|
Cookbooks
A cookbook or cookery book is a kitchen reference containing recipes. Cookbooks may be general, or may specialize in a particular cuisine or category of food. Recipes in cookbooks are organized in various ways: by course (appetizer, first course, main course, dessert), by main ingredient, by cooking technique, alphabetically, by region or country, and so on. They may include illustrations of finished dishes and preparation steps; discussions of cooking techniques, advice on kitchen equipment, ingredients, tips, and substitutions; historical and cultural notes; and so on. Cookbooks may be written by individual authors, who may be chefs, cooking teachers, or other food writers; they may be written by collectives; or they may be anonymous. They may be addressed to home cooks, to professional restaurant cooks, to institutional cooks, or to more specialized audiences. Some cookbooks are didactic, with detailed recipes addressed to beginners or people learning to cook particular dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recipe
A recipe is a set of instructions that describes how to prepare or make something, especially a dish (food), dish of prepared food. A sub-recipe or subrecipe is a recipe for an ingredient that will be called for in the instructions for the main recipe. Recipe books (also called cookbooks or cookery books) are a collection of recipes, help reflect cultural identity, cultural identities and social changes as well as serve as educational tools. History Early examples The earliest known written recipes date to 1730 BC and were recorded on cuneiform tablets found in Mesopotamia. Other early written recipes date from approximately 1600 BC and come from an Akkadian language, Akkadian tablet from southern Babylonia. There are also works in ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs depicting the preparation of food. Many ancient Greek recipes are known. Mithaecus's cookbook was an early one, but most of it has been lost; Athenaeus quotes one short recipe in his ''Deipnosophistae''. Athenaeus menti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastering The Art Of French Cooking
''Mastering the Art of French Cooking'' is a two-volume French cookbook written by Simone Beck and Louisette Bertholle, both from France, and Julia Child, from the United States. The book was written for the American market and published by Knopf in 1961 (Volume 1) and 1970 (Volume 2). The success of Volume 1 resulted in Julia Child being given her own television show, '' The French Chef'', one of the first cooking programs on American television. Historian David Strauss claimed in 2011 that the publication of ''Mastering the Art of French Cooking'' "did more than any other event in the last half century to reshape the gourmet dining scene". History After World War II, interest in French cuisine rose significantly in the United States. Through the late 1940s and 1950s, Americans interested in preparing French dishes had few options. ''Gourmet'' magazine offered French recipes to subscribers monthly, and several dozen French cookbooks were published throughout the 1950s. These r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manasollasa
The ' also known as ''Abhilashitartha Chintamani'', is an early 12th-century Sanskrit text composed by the Kalyani Chalukya king Someshvara III, who ruled in present-day Karnataka. It is an encyclopedic work covering topics such as polity, governance, ethics, economics, astronomy, astrology, rhetoric, veterinary medicine, horticulture, perfumes, food, architecture, games, painting, poetry, dance and music. The text is a valuable source of socio-cultural information on 11th- and 12th-century India. The encyclopedic treatise is structured as five sub-books with a cumulative total of 100 chapters. It is notable for its extensive discussion of arts, particularly music and dance. It is also notable for including chapters on food recipes and festivals, many of which are a part of modern Indian culture. Another medieval era Sanskrit text with the title ''Mānasollāsa'' also exists, consisting of devotional praise hymns ('' stōtra''), and it is different from the encyclopedic treatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
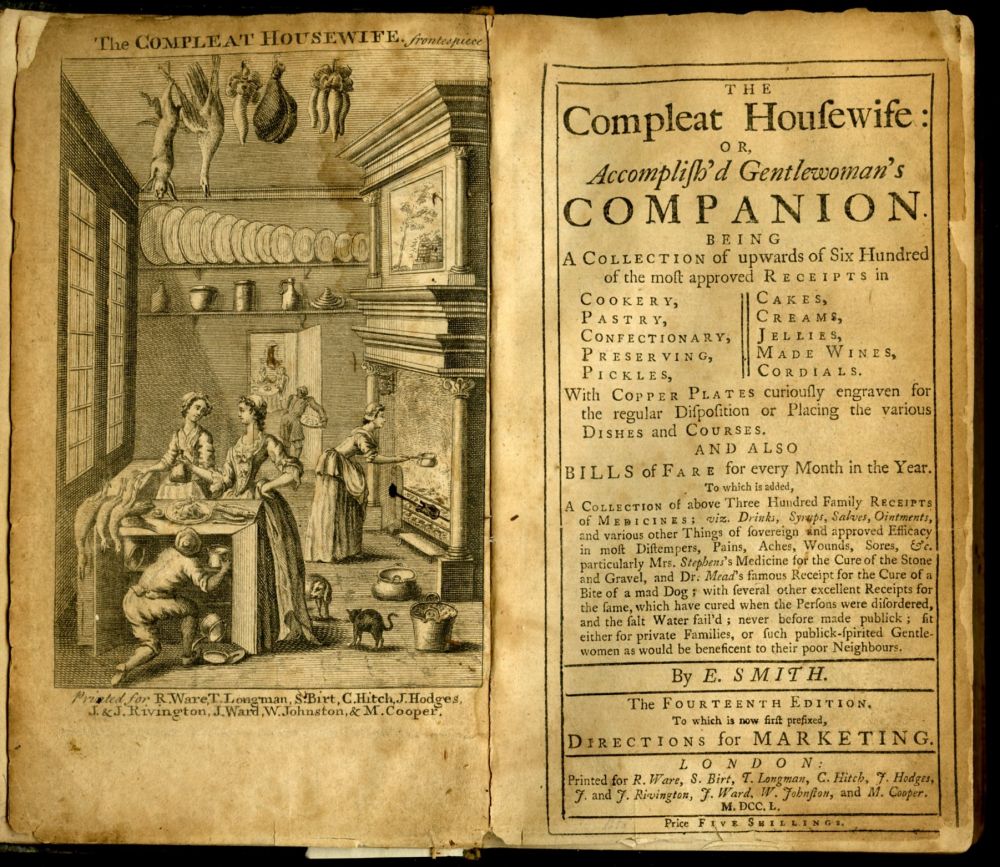
Eliza Smith The Compleat Housewife
ELIZA is an early natural language processing computer program developed from 1964 to 1967 at MIT by Joseph Weizenbaum. Created to explore communication between humans and machines, ELIZA simulated conversation by using a pattern matching and substitution methodology that gave users an illusion of natural-language understanding, understanding on the part of the program, but had no representation that could be considered really understanding what was being said by either party. Whereas the ELIZA program itself was written (originally) in SLIP (programming language), MAD-SLIP, the pattern matching directives that contained most of its language capability were provided in separate "scripts", represented in a s-expression, lisp-like representation. The most famous script, DOCTOR, simulated a Rogerian psychotherapy, psychotherapist of the Rogerian school (in which the therapist often reflects back the patient's words to the patient), and used rules, dictated in the script, to respond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Mei
Yuan Mei (; 1716–1797) was a Chinese poet of the Qing dynasty. He was often mentioned with Ji Yun as the "Nan Yuan Bei Ji" (). Biography Early life Yuan Mei was born in Qiantang (, in modern Hangzhou), Zhejiang province, to a cultured family who had never before attained high office. He achieved the degree of '' jinshi'' in 1739 at the young age of 23 and was immediately appointed to the Hanlin Academy (). Then, from 1742 to 1748, Yuan Mei served as a magistrate in four different locations in Jiangsu. However, in 1748, shortly after being assigned to administer part of Nanjing, he resigned his post and returned to his hometown to pursue his literary interest. Literary career In the decades before his death, Yuan Mei produced a large body of poetry, essays and paintings. His works reflected his interest in Chan Buddhism and the supernatural, at the expense of Daoism and institutional Buddhism - both of which he rejected. Yuan is most famous for his poetry, which has been des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, extending northward into parts of the Arctic; eastward and southward into parts of the Indian subcontinent, mounting invasions of Southeast Asia, and conquering the Iranian plateau; and reaching westward as far as the Levant and the Carpathian Mountains. The Mongol Empire emerged from the unification of several nomad, nomadic tribes in the Mongol heartland under the leadership of Temüjin, known by the title of Genghis Khan (–1227), whom a council proclaimed as the ruler of all Mongols in 1206. The empire grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out Mongol invasions, invading armies in every direction. The vast transcontinental empire connected the Eastern world, East with the Western world, West, and the Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buyantu Khan
Buyantu Khan ( Mongolian: Буянт хаан; Mongolian script: ; ), born Ayurbarwada (Mongolian: Аюурбарбад ; ), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Renzong of Yuan (, April 9, 1285 – March 1, 1320), was the fourth emperor of the Yuan dynasty of China. In addition to being the Emperor of China, he is regarded as the eighth Great Khan of the Mongol Empire, although it was only nominal due to the division of the empire. His regnal name "Buyantu Khan" means "blessed/good Khan" in the Mongolian language. His personal name "Ayurbarwada" was derived from a Sanskrit compound ''Āyurpārvata'' (), which means "the mountain of longevity", in contrast with Emperor Wuzong's name Qaišan (海山, "mountains and seas" in Chinese). Ayurbarwada was the first Yuan emperor who actively supported the adoption of Confucian principles into the administration system. The emperor, who was mentored by the Confucian academic Li Meng, succeeded peacefully to the throne and revers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hu Sihui
Hu Sihui (, 和斯輝, 忽斯慧, also Hu Zheng Qi Huei; active nr. 1314–1330) was a Chinese court therapist and dietitian during Yuan dynasty. He is known for his book '' Yinshan zhengyao'' (''Dietary Principles''), that became a classic in Chinese medicine and Chinese cuisine. He was the first to empirically discover and clearly describe deficiency diseases. Biography The career of Hu Sihui, as he states in preface to his book, was in the reign of Buyantu Khan in Yenyu years (1314—1320). His ethnicity is unclear. He has been credited as of Mongol descent by some East Asian scholars, while Western scholars have pointed out his Turkic descent, his book being "far too comfortable with Turkic and a larger Islamic culture." He was an official in Xuanhui Yuan (the Ministry of Court Supplies and Provisions), around 1315 Hu Sihui initially emerged as the therapist of Empress Dowager, soon also became the therapist of the acting Empress, and later received the rank of the chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wushi Zhongkuilu
Wushi Zhongkuilu () is a late-13th-century medieval Chinese culinary work on household cookery written by an anonymous author from the Pujiang region known only as "Madame Wu". It is the earliest known culinary work written by or attributed to a Chinese woman and is believed to have been published in during late Song dynasty or early Yuan dynasty. Content The full title of the work is "Song Dynasty Pujiang Woman of the Wu Surname Records on Household Essentials", which echoes the contents of the book as a detailed guide for preparing essential household dietary ingredients and dishes of the period. This includes cooked items as well as various pickled and preserved foods that can be eaten straight or used as ingredients. Wu's work consists of three chapters grouped according to the types of recipes and originating ingredients: # "Preserved Meats and Pickled Fish" (): 20 sections # "Vegetable preparations" (): 38 sections # "Sweet foods" (): 15 sections It is also the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuisines
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs and ingredients combine to enable dishes unique to a region. Etymology Used in English since the late 18th century, the word cuisine—meaning manner or style of cooking—is borrowed from the French for 'style of cooking' (literally 'kitchen'), as originally derived from Latin ''coquere'', 'to cook'. Influences on cuisine A cuisine is partly determined by ingredients that are available locally or through trade. Regional ingredients are developed and commonly contribute to a regional or national cuisine, such as Japanese rice in Japanese cuisine. Religious food laws can also exercise an influence on cuisine, such as Indian cuisine and Hinduism that is mainly lacto-vegetarian (avoiding meat and eggs) due to sacred animal worship. Sikhism in Punjabi cuisine, Buddhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |