|
Coriolopsis Gallica
''Coriolopsis gallica'' is a fungus found growing on decaying wood. It is not associated with any plant disease, therefore it is not considered pathogenic. For various ''Coriolopsis gallica'' strains isolated, it has been found, as a common feature of the division ''Basidiomycota'', that they are able to degrade wood components, mainly lignin and to lesser extent cellulose, which results in a degradation area covered by the accumulating -white- cellulose powder. Therefore, ''C. gallica'' might generically be called, as with many other basidiomycetes, a "white-rot" fungus. This feature of preferential degradation of lignin components, such as melanoidins, polyphenols, and other aromatic compounds is of biotechnological interest in the industries of paper (recycling and bleaching), beer and sugar cane production and for the bioremediation of waste waters produced in these and other industrial activities. While in Basidiomycota, the lignolytic activities are jointly played by enzymes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanoidin
Melanoidins are brown, high molecular weight heterogeneous polymers that are formed when sugars and amino acids combine (through the Maillard Reaction) at high temperatures and low water activity. They were discovered by Schmiedeberg in 1897. Melanoidins are commonly present in foods that have undergone some form of non-enzymatic browning, such as barley malts (Vienna and Munich), bread crust, bakery products and coffee. They are also present in the wastewater of sugar refineries, necessitating treatment in order to avoid contamination around the outflow of these refineries. The polymers make the constituting dietary sugars and fats unavailable to the normal carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Dietary melanoidins themselves produce various effects in the organism: they decrease Phase I liver enzyme activity and promote glycation in vivo, which may contribute to diabetes, reduced vascular compliance and Alzheimer's disease. Some of the melanoidins are metabolized by the intestinal micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phanerochaete
''Phanerochaete'' is a genus of crust fungi in the family Phanerochaetaceae. Taxonomy The genus was circumscribed by Finnish mycologist Petter Karsten in 1889. Marinus Anton Donk redefined the limits of the genus in two publications in 1957 and 1962. ''Phanerochaete'' has traditionally been delimited based on the overall morphology of the fruit body, as well as microscopic characteristics including the nature of the hyphal structure, cystidia, and spores. Molecular analyses demonstrate that the genus is polyphyletic, containing members placed throughout the phlebioid clade of the Polyporales. The genus name is derived from the Greek words φανεφός ("distinct") and χαίτη ("hair"). Description ''Phanerochaete'' species have membranaceous, crust-like fruit bodies. The hyphal system is monomitic, with simple-septate generative hyphae; single or multiple clamps may be present in the subiculum. The basidia (spore-bearing cells) are club-shaped and smooth. Spores of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trametes
''Trametes'' is a genus of fungi that is distinguished by a pileate basidiocarp, di- to trimitic hyphal systems, smooth non-dextrinoid spores, and a hymenium usually without true hymenial cystidia.Ryvarden L. (1991). "Genera of polypores: Nomenclature and taxonomy." ''Syn. Fung.'' 5: 1–363. The genus has a widespread distribution and contains about fifty species. The genus was circumscribed by Elias Magnus Fries in 1836. ''Trametes'' fungi are food for caterpillars of certain Lepidoptera, mainly fungus moths (Tineidae) such as ''Triaxomera parasitella''. Biotechnology Several species of ''Trametes'' have been investigated for biotechnological application of their lignin-degrading enzymes (particularly laccase and manganese peroxidase) for analytical, industrial or environmental sciences. Selected species *''Trametes gibbosa'' – Lumpy bracket *''Trametes hirsuta'' – Hairy bracket *''Trametes nivosa'' *''Trametes pubescens'' *''Trametes versicolor ''Trametes versicol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignin Peroxidase
In enzymology, a lignin peroxidase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :1,2-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diol + H2O2 \rightleftharpoons 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde + 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethane-1,2-diol + H2O Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 1,2-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diol and H2O2, whereas its 3 products are 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethane-1,2-diol, and H2O. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on a peroxide as acceptor (peroxidases) and can be included in the broad category of ligninases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 1,2-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diol:hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include diarylpropane oxygenase, ligninase I, diarylpropane peroxidase, LiP, diarylpropane:oxygen,hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase (C-C-bond-cleaving). It employs one cofactor, heme. Background Lignin is highly resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese Peroxidase
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese was first isolated in 1774. It is familiar in the laboratory in the form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laccase
Laccases () are multicopper oxidases found in plants, fungi, and bacteria. Laccases oxidize a variety of phenolic substrates, performing one-electron oxidations, leading to crosslinking. For example, laccases play a role in the formation of lignin by promoting the oxidative coupling of monolignols, a family of naturally occurring phenols. Other laccases, such as those produced by the fungus ''Pleurotus ostreatus'', play a role in the degradation of lignin, and can therefore be classed as lignin-modifying enzymes. Other laccases produced by fungi can facilitate the biosynthesis of melanin pigments. Laccases catalyze ring cleavage of aromatic compounds. Laccase was first studied by Hikorokuro Yoshida in 1883 and then by Gabriel Bertrand in 1894 in the sap of the Japanese lacquer tree, where it helps to form lacquer, hence the name laccase. Active site The active site consists of four copper centers, which adopt structures classified as type I, type II, and type III. A tric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
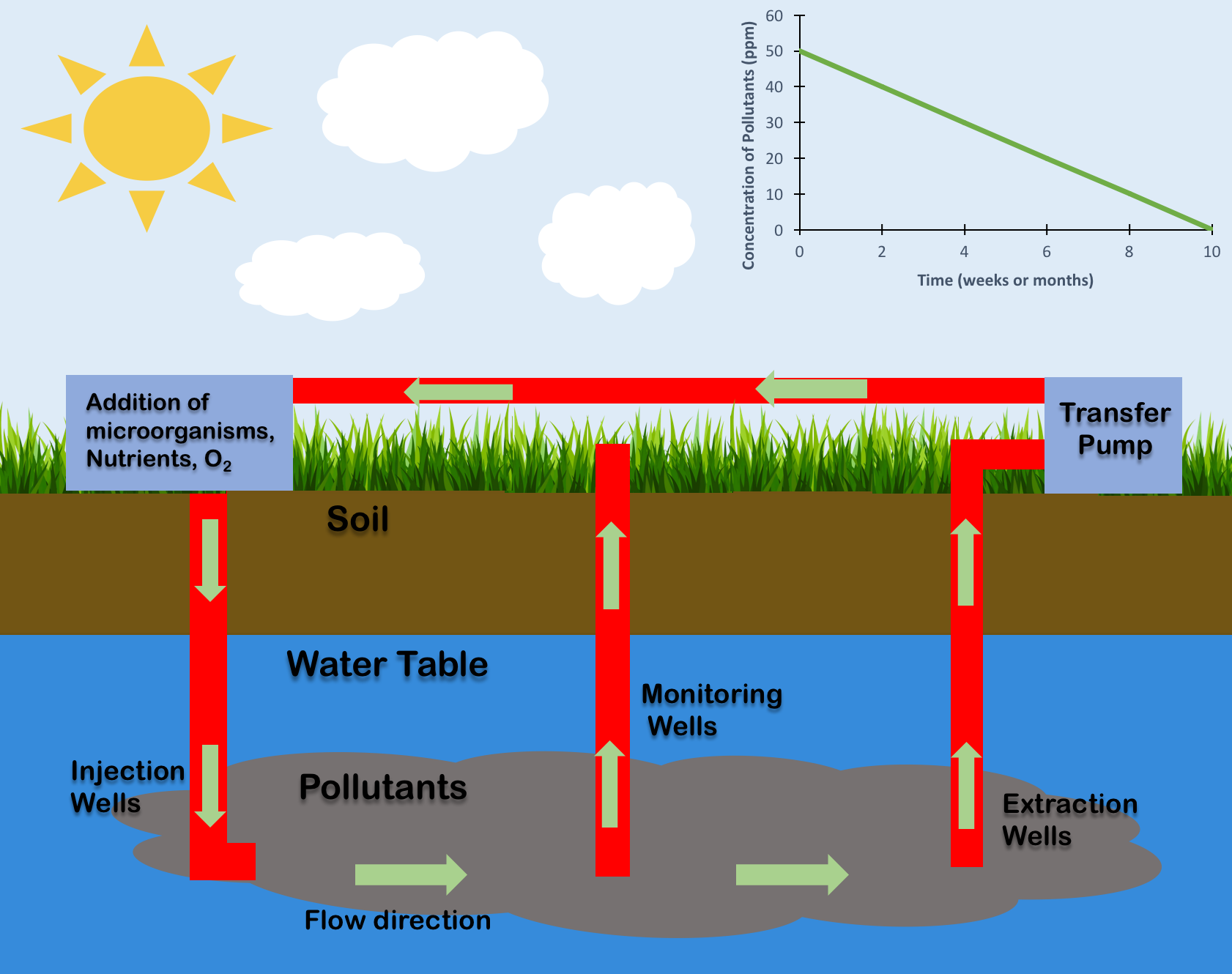
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer considerable advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote the growth. In principle, bioremediation could be used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphenol
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments. Etymology The name derives from the Ancient Greek word (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and the word phenol which refers to a chemical structure formed by attaching to an aromatic benzenoid (phenyl) ring to a hydroxyl (-OH) group as is found in alcohols (hence the ''-ol'' suffix). The term polyphenol has been in use at least since 1894. Definition The term polyphenol is not well-defined, but is generally agreed that they are natural products "having a polyphenol structure (i.e., several hydroxyl groups on aromatic rings)" including four principal classes: "phenolic acids, flavonoids, stilbenes, and lignans". *Flavonoids include flavones, flavonols, flavanols, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fiber is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%. Cellulose is mainly used to produce paperboard and paper. Smaller quantities are converted into a wide variety of derivative products such as cellophane and rayon. Conversion of cellulose from energy crops into biofuels such as cellulosic ethanol is under development as a renewable fuel source. Cellulose for industrial use is mainly obtained from wood pulp and cotton. Some animals, particularly ruminants and termites, can digest cellulose with the help of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and ''Cryptococcus'', the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycota-yeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four). These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually (discussed below) can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance “lignine”, which is derived from the Latin word '' lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose. Lignin constitutes 30% of non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 35% of the dry mass of wood. Lignin is present in red algae, which suggest that the common ancestor of plants and red algae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)