|
Corlissina
''Corlissina'' is a genus of karyorelict ciliates in the family Geleiidae. Only the type species ''Corlissina maricaensis'' is assigned to this genus. ''Corlissina'' is characterized by a paroral ciliature with two rows of polykineties forming a loop at the posterior end. The dikinetids of the adoral zone are organized in short polykineties, followed by a row of monokinetids. The two globular macronuclei are linked by a single micronucleus, a pattern found in most Geleiidae. The genus name is a taxonomic patronym honoring the protistologist John O. Corliss. Comparison and phylogenetic analysis of 18S rRNA sequences showed that ''Corlissina maricaensis'' is the sister group to ''Parduczia orbis''. In turn, these two genera form a clade with ''Geleia ''Geleia'' is a genus of karyorelict ciliates in the family Geleiidae. The genus name is a taxonomic patronym honoring the Hungarian protistologist József von Gelei (1885-1952). Systematics 17 species are currently desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parduczia
''Parduczia'' is a genus of karyorelict ciliates in the family Geleiidae. ''Parduczia'' species are filiform to serpentiform ciliates characterized by their giant size (1200 to 2500 µm on average) and their very long buccal split. The genus name is a taxonomic patronym honoring the protistologist Béla Párducz (1911–1964). Systematics Five species are currently described in the genus ''Parduczia''. * ''Parduczia arcachonense'' (Nouzarède, 1965) Dragesco, 1999 * ''Parduczia filiformis'' (Nouzarède, 1977) Dragesco, 1999 * ''Parduczia martinicense'' (Nouzarède, 1977) Dragesco, 1999 * ''Parduczia murmanica'' (Raikov, 1962) Dragesco, 1999 * ''Parduczia orbis'' (Fauré-Fremiet, 1950) Dragesco, 1999 is the type species of the genus. Phylogeny Comparison and phylogenetic analysis of 18S rRNA sequences showed that ''Parduczia orbis'' is the sister group to '' Corlissina maricaensis''. In turn, these two genera form a clade with ''Geleia''. Alternative genetic code An alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geleia
''Geleia'' is a genus of karyorelict ciliates in the family Geleiidae. The genus name is a taxonomic patronym honoring the Hungarian protistologist József von Gelei (1885-1952). Systematics 17 species are currently described in the genus ''Geleia''. * ''Geleia acuta'' Dragesco, 1960 * '' Geleia decolor'' Kahl, 1933 * '' Geleia filiformes'' Nouzarède, 1976 * '' Geleia fossata'' Kahl, 1933 is the type species of the genus. * '' Geleia heterotricha'' Dragesco, 1960, redescribed as '' Gellertia heterotricha'' Dragesco, 1999 * '' Geleia hyalina'' Dragesco, 1960 * '' Geleia luci'' Dragesco, 1960 * '' Geleia major'' Dragesco, 1954 * '' Geleia martinicense'' Nouzarède, 1976 * '' Geleia murmanica'' Raikov, 1962 * ''Geleia nigriceps'' Kahl, 1933 * '' Geleia obliqua'' Dragesco, 1960 * '' Geleia orbis'' Fauré-Fremiet, 1951 * ''Geleia simplex'' Fauré-Fremiet, 1951 * ''Geleia swedmarki'' Dragesco * ''Geleia tenuis'' Dragesco, 1954 * ''Geleia vacuolata'' Dragesco, 1960 Phylogeny C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karyorelictea
Karyorelictea is a class of ciliates in the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora. Most species are members of the microbenthos community, that is, microscopic organisms found in the marine interstitial habitat, though one genus, ''Loxodes'', is found in freshwater. The majority of karyorelict taxa have not been cultivated in the laboratory, although clonal lines of ''Loxodes'' have been developed. Systematics According to Lynn (2008), the Karyorelictea class is divided into three orders: * Loxodida, containing the families Cryptopharyngidae and Loxodidae; * Protoheterotrichida, containing the families Aveliidae and Geleiidae; * Protostomatida, containing the families Kentrophoridae and Trachelocercidae. These three orders were defined morphologically, and have been confirmed with molecular phylogenetics. An additional family, Wilbertomorphidae, is of uncertain affiliation and has not been assigned to an order. Nuclear dimorphism All ciliates, including karyorelicteans, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
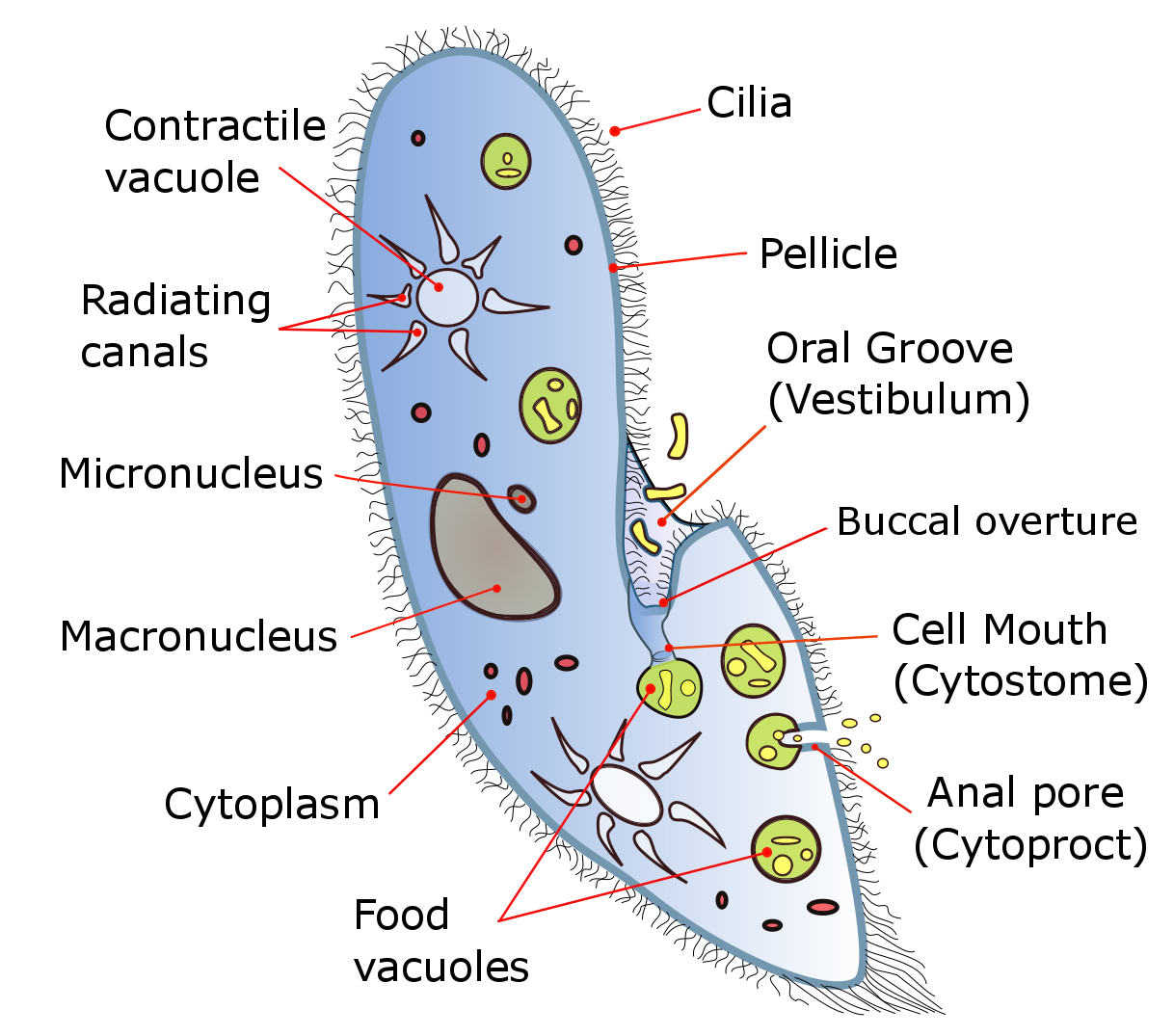
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative parasite, opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patronym (taxonomy)
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zoolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Analysis
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18S RRNA
18S may refer to: *18S ribosomal RNA *18S rRNA (adenine1779-N6/adenine1780-N6)-dimethyltransferase *18SEH The Family II is a straight-4 piston engine that was originally developed by Opel in the 1970s, debuting in 1979. Available in a wide range of cubic capacities ranging from 1598 to 2405 cc, it simultaneously replaced the Opel OHV, Opel CIH a ... See also * S18 (other) {{Letter-Number Combination Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliate Genera
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some obligate and opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species range in size from as little as 10 µm in some colpodeans to as much as 4 mm in length in some gel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |