|
Corippus
Flavius Cresconius Corippus (floruit 565) was a Roman African epic poet who flourished under East Roman emperors Justinian I and Justin II. His major works are the epic poem '' Iohannis'', a panegyric called "Panegyric of Anastasius", and a poem in praise of the Emperor Justin II, ''In laudem Iustini minoris''. Corippus was probably the last important Latin author of Late Antiquity. Biography Flavius Cresconius Corippus' name is known on a basis of just one document. He was a native of Africa, and in one of the medieval manuscripts is called ''africanus grammaticus''. He has sometimes been identified, but on insufficient grounds, with Cresconius Africanus, a Catholic bishop (7th century), author of a ''Concordia Canonum'', or collection of the laws of the church. Nothing is known of Corippus beyond what is contained in his own poems. He appears to have held the office of tribune or notary ('' scriniarius'') under Anastasius, imperial treasurer and chamberlain of Justinian I, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
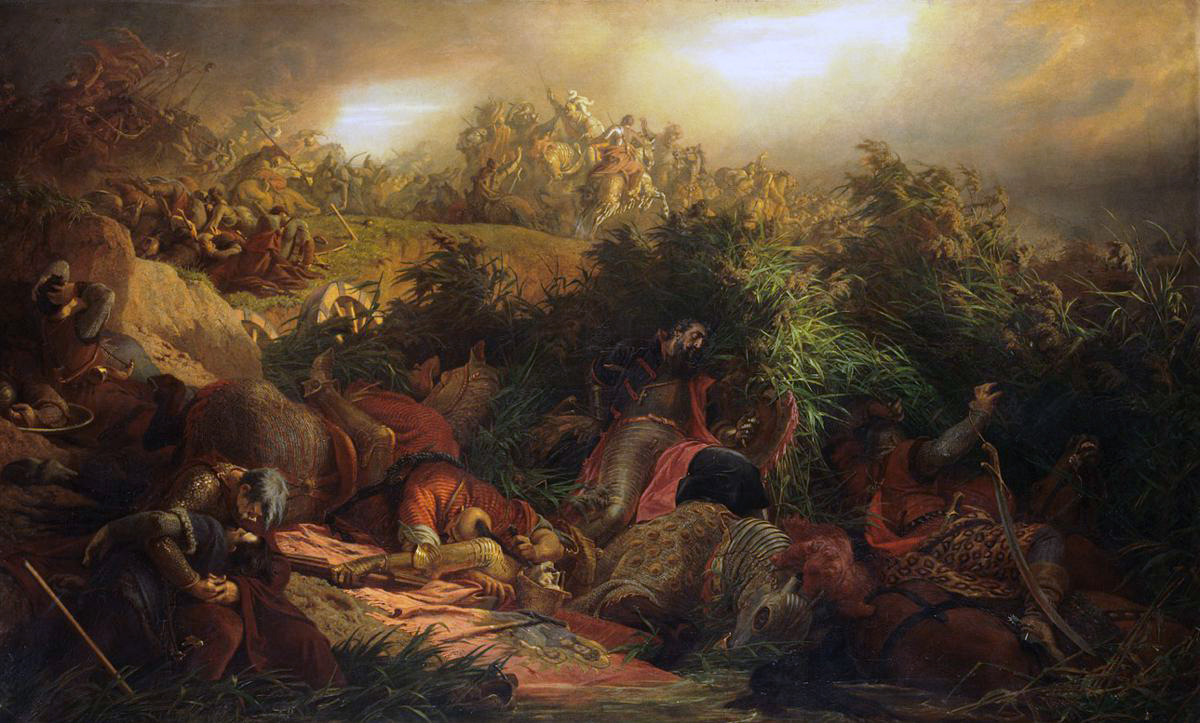
John Troglita
John Troglita (, ) was a 6th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine general. He participated in the Vandalic War and served in North Africa as a regional military governor during the years 533–538, before being sent east to the wars with the Sassanid Empire, Sassanid Persians. As ''dux Mesopotamiae'', Troglita distinguished himself in several battles, and was noticed by agents of the Byzantine emperor, Justinian I (reign, r. 527–565). In summer 546, Justinian chose John Troglita to assume overall command of Byzantine forces in Africa, where a succession of revolts by the indigenous Berbers, Moorish tribes and within the imperial army itself had seriously reduced the Byzantine position. Troglita quickly secured an initial victory in the winter of 546/547 against the Moors of Byzacena, but was defeated in summer 547 by the tribes of Tripolitania, and Africa was once again laid open to destructive raids. Troglita reorganized his army and secured the assistance of some tribal leaders, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justin II
Justin II (; ; died 5 October 578) was Eastern Roman emperor from 565 until 578. He was the nephew of Justinian I and the husband of Sophia, the niece of Justinian's wife Theodora. Justin II inherited a greatly enlarged but overextended empire, with far fewer resources at his disposal compared to Justinian I. He ended the payment of tributes and adopted a hardline stance against the empire's neighbors, which resulted in rekindling of war with the Sassanid Empire, and in a Lombard invasion which cost the Romans much of their territory in Italy. Family He was a son of Vigilantia and Dulcidio (sometimes rendered as Dulcissimus), respectively the sister and brother-in-law of Justinian. His siblings included Marcellus and Praejecta. With Sophia he had a daughter Arabia and possibly a son, Justus, who died young. He also had a niece named Helena. Early life Justin's early years are largely obscure. A thirteenth-century chronicle suggests 511 as Justin's birth date, but its re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
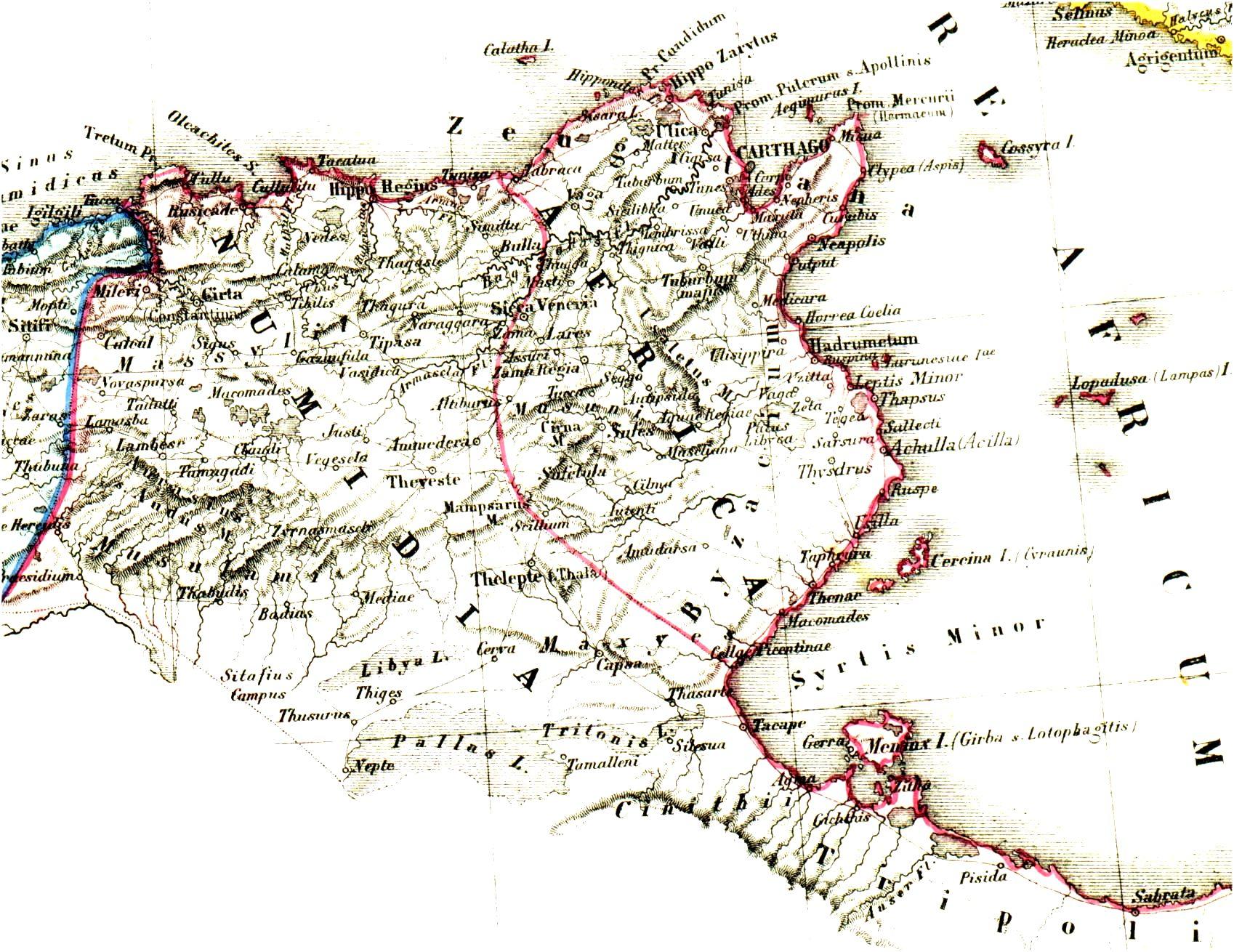
Vandalic War
The Vandalic War (533–534) was a conflict fought in North Africa between the forces of the Byzantine Empire (also known as the Eastern Roman Empire) and the Germanic Vandal Kingdom. It was the first war of Emperor Justinian I's , wherein the Byzantines attempted to reassert Roman sovereignty over territory formerly controlled by the Western Roman Empire. The Vandals occupied Roman North Africa in the early 5th century and established an independent kingdom there. Under their king, Geiseric, the Vandal navy carried out pirate attacks across the Mediterranean, Sack of Rome (455), sacked Rome in 455, and defeated a Roman invasion in 468. After Geiseric's death in 477, relations with the Eastern Roman Empire were normalized, although tensions flared up occasionally due to the Vandals' adherence to Arianism and their persecution of the Nicene native population. In 530, a palace coup happened in Carthage due to a defeat against the Moorish Chieftain and war chief of the Frexes trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cresconius Africanus
Cresconius Africanus (Crisconius) was a Latin canon lawyer, of uncertain date and place. He flourished, probably, in the latter half of the 7th century. He was probably a Christian bishop of the African Church. Concordia canonum Cresconius made a collection of canons, known as ''Concordia canonum'', inclusive of the Apostolic Canons, nearly all the canons of the fourth- and fifth-century councils, and many papal decretals from the end of the fourth to the end of the fifth century. It was much used as a handy manual of ecclesiastical legislation by the churches of Africa and Gaul as late as the tenth century. Few of its manuscripts postdate that period. The content is taken from the collection of Dionysius Exiguus, but the division into titles (301) is copied from the ''Breviatio canonum'' of Fulgentius Ferrandus, a sixth-century deacon of Carthage. In many manuscripts the text of Cresconius is preceded by an index or table of contents (''breviarium'') of the titles, first edited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565. His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was expressed by the partial recovery of the territories of the defunct Western Roman Empire. His general, Belisarius, swiftly conquered the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Subsequently, Belisarius, Narses, and other generals Gothic War (535–554), conquered the Ostrogothic Kingdom, restoring Dalmatia, Sicily, Italian peninsula, Italy, and Rome to the empire after more than half a century of rule by the Ostrogoths. The Liberius (praetorian prefect), praetorian prefect Liberius reclaimed the south of the Iberian Peninsula, establishing the province of Spania. These campaigns re-established Roman control over the western Mediterranean, increasing the Empire's annual revenue by over a million ''solidi''. During his reign, Justinian also subdued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodization has since been widely accepted. Late antiquity represents a cultural sphere that covered much of the Mediterranean world, including parts of Europe and the Near East.Brown, Peter (1971), ''The World of Late Antiquity (1971), The World of Late Antiquity, AD 150-750''Introduction Late antiquity was an era of massive political and religious transformation. It marked the origins or ascendance of the three major monotheistic religions: Christianity, rabbinic Judaism, and Islam. It also marked the ends of both the Western Roman Empire and the Sasanian Empire, the last Persian empire of antiquity, and the beginning of the early Muslim conquests, Arab conquests. Meanwhile, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine (Eastern Roman) Empire became a milit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magister Militum
(Latin for "master of soldiers"; : ) was a top-level military command used in the late Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, the emperor remaining the supreme commander) of the empire. The office continued to exist end evolve during the early Byzantine Empire. In Greek language, Greek sources, the term is translated either as ''strategos#Byzantine use, strategos'' or as ''stratelates'' (although these terms were also used non-technically to refer to commanders of different ranks). Establishment and development of the command The office of ''magister militum'' was created in the early 4th century, most likely when the Western Roman emperor Constantine the Great defeated all other contemporary Roman emperors, which gave him control over their respective armies. Because the Praetorian Guards and their leaders, the praetorian prefect, Praetorian Prefects, had suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexameter
Hexameter is a metrical line of verses consisting of six feet (a "foot" here is the pulse, or major accent, of words in an English line of poetry; in Greek as well as in Latin a "foot" is not an accent, but describes various combinations of syllables). It was the standard epic metre in classical Greek and Latin literature, such as in the ''Iliad'', '' Odyssey'' and ''Aeneid''. Its use in other genres of composition include Horace's satires, Ovid's '' Metamorphoses,'' and the Hymns of Orpheus. According to Greek mythology, hexameter was invented by Phemonoe, daughter of Apollo and the first Pythia of Delphi. __TOC__ Classical hexameter In classical hexameter, the six feet follow these rules: * A foot can be made up of two long syllables a spondee; or a long and two short syllables, a dactyl * The first four feet can contain either one of them. * The fifth is almost always a dactyl, and last must be a spondee / trochee (together forming an adonic). Exceptions can o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Cuspinianus
Johannes Cuspinianus (December 1473 – 19 April 1529), born Johan Spießhaymer (or Speißheimer), was a German-Austrian humanist, scientist, diplomat, and historian. Born in Spießheim near Schweinfurt in Franconia, of which ''Cuspinianus'' is a Latinization, he studied in Leipzig and Würzburg. He went to Vienna in 1492 and became a professor of medicine at the University of Vienna. He became Rector of the university in 1500 and also served as Royal Superintendent until his death. A leading scholar, he was the author of ''De Caesaribus et Imperatoribus'' and was also given a poet's laurel wreath by Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor. He was part of an intellectual circle that included Joachim Vadianus and Stiborius. He rendered important service as the discoverer and editor of classical and medieval historical texts. His unfinished ''Austria'' (1527-8) was an important historical-geographical regional survey of Lower Austria. Early life In 1490 he matriculated at the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buda
Buda (, ) is the part of Budapest, the capital city of Hungary, that lies on the western bank of the Danube. Historically, “Buda” referred only to the royal walled city on Castle Hill (), which was constructed by Béla IV between 1247 and 1249 and subsequently served as the capital of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1361 to 1873. In 1873, Buda was administratively unified with Pest, Hungary, Pest and Óbuda to form modern Budapest. Royal Buda is called the ''Castle Quarter (Budapest), Várnegyed'' () today, while “Buda” ''pars pro toto'' denotes Budapest’s I., II., III., XI., XII. and XXII. districts. This colloquial definition thus includes medieval Óbuda and amounts to a third of the city’s total area, much of it forested. Buda's landmarks include the Royal Palace (Budapest), Royal Palace, Matthias Church, the Citadella, Gellért Baths, the Buda Hills, the Carmelite Monastery of Buda, and the residence of the President of Hungary, Sándor Palace. Etymology Accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suleiman The Magnificent
Suleiman I (; , ; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the Western world and as Suleiman the Lawgiver () in his own realm, was the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sultan between 1520 and his death in 1566. Under his administration, the Ottoman Empire ruled over at least 25 million people. After succeeding his father Selim I on 30 September 1520, Suleiman began his reign by launching military campaigns against the Christendom, Christian powers of Central and Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean; Siege of Belgrade (1521), Belgrade fell to him in 1521 and Siege of Rhodes (1522), Rhodes in 1522–1523, and at Battle of Mohács, Mohács in 1526, Suleiman broke the strength of the Kingdom of Hungary in the Middle Ages, Kingdom of Hungary. Presiding over the apex of the Ottoman Empire's economic, military, and political strength, Suleiman rose to become a prominent monarch of 16th-century Europe, as he personally led Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |