaine. It also plays a role in many traditional Amazonian and Andean cultures as well as the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta in northern Colombia. The cocaine alkaloid content of dry ''Erythroxylum coca'' var. ''coca'' leaves was measured ranging from 0.23% to 0.96%. Coca-Cola used coca leaf extract in its products from 1885 until about 1903, when it began using decocainized leaf extract. Extraction of cocaine from coca requires severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yungas Road
The Yungas Road is a cycle route about 60 km long that links the city of La Paz and the Yungas region of Bolivia. It draws about 25,000 tourists per year and is a major La Paz tourist attraction. Many tour operators cater to downhill mountain biking, providing information, guides, transport and equipment. At least 18 cyclists have died on the road since 1998. The tourist route is a 64 km-long road with 3500 metres of descent. The route includes the Cotapata-Santa Bárbara section. It replaced the old road, built in 1930. It was considered dangerous because of its steep slopes, narrow single track, lack of guardrails, rain, and fog, and was nicknamed the "Road of Death". However, it was not the most dangerous road in the region. Unlike the rest of the country, traffic was left-hand, to allow the driver to assess the distance of their outer wheel from the edge of the road. A new alternative route, now part of Route 3, was built during a 20-year period ending in 2006. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

.png)