|
Cork City F.C. Managers
Cork or CORK may refer to: Materials * Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product ** Cork (plug), a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container ***Wine cork Places Ireland * Cork (city) ** Metropolitan Cork, also known as Greater Cork ** Cork Airport * County Cork Historical parliamentary constituencies * Cork City (Parliament of Ireland constituency) * Cork County (Parliament of Ireland constituency) * Cork City (UK Parliament constituency) * Cork County (UK Parliament constituency) United States * Cork, Georgia * Cork, Kentucky Organisations * Cork GAA, responsible for Gaelic games in County Cork * Ye Antient Order of Noble Corks, a masonic order, also known as "The Cork" * Cork City F.C., a football club * Cork City W.F.C., a women's football club Other uses * A particular kind of trick in snowboarding and skiing. See List of snowboard tricks. * Cork (surname) * Cork City (barony) * Cork encoding, a digital data format * Cork taint, a wine fault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork (material)
Cork is an Permeability (earth sciences), impermeable buoyancy, buoyant material, the Cork cambium, phellem layer of bark (botany), bark tissue that is harvested for commercial use primarily from ''Quercus suber'' (the cork oak), which is native to southwest Europe and northwest Africa. Cork is composed of suberin, a hydrophobic substance. Because of its impermeable, buoyant, elastic, and fire retardant properties, it is used in a variety of products, the most common of which is wine stoppers. The Dehesa (pastoral management), montado landscape of Portugal produces approximately half of the cork harvested annually worldwide, with Corticeira Amorim being the leading company in the industry. Cork was examined microscopically by Robert Hooke, which led to his discovery and naming of the cell (biology), cell. Cork composition varies depending on Geography, geographic origin, climate and soil conditions, Genetics, genetic origin, tree dimensions, age (virgin or reproduction), and gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
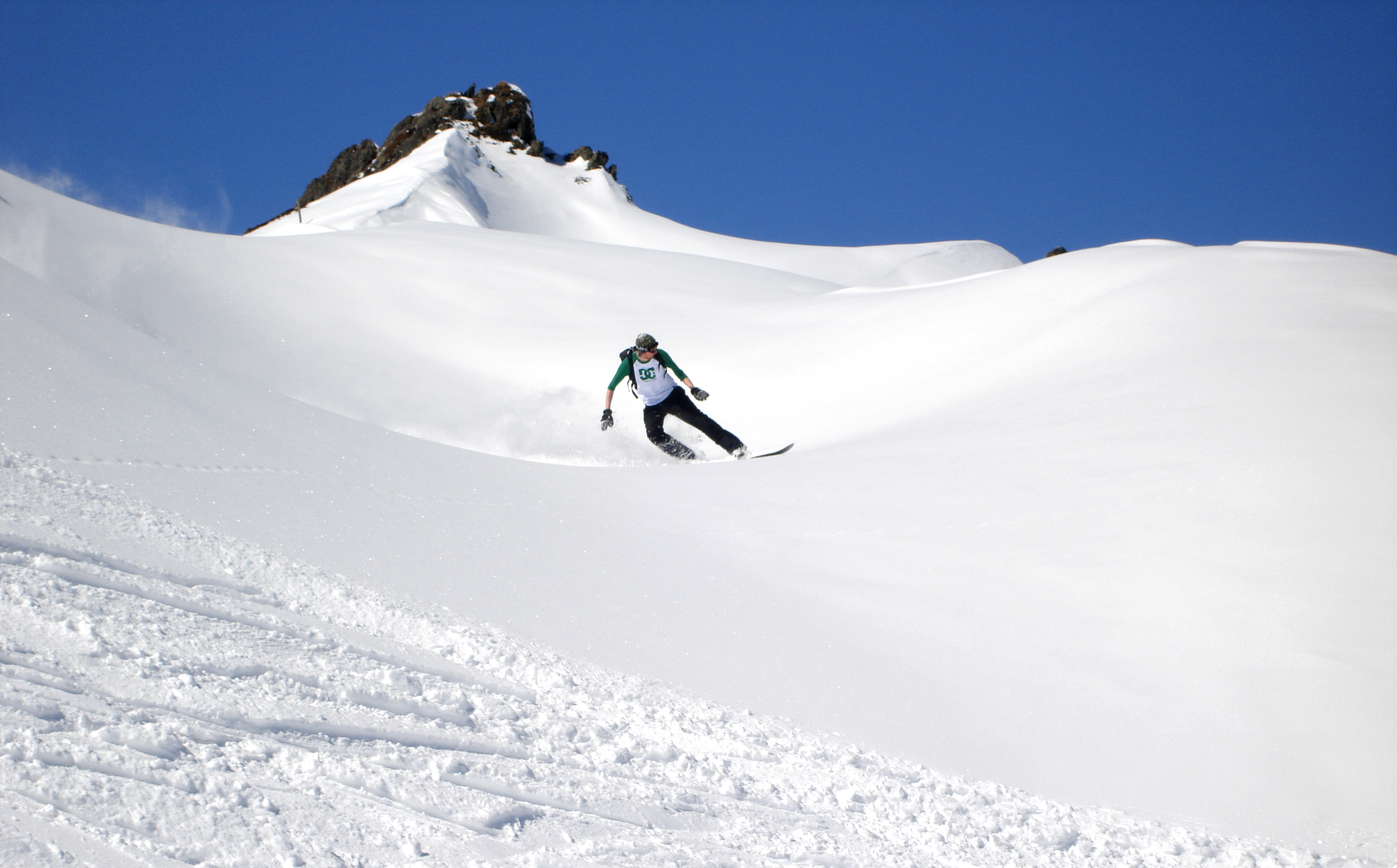
Snowboarding
Snowboarding is a recreational and competitive activity that involves descending a snow-covered surface while standing on a snowboard that is almost always attached to a rider's feet. It features in the Winter Olympic Games and Winter Paralympic Games. Snowboarding was developed in the United States, inspired by skateboarding, sledding, surfing, and skiing. It became popular around the globe, and was introduced as a Winter Olympic Sport at Nagano in 1998 and featured in the Winter Paralympics at Sochi in 2014. , its popularity (as measured by equipment sales) in the United States peaked in 2007 and has been in a decline since. History The first snowboards were developed in 1965 when Sherman Poppen, an engineer in Muskegon, Michigan, invented a toy for his daughters by fastening two skis together and attaching a rope to one end so he would have some control as they stood on the board and glided downhill. Dubbed the "snurfer" (combining snow and surfer) by his wife Nancy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Suber
''Quercus suber'', commonly called the cork oak, is a medium-sized, evergreen oak tree in the section ''Quercus'' sect. ''Cerris''. It is the primary source of cork for wine bottle stoppers and other uses, such as cork flooring and as the cores of cricket balls. It is native to southwest Europe and northwest Africa. In the Mediterranean basin the tree is an ancient species with fossil remnants dating back to the Tertiary period. It endures drought and makes little demand on the soil quality and is regarded as a defence against desertification. Cork oak forests are home to a multitude of animal and plant species. Since cork is increasingly being displaced by other materials as a bottle cap, these forests are at risk as part of the cultural landscape and animal species such as the Iberian lynx are threatened with extinction. Description General appearance and bark The cork oak grows as an evergreen tree, reaching an average height of or in rare cases up to 25 m and a tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork Tree (other) '', a 2005 album by Fall Out Boy
{{Plant common name ...
Cork tree or corktree may refer to: * Cork oak, ''Quercus suber'', the tree from which most cork is harvested * Chinese cork oak, ''Quercus variabilis'', a tree from which cork is occasionally harvested * Cork-tree, a species of ''Phellodendron'' *''Euonymus phellomanus'', a large deciduous shrub with corky “wings” * Indian cork tree, ''Millingtonia hortensis'' * ''From Under The Cork Tree ''From Under the Cork Tree'' is the second studio album by the American rock band Fall Out Boy, released on May 3, 2005, through Island Records as the band's major label debut. The music was composed by lead vocalist and guitarist Patrick Stump, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Cork And Ross
The Diocese of Cork and Ross ( ga, Deoise Chorcaí agus Rosa) is a Roman Catholic diocese in southern Ireland, one of six suffragan dioceses in the ecclesiastical province of Cashel and Emly. The cathedral church of the diocese is Cathedral of St Mary and St Anne in Cork city. The incumbent bishop of the diocese is Fintan Gavin. History Diocese of Cork (1111-1429) The original Diocese of Cork was established by the Synod of Ráth Breasail in 1111, but was reduced in size by the establishment of separate Dioceses of Cloyne and Ross at the Synod of Kells in 1152. Diocese of Cork and Cloyne (14291748) On petition of King Edward II, Pope John XXII issued a papal bull for the union of the Dioceses of Cork and Cloyne on 30 July 1326, with effect from the death of either bishop. The union should have taken effect on the death of Philip of Slane in 1327, but bishops were still appointed to both dioceses. The dioceses were eventually united on the episcopal appointment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
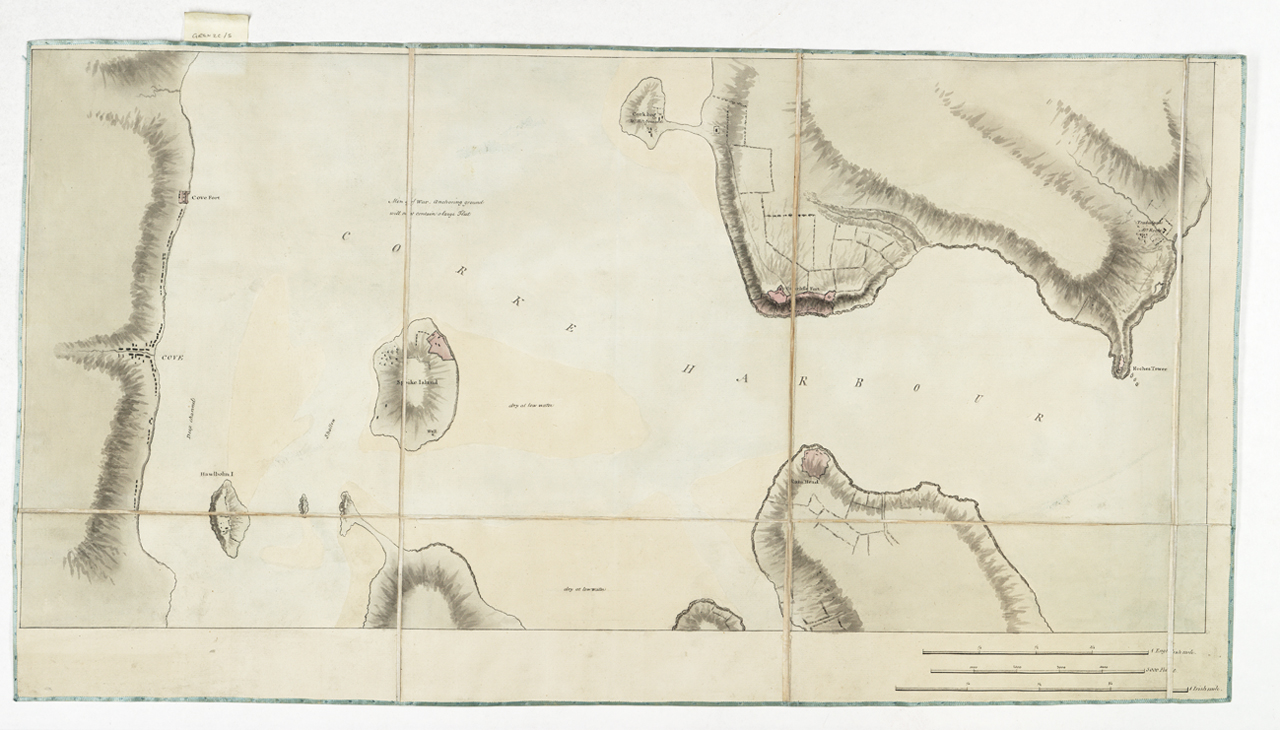
Cork Harbour
Cork Harbour () is a natural harbour and river estuary at the mouth of the River Lee in County Cork, Ireland. It is one of several which lay claim to the title of "second largest natural harbour in the world by navigational area" (after Port Jackson, Sydney). Other contenders include Halifax Harbour in Canada, Trincomalee Harbour in Sri Lanka and Poole Harbour in England. The harbour has been a working port and a strategic defensive hub for centuries, and it has been one of Ireland's major employment hubs since the early 1900s. Traditional heavy industries have waned since the late 20th century, with the likes of the closure of Irish Steel in Haulbowline and shipbuilding at Verolme. It still has strategic significance in energy generation, shipping, refining and pharmaceuticals development. Geography The main tributary to the harbour is the River Lee which, after flowing through Cork city, passes through the upper harbour (Lough Mahon) in the northwest before passing to the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork County Council
Cork County Council ( ga, Comhairle Contae Chorcaí) is the authority responsible for local government in County Cork, Ireland. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and development, amenity and culture, and environment. The council has 55 elected members. Elections are held every five years and are by single transferable vote. The head of the council has the title of Mayor. The county administration is headed by a Chief Executive, Tim Lucey. The county seat is Cork. History Originally meetings of Cork County Council were held in the back portion of the top floor of Cork Courthouse. By the 1950s these premises were becoming inadequate and County Hall opened in April 1968. Boundary change The area of Cork County Council was reduced on 31 May 2019, ceding territory to Cork City Council. This implemented changes under the Local Government Act 2019. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork (film)
''Cork'' ( ca, Suro, links=no) is a 2022 Spanish rural drama film directed by Mikel Gurrea which stars Vicky Luengo and Pol López alongside Ilyass El Ouahdani. It is shot in Catalan. Plot Set in rural Catalonia, the plot follows a couple (Elena and Iván) who moves from the city to the countryside to run an inherited cork plantation, involving as outsiders in the escalating tension between local and immigrant cork workers. Cast * Vicky Luengo as Elena * Pol López as Iván * Ilyass El Ouahdani as Karim Production Gurrea's debut feature, the project was developed at the San Sebastián's Ikusmira Berriak 2016 Residency, Sources2 and the Sam Spiegel Film Lab. The screenplay was penned by Gurrea alongside Francisco Kosterlitz. Laia Costa was originally a cast choice for one of the leads, but eventually Vicky Luengo was cast as the protagonist. The film was produced by Lastor Media alongside Malmo Pictures and Irusoin, with the participation of TV3, EiTB, and funding from IC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork (band)
Cork is a rock duo/supergroup consisting of Eric Schenkman (formerly of the Spin Doctors) and Corky Laing (formerly of Mountain). Though not an official member, the duo have worked closely with Noel Redding (formerly of The Jimi Hendrix Experience), who has both toured with and recorded with Cork. The group has released two albums, 1999's ''Speed of Thought'' and 2003's ''Out There''. Songs from the Cork albums ''Speed of Thought'' and ''Out There'' were used in the documentary film ''Liberty Village - Somewhere in Heaven''. Corky Laing is a resident of Toronto's Liberty Village Liberty Village is a neighbourhood in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is bordered to the north by King Street West, to the west by Dufferin Street, to the south by the Gardiner Expressway, to the east by Strachan Avenue, and to the northeast by the ... and was interviewed in the film. References * American rock music groups Rock music supergroups Rock music duos Musical groups established in 1997 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Olympic-training Regatta, Kingston
The Canadian Olympic-training Regatta, Kingston (CORK) is an annual multi-class sailing regatta held off the shores of Kingston, Ontario Kingston is a city in Ontario, Canada. It is located on the north-eastern end of Lake Ontario, at the beginning of the St. Lawrence River and at the mouth of the Cataraqui River (south end of the Rideau Canal). The city is midway between Toro ..., Canada. External linksCanadian Olympic Regatta Kingston ca. 1972, Archives of Ontario YouTube Channel Annual sporting events in Canada [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork Taint
Cork taint is a broad term referring to a wine fault characterized by a set of undesirable smells or tastes found in a bottle of wine, especially spoilage that can only be detected after bottling, aging and opening. Though modern studies have shown that other factors can also be responsible for taint – including wooden barrels, storage conditions and the transport of corks and wine – the cork stopper is normally considered to be responsible, and a wine found to be tainted on opening is said to be corked or "corky". Cork taint can affect wines irrespective of price and quality level. The chief cause of cork taint is the presence of the chemical compounds 2,4,6-trichloroanisole (TCA) or 2,4,6-tribromoanisole (TBA) in the wine, which in many cases will have been transferred from the cork, but which also can have been transferred through the cork rather than from it. TCA is a compound which does not occur naturally. It is created when some fungi are treated with chlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork Encoding
The Cork (also known as T1 or EC) encoding is a character encoding used for encoding glyphs in fonts. It is named after the city of Cork in Ireland, where during a TeX Users Group (TUG) conference in 1990 a new encoding was introduced for LaTeX. It contains 256 characters supporting most west and east-European languages with the Latin alphabet. Details In 8-bit TeX engines the font encoding has to match the encoding of hyphenation patterns where this encoding is most commonly used. In LaTeX one can switch to this encoding with \usepackage 1/code>, while in ConTeXt MkII this is the default encoding already. In modern engines such as XeTeX and LuaTeX Unicode is fully supported and the 8-bit font encodings are obsolete. Character set Notes * Hexadecimal values under the characters in the table are the Unicode character codes. * The first 12 characters are often used as combining characters. Supported languages The encoding supports most European languages written in Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |