|
Cordova, AK
Cordova ( ) is a city in Chugach Census Area, Alaska, United States. It lies near the mouth of the Copper River, at the head of Orca Inlet on the east side of Prince William Sound. The population was 2,609 at the 2020 census, up from 2,239 in 2010. Cordova was named ''Puerto Córdoba'' (after Córdoba, Spain) by Spanish explorer Salvador Fidalgo in 1790. No roads connect Cordova to other Alaskan communities, so a plane or ferry is required to travel there. In the Exxon Valdez oil spill of March 1989, an oil tanker ran aground northwest of Cordova, heavily damaging ecology and fishing. It was cleaned up shortly after, but there are lingering effects, such as a lowered population of some birds. History In 1790 the inlet in front of the current Cordova townsite was named Puerto Cordova by Spanish explorer Salvador Fidalgo, after Spanish admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova. The city of Cordova was named after it, although the inlet itself was later renamed the Orca Inlet. Cordo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City (Alaska)
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Central Alaskan Yup'ik language, Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a U.S. state, state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A enclave and exclave, semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a Maritime boundary, maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi Sea, Chukchi and Beaufort Sea, Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the list of U.S. states and territories by area, largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the list of country subdivisions by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Time Zone
The Alaska Time Zone observes standard time by subtracting nine hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC−09:00). During daylight saving time its time offset is eight hours (UTC−08:00). The clock time in this zone is based on mean solar time at the 135th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory. The zone includes nearly all of the U.S. state of Alaska and is one hour behind the Pacific Time Zone. *standard time: Alaska Standard Time (AKST) *daylight saving time: Alaska Daylight Time (AKDT) The western Aleutian Islands observe Hawaii–Aleutian Time Zone, Hawaii–Aleutian Time, one hour behind the remainder of the state. The largest city in the Alaskan Time Zone is Anchorage, Alaska. The Anchorage Metropolitan Area is the largest metropolitan area in the zone. Effective from 2007, the local time changes from AKST to AKDT at 02:00 LST to 03:00 LDT on the second Sunday in March and returns at 02:00 LDT to 01:00 LST on the first Sunday in November. History Two time zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
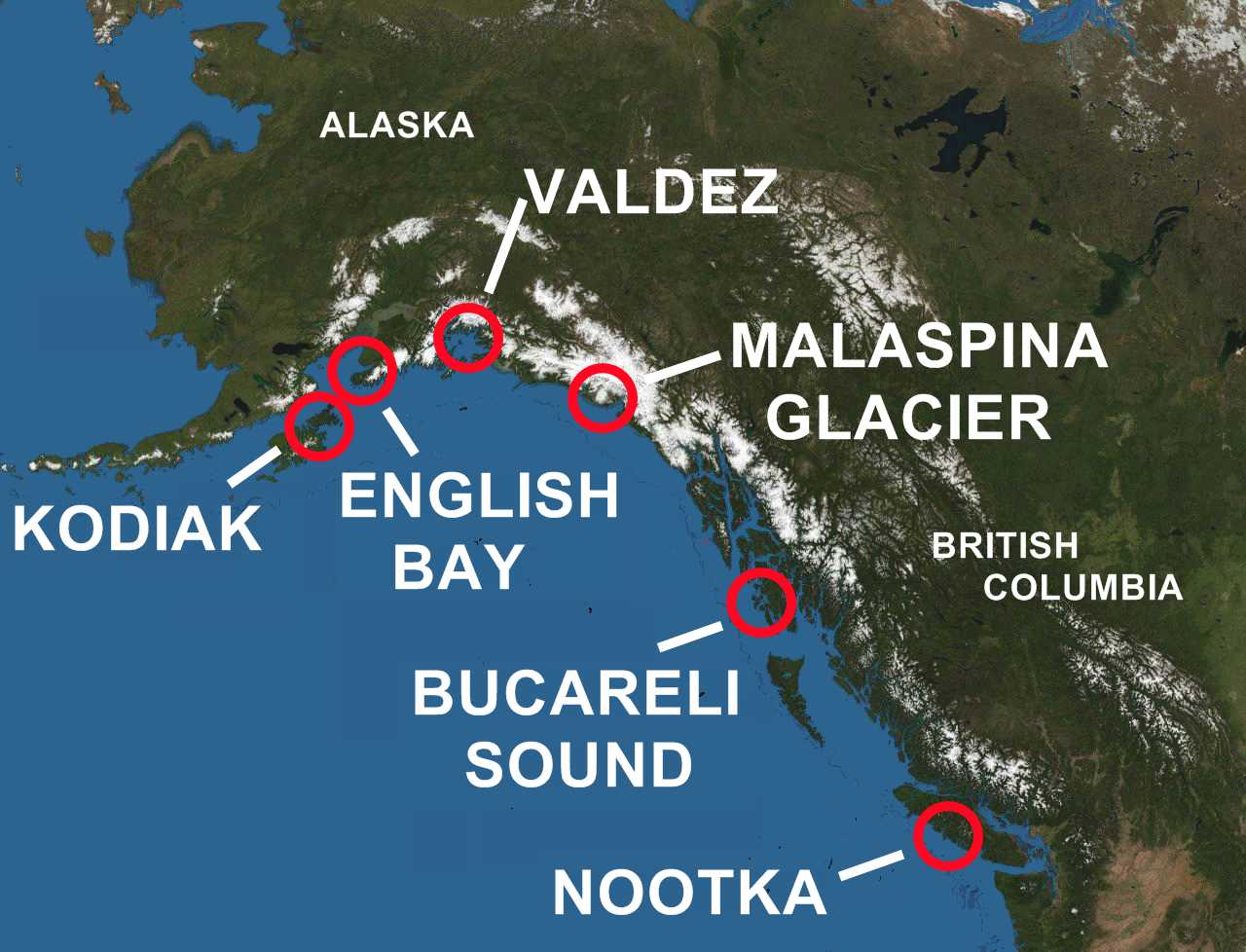
Exxon Valdez Oil Spill
The ''Exxon Valdez'' oil spill occurred in Prince William Sound, Alaska, on March 24, 1989. ''Exxon Valdez'', an oil supertanker owned by Exxon Shipping Company bound for Long Beach, California struck Prince William Sound's Bligh Reef, west of Tatitlek, Alaska at 12:04 a.m. and spilled (or 37,000 tonnes) of crude oil over the next few days. The ''Exxon Valdez'' spill is the second largest in U.S. waters, after the 2010 ''Deepwater Horizon'' oil spill, in terms of volume of oil released. Prince William Sound's remote location, accessible only by helicopter, plane, or boat, made government and industry response efforts difficult and made existing response plans especially hard to implement. The region is a habitat for salmon, sea otters, seals, and seabirds. The oil, extracted from the Prudhoe Bay Oil Field, eventually affected of coastline, of which were heavily or moderately oiled. Spill ''Exxon Valdez'' was carrying of oil, of which approximately were spilled int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salvador Fidalgo
Salvador Fidalgo y Lopegarcía (6 August 1756 – 27 September 1803) was a Spanish explorer. He commanded an exploring expedition for Spain to Alaska and the Pacific Northwest during the late 18th century. Early career Fidalgo was born in La Seu d'Urgell in the province of Lérida, in the region of Catalonia, Spain, the heir of a noble Navarrese family. He entered joined the Spanish Navy as a guardiamarina (midshipman) at the Real Colegio de Guardiamarinas in Cádiz. He graduated in 1775 and given the rank of Alférez de Fragata (Frigate Ensign). He was chosen to be a member of Vicente Tofiño's team of cartographers working during the 1780s on the first atlas of Spain's ports and coastal waters. He served on various assignments in the Mediterranean and saw action against the British and Portuguese. In 1778 he was promoted to Teniente de Navío (Lieutenant) and assigned to the Spanish naval station at San Blas, Mexico. online aGoogle Books/ref> Spain and the Pacific Northwest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Córdoba, Spain
Córdoba (; ),, Arabic: قُرطبة DIN 31635, DIN: . or Cordova () in English, is a city in Andalusia, Spain, and the capital of the Province of Córdoba (Spain), province of Córdoba. It is the third most populated Municipalities in Spain, municipality in Andalusia and the 11th overall in the country. The city primarily lies on the right bank of the Guadalquivir, in the south of the Iberian Peninsula. Once a Roman settlement, it was taken over by the Visigothic Kingdom, Visigoths, followed by the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, Muslim conquests in the eighth century and later becoming the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba. During these Islamic Golden Age, Muslim periods, Córdoba was transformed into a world leading center of education and learning, producing figures such as Maimonides, Averroes, Ibn Hazm, and Al-Zahrawi, and by the 10th century it had grown to be the second-largest city in Europe. Following the Siege of Córdoba (1236), Christian conquest in 1236, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2020 United States Census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to offer options to respond online or by phone, in addition to the paper response form used for previous censuses. The census was taken during the COVID-19 pandemic, which affected its administration. The census recorded a resident population of 331,449,281 in the fifty states and the District of Columbia, an increase of 7.4 percent, or 22,703,743, over the preceding decade. The growth rate was the second-lowest ever recorded, and the net increase was the sixth highest in history. This was the first census where the ten most populous states each surpassed 10 million residents as well as the first census where the ten most populous cities each surpassed 1 million residents. Background As required by the United States Constitution, the U.S. cens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince William Sound
Prince William Sound (Sugpiaq: ''Suungaaciq'') is a sound of the Gulf of Alaska on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the east side of the Kenai Peninsula. Its largest port is Valdez, at the southern terminus of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System. Other settlements on the sound, which contains numerous small islands, include Cordova and Whittier plus the Alaska native villages of Chenega and Tatitlek. History James Cook entered Prince William Sound in 1778 and initially named it Sandwich Sound, after his patron the Earl of Sandwich. Later that year, the Sound was named to honour George III's third son Prince William Henry, then aged 13 and serving as a midshipman in the Royal Navy. In 1790, the Spanish explorer Salvador Fidalgo entered the sound, naming many of its features. Some places in the sound still bear the names given by Fidalgo, as Port Valdez, Port Gravina or Cordova. The explorer landed on the actual site of Cordova and took possession of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orca Inlet
Orca Inlet is an arm of Prince William Sound in southern Alaska. The town of Cordova was founded on its coast in 1906. All marine traffic reaches the town through Orca Inlet. Geography Orca Inlet lies south and east of Hawkins Island at . The Inlet is about long running southwest and about wide at its widest point. The south end opens into the Gulf of Alaska while the north end joins with Orca Bay. The city of Cordova, Alaska is situated on the southeast shore of Orca Inlet. History Orca Inlet was listed in the Geographic Dictionary of Alaska in 1906, citing J.F. Moser's report from 1897. The Orca Cannery operated on the south shore of the inlet; there was a post office at that location from 1894. The Odiak Cannery was located 3 miles (4.8 km) southwest of Orca, at the present location of Cordova. There were once large Pacific razor clam beds in the intertidal zones of Orca Inlet which were harvested and shipped out of Cordova. Harvests reached 3.5 million pounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper River (Alaska)
The Copper River or Ahtna River (), Ahtna Athabascan ‘Atna’tuu (), "river of the Ahtnas", Tlingit Eeḵhéeni (), "river of copper", is a 290-mile (470 km) river in south-central Alaska in the United States. It drains a large region of the Wrangell Mountains and Chugach Mountains into the Gulf of Alaska. It is known for its extensive delta ecosystem, as well as for its prolific runs of wild salmon, which are among the most highly prized stocks in the world. The river is the tenth largest in the United States, as ranked by average discharge volume at its mouth. Description The Copper River rises out of the Copper Glacier, which lies on the northeast side of Mount Wrangell, in the Wrangell Mountains, within Wrangell-Saint Elias National Park. It begins by flowing almost due north in a valley that lies on the east side of Mount Sanford, and then turns west, forming the northwest edge of the Wrangell Mountains and separating them from the Mentasta Mountains to the northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valdez–Cordova Census Area, Alaska
Valdez–Cordova Census Area was a census area located in the state of Alaska, United States. As of the 2010 census, the population was 9,636. It was part of the Unorganized Borough and therefore has no borough seat. On January 2, 2019, it was abolished and replaced by the Chugach Census Area and the Copper River Census Area. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the census area has a total area of , of which is land and (15.1%) is water. Adjacent boroughs and census areas * Southeast Fairbanks Census Area, Alaska – north * Yakutat City and Borough, Alaska – southeast * Kenai Peninsula Borough, Alaska – west * Municipality of Anchorage, Alaska – west * Matanuska-Susitna Borough, Alaska – west * Yukon Territory, Canada – east National protected areas * Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge (part of Gulf of Alaska unit) ** Middleton Island * Chugach National Forest (part) * Tetlin National Wildlife Refuge (part) * Wrangell-St. Elias National Park ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Names Information System
The Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) is a database of name and locative information about more than two million physical and cultural features throughout the United States and its territories, Antarctica, and the associated states of the Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, and Palau. It is a type of gazetteer. It was developed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) in cooperation with the United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) to promote the standardization of feature names. Data were collected in two phases. Although a third phase was considered, which would have handled name changes where local usages differed from maps, it was never begun. The database is part of a system that includes topographic map names and bibliographic references. The names of books and historic maps that confirm the feature or place name are cited. Variant names, alternatives to official federal names for a feature, are also recorded. Each feature receives a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |