Copper River (Alaska) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
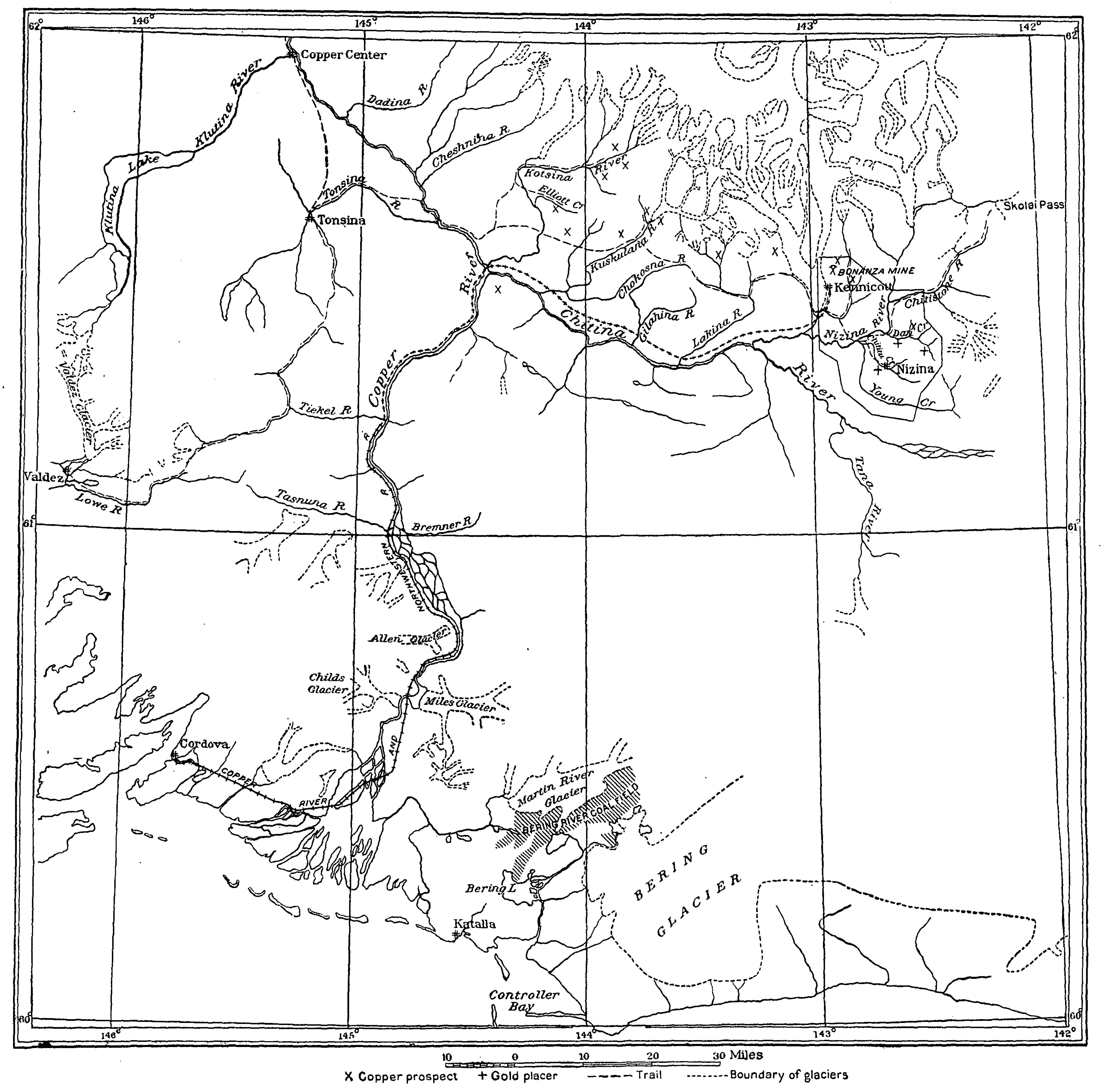 The Copper River or Ahtna River (), Ahtna Athabascan ‘Atna’tuu (), "river of the Ahtnas",
The Copper River or Ahtna River (), Ahtna Athabascan ‘Atna’tuu (), "river of the Ahtnas",
Tlingit
The Tlingit ( or ; also spelled Tlinkit) are indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America. Their language is the Tlingit language (natively , pronounced ),
Eeḵhéeni (), "river of copper", is a 290-mile (470 km) river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
in south-central Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
in the United States. It drains a large region of the Wrangell Mountains
The Wrangell Mountains are a high mountain range of eastern Alaska in the United States. Much of the range is included in Wrangell-Saint Elias National Park and Preserve. The Wrangell Mountains are almost entirely volcanic in origin, and they i ...
and Chugach Mountains
The Chugach Mountains of southern Alaska are the northernmost of the several mountain ranges that make up the Pacific Coast Ranges of the western edge of North America. The range is about long and wide, and extends from the Knik and Turnagain ...
into the Gulf of Alaska
The Gulf of Alaska (Tlingit: ''Yéil T'ooch’'') is an arm of the Pacific Ocean defined by the curve of the southern coast of Alaska, stretching from the Alaska Peninsula and Kodiak Island in the west to the Alexander Archipelago in the east, ...
. It is known for its extensive delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), a letter of the Greek alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* D ( NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta")
* Delta Air Lines, US
* Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19
Delta may also ...
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
, as well as for its prolific runs of wild salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
, which are among the most highly prized stocks in the world. The river is the tenth largest in the United States, as ranked by average discharge volume at its mouth.
Description
The Copper River rises out of the Copper Glacier, which lies on the northeast side ofMount Wrangell
Mount Wrangell, in Ahtna K’ełt’aeni or K’ełedi when erupting, is a massive shield volcano located in Wrangell-St. Elias National Park and Preserve in southeastern Alaska, United States. The shield rises over above the Copper River to it ...
, in the Wrangell Mountains
The Wrangell Mountains are a high mountain range of eastern Alaska in the United States. Much of the range is included in Wrangell-Saint Elias National Park and Preserve. The Wrangell Mountains are almost entirely volcanic in origin, and they i ...
, within Wrangell-Saint Elias National Park. It begins by flowing almost due north in a valley that lies on the east side of Mount Sanford, and then turns west, forming the northwest edge of the Wrangell Mountains and separating them from the Mentasta Mountains
The Mentasta Mountains in the eastern part of the U.S. state of Alaska form the eastern end of the Alaska Range.
They lie south of the Alaska Highway, east of the Glenn Highway, north of the Wrangell Mountains, and west of the Nabesna River. Acro ...
to the northeast. It continues to turn southeast, through a wide marshy plain to Chitina, where it is joined from the southeast by the Chitina River
The Chitina River ( Ahtna Athabascan Tsedi Na’ < ''tsedi'' "" + ''na’'' " ( Ahtna Athabascan Tsedi Na' < ''tsedi'' "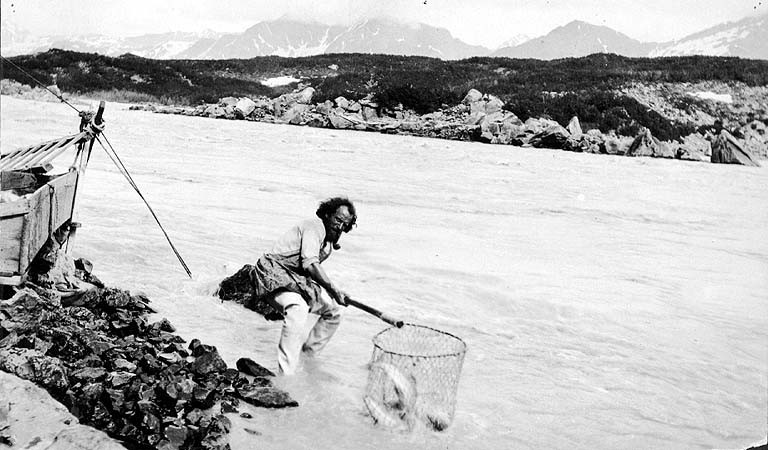 The Copper River is approximately long. It drops an average of about , and drains more than —an area the size of West Virginia. The river runs at an average of .
Downstream from its confluence with the Chitina it flows southwest, passing through a narrow glacier-lined gap in the
The Copper River is approximately long. It drops an average of about , and drains more than —an area the size of West Virginia. The river runs at an average of .
Downstream from its confluence with the Chitina it flows southwest, passing through a narrow glacier-lined gap in the
 The river's famous salmon runs arise from the use of the river watershed by over 2 million salmon each year for spawning. The extensive runs result in many unique varieties, prized for their fat content. The river's commercial salmon season is very brief, beginning in May for
The river's famous salmon runs arise from the use of the river watershed by over 2 million salmon each year for spawning. The extensive runs result in many unique varieties, prized for their fat content. The river's commercial salmon season is very brief, beginning in May for
File:Miles Glacier Bridge, damage and kludge, 1984.jpg, Miles Glacier Bridge, showing earthquake damage and temporary repair, 1984
File:Copper River Alaska with river rafters.jpg, Rafters and Child's Glacier on the lower Copper River
File:Copper River fishwheels.jpg, Fishwheels on the Copper River
Image:Copper2.jpg, Sand dunes on the Copper River
File:Copper River near Chitina.jpg, Copper River near Chitina, looking south from the bridge
Image:Picea mariana taiga.jpg,
''Geomorphology of the Lower Copper River, Alaska''
.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1581 Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey.
Ecotrust Copper River ProgramCopper River salmon habitat management study
Prepared for Ecotrust by Marie E. Lowe of the Institute of Social and Economic Research, hosted by Alaska State Publications Program
Alaska Department of Fish and Game: Copper River SalmonEyak Preservation CouncilNVE Fisheries Research and Seasonal Employment on the Copper RiverCordova District Fishermen UnitedWrangell-St. Elias National Park information
{{Authority control Ahtna Rivers of Alaska Rivers of Chugach Census Area, Alaska Rivers of Copper River Census Area, Alaska Rivers of Unorganized Borough, Alaska
copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
" + ''na’'' "river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
").
 The Copper River is approximately long. It drops an average of about , and drains more than —an area the size of West Virginia. The river runs at an average of .
Downstream from its confluence with the Chitina it flows southwest, passing through a narrow glacier-lined gap in the
The Copper River is approximately long. It drops an average of about , and drains more than —an area the size of West Virginia. The river runs at an average of .
Downstream from its confluence with the Chitina it flows southwest, passing through a narrow glacier-lined gap in the Chugach Mountains
The Chugach Mountains of southern Alaska are the northernmost of the several mountain ranges that make up the Pacific Coast Ranges of the western edge of North America. The range is about long and wide, and extends from the Knik and Turnagain ...
within the Chugach National Forest east of Cordova Peak. There is an extensive area of linear sand dunes up to in height radiating from the mouth of the Copper River. Both Miles Glacier
Miles Glacier is a -long glacier in the U.S. state of Alaska. It flows west to its terminus at Miles Lake, north of Katalla. It was named in 1885 after U.S. Army Maj. Gen. Nelson A. Miles
Nelson Appleton Miles (August 8, 1839 – May 15, 1925 ...
and Childs Glacier calve directly into the river. The Copper enters the Gulf of Alaska
The Gulf of Alaska (Tlingit: ''Yéil T'ooch’'') is an arm of the Pacific Ocean defined by the curve of the southern coast of Alaska, stretching from the Alaska Peninsula and Kodiak Island in the west to the Alexander Archipelago in the east, ...
southeast of Cordova where it creates a delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), a letter of the Greek alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* D ( NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta")
* Delta Air Lines, US
* Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19
Delta may also ...
nearly wide.
History
The name of the river comes from the abundantcopper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
deposits along the upper river that were used by Alaska Native
Alaska Natives (also known as Alaskan Natives, Native Alaskans, Indigenous Alaskans, Aboriginal Alaskans or First Alaskans) are the indigenous peoples of Alaska and include Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and a numbe ...
population and then later by settlers from the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
and the United States. Extraction of the copper resources was problematic due to navigation difficulties at the river's mouth. The construction of the Copper River and Northwestern Railway
The Copper River and Northwestern Railway (CR&NW) consisted of two rail lines, the Copper River line and the Northwestern line. Michael James Heney had secured the right-of-way up the Copper River in 1904. He started building the railway from Co ...
from Cordova through the upper river valley from 1908 to 1911 allowed widespread extraction of the mineral resources, in particular from the Kennecott Mine, discovered in 1898. The mine was abandoned in 1938 and is now a ghost town
Ghost Town(s) or Ghosttown may refer to:
* Ghost town, a town that has been abandoned
Film and television
* Ghost Town (1936 film), ''Ghost Town'' (1936 film), an American Western film by Harry L. Fraser
* Ghost Town (1956 film), ''Ghost Town'' ...
tourist attraction and historic district maintained by the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
.
Copper River Highway (Alaska Route 10) runs from Cordova to the lower Copper River near Childs Glacier, following the old railroad route and ending at the reconstructed Million Dollar Bridge
The Miles Glacier Bridge, also known as the Million Dollar Bridge, was built in the early 1900s across the Copper River fifty miles from Cordova in what is now the U.S. state of Alaska. It is a multiple-span Pennsylvania truss bridge which compl ...
across the river. The Tok Cut-Off (Alaska Route 1) follows the Copper River Valley on the north side of the Chugach Mountains
The Chugach Mountains of southern Alaska are the northernmost of the several mountain ranges that make up the Pacific Coast Ranges of the western edge of North America. The range is about long and wide, and extends from the Knik and Turnagain ...
.
Fisheries
 The river's famous salmon runs arise from the use of the river watershed by over 2 million salmon each year for spawning. The extensive runs result in many unique varieties, prized for their fat content. The river's commercial salmon season is very brief, beginning in May for
The river's famous salmon runs arise from the use of the river watershed by over 2 million salmon each year for spawning. The extensive runs result in many unique varieties, prized for their fat content. The river's commercial salmon season is very brief, beginning in May for chinook salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus ''Oncorhynchus''. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other ve ...
and sockeye salmon for periods lasting days or hours at a time. Sport fishing by contrast is open all year long, but peak season on the Copper River lasts from August to September when the coho salmon
The coho salmon (''Oncorhynchus kisutch;'' Karuk: achvuun) is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family (biology), family and one of the five Pacific salmon species. Coho salmon are also known as silver salmon or "silvers". The scientif ...
runs. The fisheries are co-managed by the Alaska Department of Fish and Game
The Alaska Department of Fish and Game (ADF&G) is a department within the government of Alaska. ADF&G's mission is to protect, maintain, and improve the fish, game, and aquatic plant resources of the state, and manage their use and development in ...
(ADF&G) and the Department of the Interior Federal Subsistence Board. Management data are obtained primarily by ADF&G at the Miles Lake
Miles Lake is a long glacial lake in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located in the valley of the Copper River, which pools to create it. The lake includes the terminus of Miles Glacier, north of Katalla, Chugach Mountains, and flows into the l ...
sonar station and the native village of Eyak
The Eyak ( Eyak: ʔi·ya·ɢdəlahɢəyu·, literally "inhabitants of Eyak Village at Mile 6"Krauss, Michael E. 1970. ''Eyak dictionary''. University of Alaska and Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1963-1970) are a Native American indigenous ...
at the Baird Canyon and Canyon Creek research stations.
Birding
The Copper River Delta, which extends for 700,000 acres (2,800 km2), is the largest contiguouswetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
along the Pacific coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas
Countries on the western side of the Americas have a Pacific coast as their western or southwestern border, except for Panama, where the Pac ...
of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. It is used annually by 16 million shorebirds, including the world's entire population of western sandpiper
The western sandpiper (''Calidris mauri'') is a small shorebird. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''kalidris'' or ''skalidris'', a term used by Aristotle for some grey-coloured waterside birds. The specific ''mauri'' commemorates Italian bota ...
s and dunlin
The dunlin (''Calidris alpina'') is a small wader, formerly sometimes separated with the other "stints" in the genus ''Erolia''. The English name is a dialect form of "dunling", first recorded in 1531–1532. It derives from ''dun'', "dull brown ...
s. It is also home to the world's largest population of nesting trumpeter swan
The trumpeter swan (''Cygnus buccinator'') is a species of swan found in North America. The heaviest living bird native to North America, it is also the largest extant species of waterfowl, with a wingspan of 185 to 250 cm (6 ft 2 in to 8 ft 2 ...
s and is the only known nesting site for the dusky Canada goose subspecies (''Branta canadensis occidentalis'').
Black spruce
''Picea mariana'', the black spruce, is a North American species of spruce tree in the pine family. It is widespread across Canada, found in all 10 provinces and all 3 territories. It is the official tree of the province of Newfoundland and Labra ...
taiga along the Copper River
Image:Glacial Dust off Alaska.jpg, Wind picks up fine sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand an ...
from the riverbank and carries it over the ocean.
See also
*List of rivers of Alaska
This is a List of rivers in Alaska, which are at least fifth-order according to the Strahler method of stream classification, and an incomplete list of otherwise-notable rivers and streams. Alaska has more than 12,000 rivers, and thousands more st ...
References
Further reading
*Brabets, Timothy P. (1997)''Geomorphology of the Lower Copper River, Alaska''
.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1581 Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey.
External links
Ecotrust Copper River Program
Prepared for Ecotrust by Marie E. Lowe of the Institute of Social and Economic Research, hosted by Alaska State Publications Program
Alaska Department of Fish and Game: Copper River Salmon
{{Authority control Ahtna Rivers of Alaska Rivers of Chugach Census Area, Alaska Rivers of Copper River Census Area, Alaska Rivers of Unorganized Borough, Alaska