|
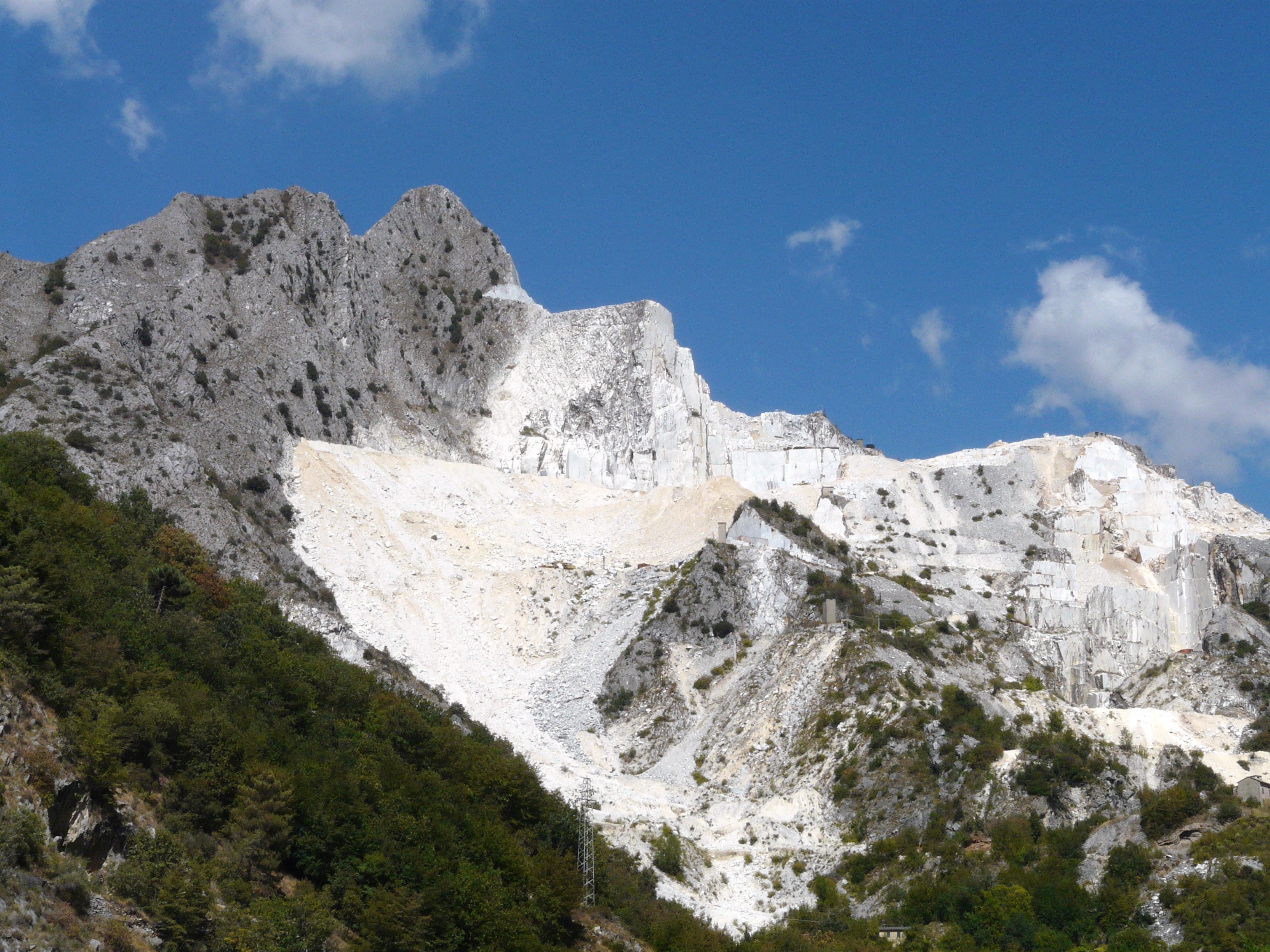
Corncockle Quarry
Corncockle Quarry was a large and historically important sandstone quarry near Templand in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. Stone from here was used in the late Victorian era to build tenements in Edinburgh and Glasgow, and also to construct New York ' brownstones'. Geology The sandstone in Corncockle Quarry is the Corncockle Sandstone Formation and dates from the Cisuralian, the Lower Permian between 298.9 - 272.3 Mya. Fossil footprints were found there in the early 1800s, uncovered during quarrying. They are often wrongly referred to as dinosaur footprints, but dinosaurs did not exist at this time. They belong instead to other extinct reptiles such as therapsids - the group that would eventually lead to mammals, and includes animals like '' Dimetrodon''. The footprints from Corncockle were the first ever described scientifically, by Mr. J Grierson, and the Reverend Henry Duncan in 1828. Rev Duncan then published his paper on the footprints in 1831. The name for the study of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelichnus Duncani
''Chelichnus'' is an ichnogenus of Permian tetrapod footprint. The name means ''tortoise traces'', because the shape of the prints was originally mistakenly thought to be produced by a tortoise. This is now known to be incorrect, as tortoises did not evolve until much later. It was first found in Corncockle Quarry in Dumfries, Scotland, and described by Rev. Henry Duncan. In ichnology, footprints and other traces are given a genus and species name, the ichnogenus and ichnospecies, that is based on the shape of the print. However, it is almost impossible to match a trackmark to the animal that made it. ''Chelichnus'' has been argued to belong to either a therapsid Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more ..., or a reptile.McKeever, PJ. 1994. The behavioural and biostratigrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir William Jardine, 7th Baronet
Sir William Jardine, 7th Baronet of Applegarth FRS FRSE FLS FSA (23 February 1800 – 21 November 1874) was a Scottish naturalist. He is known for his editing of a long series of natural history books, ''The Naturalist's Library''. Life and work Jardine was born on 23 February 1800 at 28 North Hanover Street in Edinburgh, the son of Sir Alexander Jardine, 6th baronet of Applegarth and his wife, Jane Maule. He was educated in both York and Edinburgh then studied medicine at Edinburgh University. From 1817 to 1821 he lodged with Rev Dr Andrew Grant at James Square, an arrangement made by his father. Grant was minister of St Andrew's Church on George Street. In his early years, aged only 25, he was elected a fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh his proposer being Sir David Brewster. He was a co-founder of the Berwickshire Naturalists' Club, and contributed to the founding of the Ray Society. He was "keenly addicted to field-sports, and a master equally of the rod a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
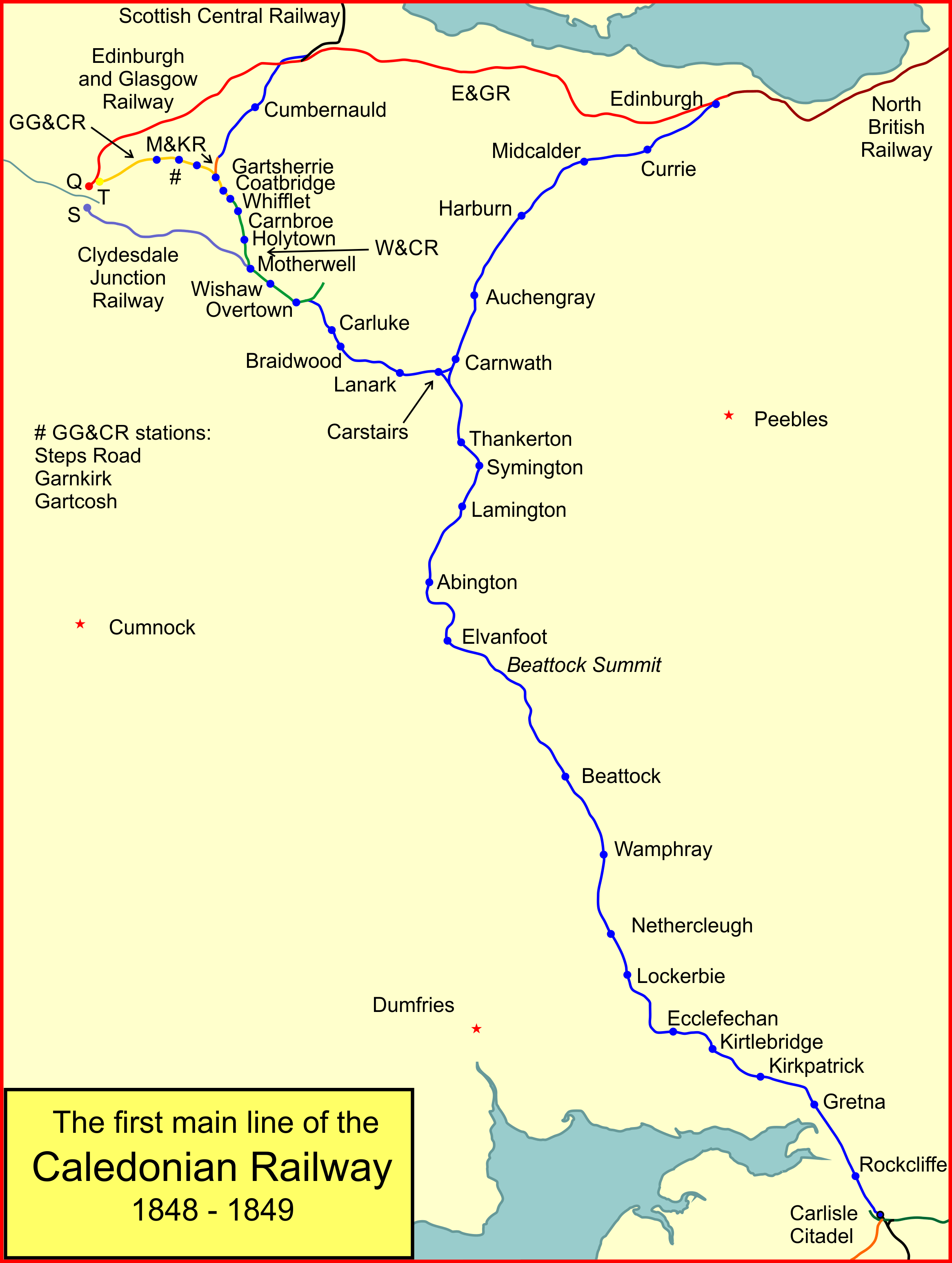
Caledonian Main Line
The Caledonian Railway main line in Scotland connected Glasgow and Edinburgh with Carlisle, via Carstairs and Beattock. It was opened in 1847 by the Caledonian Railway. The approach to Glasgow used railways already built, primarily for mineral traffic; these were later by-passed by a more direct route. Today, the route forms the northern section of the West Coast Main Line, and was electrified in the early 1970s. Opening From 1830 onwards considerable attention was given to the means by which Glasgow and Edinburgh might be connected to London, and as English railways began to develop into a network, the urgency of making a railway accelerated. The difficult terrain of the Southern Uplands and Cumberland made the selection of a route controversial. After much difficulty, the Caledonian Railway was authorised to build a line via Beattock; this was known as the ''Annandale Route''. On 10 September 1847 the line was opened between Carlisle and Beattock. The station at Carlisle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Scotland
The National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland, was formed in 2006 with the merger of the new Museum of Scotland, with collections relating to Scottish antiquities, culture and history, and the adjacent Royal Scottish Museum (opened in 1866 as the Edinburgh Museum of Science and Art, renamed in 1904, and for the period between 1985 and the merger named the Royal Museum of Scotland or simply the Royal Museum), with international collections covering science and technology, natural history, and world cultures. The two connected buildings stand beside each other on Chambers Street, by the intersection with the George IV Bridge, in central Edinburgh. The museum is part of National Museums Scotland. Admission is free. The two buildings retain distinctive characters: the Museum of Scotland is housed in a modern building opened in 1998, while the former Royal Museum building was begun in 1861 and partially opened in 1866, with a Victorian Venetian Renaissance facade and a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfries Museum
Dumfries Museum and Camera Obscura, located in Dumfries in Dumfries & Galloway, is the largest museum in the region. The museum has extensive collections relating to local and history from the pre-historic era. The museum also has the world's oldest working Camera Obscura. Admission is free, however a small fee applies for the Camera Obscura. Collections The museum's collections cover all material relating to the natural history and human pre-history of the region, from geology to dress, folk material, archaeology and early photographs. Notable artefacts include: * A cast of the skull of Robert the Bruce as well as femur and foot bones. * A Bronze Age cist burial including the remains of a 35-year-old man from the beaker people. * A large collection of Roman and Celtic stone crosses and funerary monuments. * A replica of the first bicycle, as designed by Kirkpatrick Macmillan. * The photographic archive of Dr Werner Kissling. * Personal items belonging to Thomas Carlyle *Foss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Buckland
William Buckland Doctor of Divinity, DD, Royal Society, FRS (12 March 1784 – 14 August 1856) was an English theologian who became Dean of Westminster. He was also a geologist and paleontology, palaeontologist. Buckland wrote the first full account of a fossil dinosaur, which he named ''Megalosaurus''. His work proved that Kirkdale Cave in North Yorkshire had been a prehistoric hyena den, for which he was awarded the Copley Medal. It was praised as an example of how scientific analysis could reconstruct distant events. He pioneered the use of fossilised Feces, faeces in reconstructing ecosystems, coining the term coprolites. Buckland followed the Gap creationism, Gap Theory in interpreting the biblical account of ''Genesis'' as two widely separated episodes of creation. It had emerged as a way to reconcile the scriptural account with discoveries in geology suggesting the earth was very old. Early in his career Buckland believed he had found evidence of the Deluge myth, biblic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir William Jardine
Sir William Jardine, 7th Baronet of Applegarth FRS FRSE FLS FSA (23 February 1800 – 21 November 1874) was a Scottish naturalist. He is known for his editing of a long series of natural history books, ''The Naturalist's Library''. Life and work Jardine was born on 23 February 1800 at 28 North Hanover Street in Edinburgh, the son of Sir Alexander Jardine, 6th baronet of Applegarth and his wife, Jane Maule. He was educated in both York and Edinburgh then studied medicine at Edinburgh University. From 1817 to 1821 he lodged with Rev Dr Andrew Grant at James Square, an arrangement made by his father. Grant was minister of St Andrew's Church on George Street. In his early years, aged only 25, he was elected a fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh his proposer being Sir David Brewster. He was a co-founder of the Berwickshire Naturalists' Club, and contributed to the founding of the Ray Society. He was "keenly addicted to field-sports, and a master equally of the rod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Duncan (minister)
Henry Duncan FRSE (8 October 1774 – 12 February 1846) was a Scottish minister, geologist and social reformer. The minister of Ruthwell in Dumfriesshire, he founded the world's first mutual savings bank that would eventually form part of the Trustee Savings Bank. He served as Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland in 1839. At the Disruption has left the Church of Scotland and sided with the Free Church. He was also a publisher, a philanthropist and an author, writing novels as well as works of science and religion. Early life Duncan was born in 1774 at Lochrutton, Kirkcudbrightshire, where his father, George Duncan, was minister. As a boy he met the poet Robert Burns, who visited Lochrutton Manse. Duncan was educated in Dumfries at the Academy. After studying for two sessions at St. Andrews University he was sent to Liverpool to begin commercial life, and under the patronage of his relative, Dr. James Currie, the biographer of Robert Burns, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to reduce their environmental impact. The word ''quarry'' can also include the underground quarrying for stone, such as Bath stone. Types of rock Types of rock extracted from quarries include: *Chalk *China clay *Cinder *Clay *Coal * Construction aggregate (sand and gravel) * Coquina * Diabase *Gabbro *Granite * Gritstone *Gypsum *Limestone *Marble *Ores *Phosphate rock *Quartz *Sandstone * Slate *Travertine Stone quarry Stone quarry is an outdated term for mining construction rocks (limestone, marble, granite, sandstone, etc.). There are open types (called quarries, or open-pit mines) and closed types ( mines and caves). For thousands of years, only hand tools had been used in quarries. In the 18th century, the use of drilling and blasting operatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimetrodon
''Dimetrodon'' ( or ,) meaning "two measures of teeth,” is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsid that lived during the Cisuralian (Early Permian), around 295–272 million years ago (Mya). It is a member of the family Sphenacodontidae. The most prominent feature of ''Dimetrodon'' is the large neural spine sail on its back formed by elongated spines extending from the vertebrae. It walked on four legs and had a tall, curved skull with large teeth of different sizes set along the jaws. Most fossils have been found in the Southwestern United States, the majority coming from a geological deposit called the Red Beds of Texas and Oklahoma. More recently, its fossils have been found in Germany. Over a dozen species have been named since the genus was first erected in 1878. ''Dimetrodon'' is often mistaken for a dinosaur or as a contemporary of dinosaurs in popular culture, but it became extinct some 40 million years before the first appearance of dinosaurs. Reptile-li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)

.jpg)



