|
Copper(II) Chloride
Copper(II) chloride is the chemical compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The anhydrous form is yellowish brown but slowly absorbs moisture to form a blue-green dihydrate. Both the anhydrous and the dihydrate forms occur naturally as the very rare minerals tolbachite and eriochalcite, respectively.Marlene C. Morris, Howard F. McMurdie, Eloise H. Evans, Boris Paretzkin, Harry S. Parker, and Nicolas C. Panagiotopoulos (1981) ''Copper chloride hydrate (eriochalcite)'', in Standard X-ray Diffraction Powder PatternsNational Bureau of Standards, Monograph 25, Section 18; page 33. Structure Anhydrous CuCl2 adopts a distorted cadmium iodide structure. In this motif, the copper centers are octahedral. Most copper(II) compounds exhibit distortions from idealized octahedral geometry due to the Jahn-Teller effect, which in this case describes the localization of one d-electron into a molecular orbital that is strongly antibonding with respect to a pair of chloride ligands. In CuCl2� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in its own right, in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and production of methyl methacrylate (and from that PMMA) as well as bisphenol A.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in |
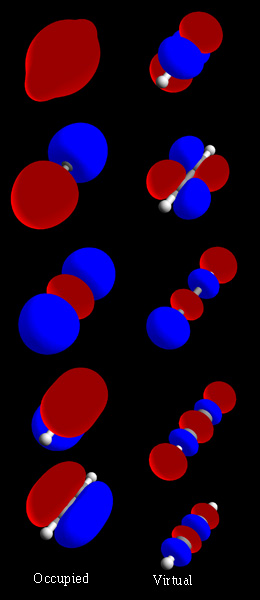
Molecular Orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms ''atomic orbital'' and ''molecular orbital'' were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean ''one-electron orbital wave functions''. At an elementary level, they are used to describe the ''region'' of space in which a function has a significant amplitude. In an isolated atom, the orbital electrons' location is determined by functions called atomic orbitals. When multiple atoms combine chemically into a molecule, the electrons' locations are determined by the molecule as a whole, so the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The electrons from the constituent atoms occupy the molecular orbitals. Mathematically, molecular orbitals are an approximate solution to the Schrö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex (chemistry)
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloride
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often very soluble in water.Green, John, and Sadru Damji. "Chapter 3." ''Chemistry''. Camberwell, Vic.: IBID, 2001. Print. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Less frequently, the word ''chloride'' may also form part of the "common" name of chemical compounds in which one or more chlorine atoms are covalently bonded. For example, methyl chloride, with the standard name chloromethane (see IUPAC books) is an organic compound with a covalent C−Cl bond in which the chlorine is not an anion. Electronic properties A chloride ion (diameter 167 pm) is much lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide ( IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of copper extraction and the burning of sulfur- bearing fossil fuels. Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support for this simple approach that does not invoke ''d'' orbital participation. In terms of electron-counting formalism, the sulfur atom has an oxidation state of +4 and a formal charge of +1. Occurrence Sulfur dioxide is found on Earth and exists in very small concentrations and in the atmosphere at about 1 ppm. On other p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride salts like ammonium chloride ( sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and hydrochloric acid (in the form of ). However, the nature of free chlorine gas as a separate substance was only recognised ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(I) Chloride
Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl2). History Copper(I) chloride was first prepared by Robert Boyle in the mid-seventeenth century from mercury(II) chloride ("Venetian sublimate") and copper metal: :HgCl2 + 2 Cu → 2 CuCl + Hg In 1799, J.L. Proust characterized the two different chlorides of copper. He prepared CuCl by heating CuCl2 at red heat in the absence of air, causing it to lose half of its combined chlorine followed by removing residual CuCl2 by washing with water. An acidic solution of CuCl was formerly used for analysis of carbon monoxide content in gases, for example in Hempel's gas apparatus. This application was significant during the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries when coal gas was widel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicopper Chloride Trihydroxide
Dicopper chloride trihydroxide is the chemical compound with the formula Cu2(OH)3Cl. It is often referred to as tribasic copper chloride (TBCC), copper trihydroxyl chloride or copper hydroxychloride. It is a greenish crystalline solid encountered in mineral deposits, metal corrosion products, industrial products, art and archeological objects, and some living systems. It was originally manufactured on an industrial scale as a precipitated material used as either a chemical intermediate or a fungicide. Since 1994, a purified, crystallized product has been produced at the scale of thousands of tons per year, and used extensively as a nutritional supplement for animals. Natural occurrence Cu2(OH)3Cl occurs as natural minerals in four polymorphic crystal forms: atacamite, paratacamite, clinoatacamite, and botallackite. Atacamite is orthorhombic, paratacamite is rhombohedral, and the other two polymorphs are monoclinic. Atacamite and paratacamite are common secondary minera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(II)chloride Crystal 01
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form (native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, c. 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(II) Hydroxide
Copper(II) hydroxide is the hydroxide of copper with the chemical formula of Cu(OH)2. It is a pale greenish blue or bluish green solid. Some forms of copper(II) hydroxide are sold as "stabilized" copper(II) hydroxide, although they likely consist of a mixture of copper(II) carbonate and hydroxide. Cupric hydroxide is a strong base, although its low solubility in water makes this hard to observe directly. Occurrence Copper(II) hydroxide has been known since copper smelting Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat a ... began around 5000 BC although the alchemy, alchemists were probably the first to manufacture it by mixing solutions of lye (sodium or potassium hydroxide) and blue vitriol (copper(II) sulfate). Sources of both compounds were available in antiquity. It was produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CuCl2 Equilibrium
Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl2). History Copper(I) chloride was first prepared by Robert Boyle in the mid-seventeenth century from mercury(II) chloride ("Venetian sublimate") and copper metal: :HgCl2 + 2 Cu → 2 CuCl + Hg In 1799, J.L. Proust characterized the two different chlorides of copper. He prepared CuCl by heating CuCl2 at red heat in the absence of air, causing it to lose half of its combined chlorine followed by removing residual CuCl2 by washing with water. An acidic solution of CuCl was formerly used for analysis of carbon monoxide content in gases, for example in Hempel's gas apparatus. This application was significant during the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries when coal gas was widel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevgeny Zavoisky
Yevgeny Konstantinovich Zavoisky (russian: Евгений Константинович Завойский; September 28, 1907 – October 9, 1976) was a Soviet physicist known for discovery of electron paramagnetic resonance in 1944. He likely observed nuclear magnetic resonance in 1941, well before Felix Bloch and Edward Mills Purcell, but dismissed the results as not reproducible. Zavoisky is also credited with design of luminescence camera for detection of nuclear processes in 1952 and discovery of magneto-acoustic resonance in plasma in 1958. Early years Zavoisky was born in 1907 in Mohyliv-Podilskyi, a town in the south of Russian Empire (now in Vinnytsia Oblast, Ukraine). His father Konstantin Ivanovich was a military doctor and mother Elizaveta Nikolaevna was trained as a teacher. In 1910, Zavoisky family moved to Kazan – a major Russian university city – for the sake of better education and well-being of their five children. There, Konstantin Ivanovich obtained a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Chloride_Precipitate.jpg)

