|
Convoy RS 3
Convoy RS 3 was a South Atlantic convoy which ran during the height of the Battle of the Atlantic in World War II. It was a small coastal convoy going from Rabat to Sierra Leone.Blair, p. 204 The convoy lost its three biggest ships to U-boat attacks in March 1943, which contributed to the fact that in March 1943 most of the ships sunk by U-boats were lost in convoys. As convoying was the key answer to the U-boat threat, this led to a temporary crisis in Allied shipping. Departure and detection When the convoy left Gibraltar, it consisted of three freighters, the cable layer ''Lady Denison-Pender'' and five tugboats. The cable layer was a particularly valuable ship. This ship was returning south after laying a cable connection between Gibraltar and Casablanca, in order to provide secure communications for the Casablanca Conference. The convoy was escorted by two corvettes and two armed naval trawlers. The German ''B-Dienst'' signals intelligence group was able to decipher some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Ensign Of Germany 1938-1945
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular or irregular military forces. Warfare refers to the common activities and characteristics of types of war, or of wars in general. Total war is warfare that is not restricted to purely legitimate military targets, and can result in massive civilian or other non-combatant suffering and casualties. While some war studies scholars consider war a universal and ancestral aspect of human nature, others argue it is a result of specific socio-cultural, economic or ecological circumstances. Etymology The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century Old English words ''wyrre'' and ''werre'', from Old French ''werre'' (also ''guerre'' as in modern French), in turn from the Frankish *''werra'', ultimately deriving from the Proto-Germanic *''we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casablanca Conference
The Casablanca Conference (codenamed SYMBOL) or Anfa Conference was held at the Anfa Hotel in Casablanca, French Morocco, from January 14 to 24, 1943, to plan the Allied European strategy for the next phase of World War II. In attendance were United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt and British prime minister Winston Churchill. Also attending were the sovereign of Morocco, Sultan Muhammad V, and representing the Free French forces, Generals Charles de Gaulle and Henri Giraud, but they played minor roles and were not part of the military planning. USSR general secretary Joseph Stalin declined to attend, citing the ongoing Battle of Stalingrad as requiring his presence in the Soviet Union. The conference's agenda addressed the specifics of tactical procedure, allocation of resources, and the broader issues of diplomatic policy. The debate and negotiations produced what was known as the Casablanca Declaration, and perhaps its most historically provocative statement of purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
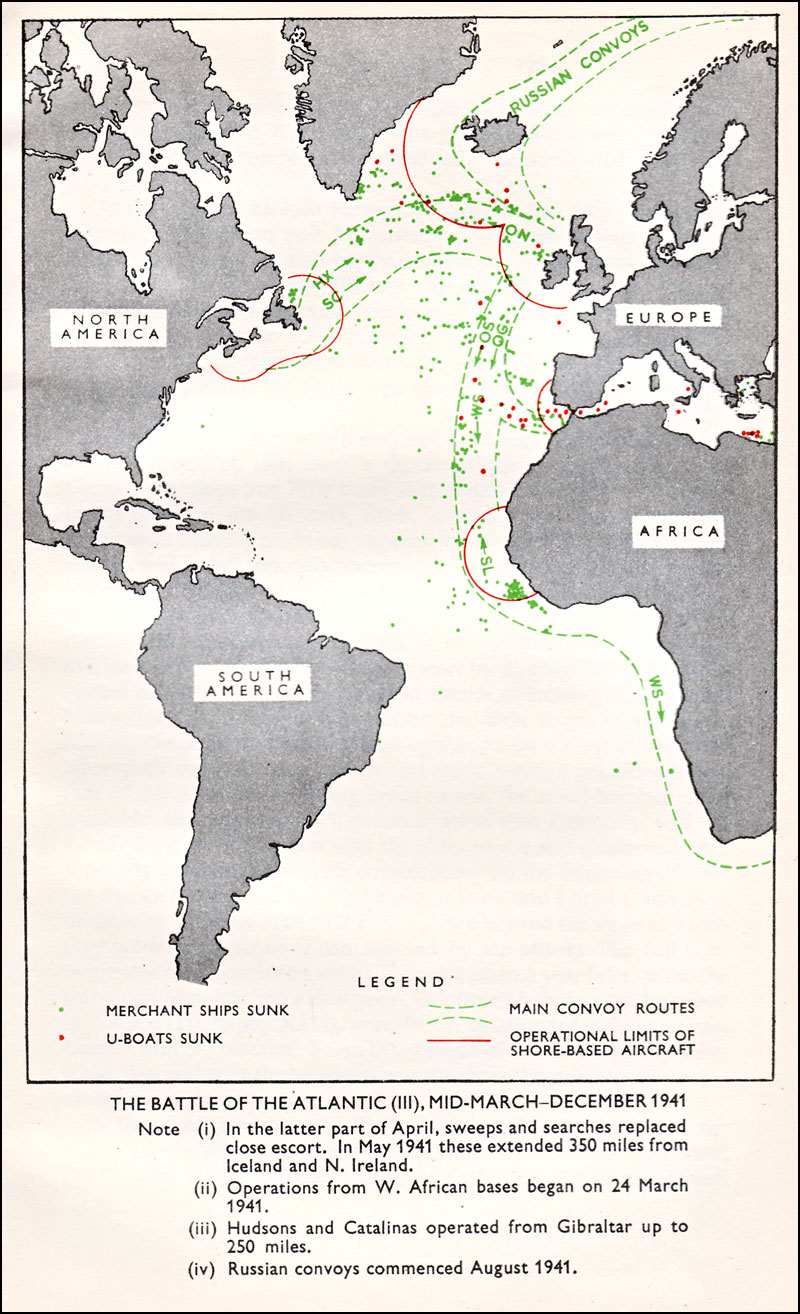
Convoys Of World War II
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used in a non-military sense, for example when driving through remote areas. Naval convoys Age of Sail Naval convoys have been in use for centuries, with examples of merchant ships traveling under naval protection dating to the 12th century. The use of organized naval convoys dates from when ships began to be separated into specialist classes and national navies were established. By the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century, effective naval convoy tactics had been developed to ward off pirates and privateers. Some convoys contained several hundred merchant ships. The most enduring system of convoys were the Spanish treasure fleets, that sailed from the 1520s until 1790. When merchant ships sailed independently, a privateer cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay Blair
Clay Drewry Blair Jr. (May 1, 1925 – December 16, 1998) was an American journalist and author, best known for his books on military history. Blair wrote some two dozen history books and hundreds of magazine articles that reached a popular audience. Early life and military service Blair was born in Lexington, Virginia. Blair enlisted in the United States Navy in 1943, during World War II. During 1944 he attended Basic Enlisted Submarine School followed by Quartermaster Class A School, after which he was assigned to ''Sperry'' (AS-12), a submarine tender. During 1945, Blair was posted to the fleet submarine ''Guardfish'' (SS-217). He was on that boat's last two war patrols off Japan. Blair served on ''Guardfish'' into 1946, after the war was over, then was discharged from the Navy. His highest rank was Quartermaster 2nd Class. Education and journalism career Blair attended both Tulane University and Columbia University. He attended the first as a prospective architectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloop-of-war
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, any vessel or a particular vessel type, akin to anti-infantry vs. anti-vehicle mines. Naval mines can be used offensively, to hamper enemy shipping movements or lock vessels into a harbour; or defensively, to protect friendly vessels and create "safe" zones. Mines allow the minelaying force commander to concentrate warships or defensive assets in mine-free areas giving the adversary three choices: undertake an expensive and time-consuming minesweeping effort, accept the casualties of challenging the minefield, or use the unmined waters where the greatest concentration of enemy firepower will be encountered. Although international law requires signatory nations to declare mined areas, precise locations remain secret; and non-complying individ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convoy Commodore
Convoy commodore also known as commodore, convoys was the title of a civilian put in charge of the good order of the merchant ships in the British convoys used during World War II. Usually the convoy commodore was a retired naval officer or a senior merchant captain drawn from the Royal Naval Reserve. He was aboard one of the merchant ships. The convoy commodore was distinguished from the commander of the convoy's escort, always a naval officer. Description Convoy commodores were based at HMS ''Eaglet'', the Royal Navy's shore establishment at Liverpool. Commodores had a peripatetic role, sailing with each convoy as assigned in a suitable ship. This ship would be the convoy flagship, but remained under the command of its master, the commodore and his team merely taking passage. The commodores were accompanied by a small team of ratings, usually a yeoman and two or three signalers; these teams would stay together and work with the same commodore throughout the campaign, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zigzag
A zigzag is a pattern made up of small corners at variable angles, though constant within the zigzag, tracing a path between two parallel lines; it can be described as both jagged and fairly regular. In geometry, this pattern is described as a skew apeirogon. From the point of view of symmetry, a regular zigzag can be generated from a simple motif like a line segment by repeated application of a glide reflection. Although the origin of the word is unclear, its first printed appearances were in French-language books and ephemera of the late 17th century. Examples of zigzags The trace of a triangle wave or a sawtooth wave is a zigzag. Pinking shears are designed to cut cloth or paper with a zigzag edge, to lessen fraying. In sewing, a ''zigzag stitch'' is a machine stitch in a zigzag pattern. The zigzag arch is an architectural embellishment used in Islamic, Byzantine, Norman and Romanesque architecture. See also *Serpentine shape *Infinite skew polygon In geometry, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; wo, Ndakaaru) (from daqaar ''tamarind''), is the capital and largest city of Senegal. The city of Dakar proper has a population of 1,030,594, whereas the population of the Dakar metropolitan area is estimated at 3.94 million in 2021. The area around Dakar was settled in the 15th century. The Portuguese established a presence on the island of Gorée off the coast of Cap-Vert and used it as a base for the Atlantic slave trade. France took over the island in 1677. Following the abolition of the slave trade and French annexation of the mainland area in the 19th century, Dakar grew into a major regional port and a major city of the French colonial empire. In 1902, Dakar replaced Saint-Louis as the capital of French West Africa. From 1959 to 1960, Dakar was the capital of the short-lived Mali Federation. In 1960, it became the capital of the independent Republic of Senegal. History The Cap-Vert peninsula was settled no later than the 15th century, by the Lebu peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocco. They are the southernmost of the autonomous communities of Spain. The islands have a population of 2.2 million people and they are the most populous special territory of the European Union. The seven main islands are (from largest to smallest in area) Tenerife, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Lanzarote, La Palma, La Gomera, and El Hierro. The archipelago includes many smaller islands and islets, including La Graciosa, Alegranza, Isla de Lobos, Montaña Clara, Roque del Oeste, and Roque del Este. It also includes a number of rocks, including those of Salmor, Fasnia, Bonanza, Garachico, and Anaga. In ancient times, the island chain was often referred to as "the Fortunate Isles". The Canary Islands are the southernmost region of Spain, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Wolfpacks Of World War II
Wolfpacks (german: U-Boot-Gruppe) were employed by Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II against Allied and neutral shipping. Outbreak of War From the outbreak of war until mid-1940 there were various groups of U-boats engaged in collective patrols. With the exception of experimental Hartmann's wolfpack in 1939, the first recognised wolfpack was led by ''KrvKpt'' Günther Prien Günther Prien (16 January 1908 – presumed 8 March 1941) was a German U-boat commander during World War II. He was the first U-boat commander to receive the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross and the first member of the ''Kriegsmarine'' to r ... in June 1940. Invasion of Norway & Denmark In preparation for the impending invasion of Norway and Denmark, in early April 1940, 31 U-boats were ready for operations between England and Norway. On 6 April, the codeword " Hartmut" was transmitted and German submarines began their designated operations. Wolfpacks Bibliography * References * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-Dienst
The ''B-Dienst'' (german: Beobachtungsdienst, observation service), also called x''B-Dienst'', X-''B-Dienst'' and χ''B-Dienst'', was a Department of the German Naval Intelligence Service (german: Marinenachrichtendienst, MND III) of the OKM, that dealt with the interception and recording, decoding and analysis of the enemy, in particular British radio communications before and during World War II. B-Dienst worked on cryptanalysis and deciphering (decrypting) of enemy and neutral states' message traffic and security control of ''Kriegsmarine'' key processes and machinery. :"The ultimate goal of all evaluation was recognizing the opponent's goal by pro-active identification of data." B-Dienst was instrumental in moulding Wehrmacht operations during the Battles of Norway and France in spring 1940, primarily due to the cryptanalysis successes it had achieved against early and less secure British Naval cyphers. B-Dienst broke British Naval Combined Cypher No. 3 in October 1941, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |