|
Continuous Training
Continuous Training, also known as continuous exercise or steady state training, is any type of physical training that involves activity without rest intervals. Continuous training can be performed at low, moderate, or high exercise intensities, and is often contrasted with interval training, often called high-intensity interval training. Some training regimens, such as Fartlek, combine both continuous and interval approaches. Exercise modes noted as suitable for continuous training include indoor and outdoor cycling, jogging, running, walking, rowing, stair climbing, simulated climbing, Nordic skiing, elliptical training, aerobic riding, aerobic dancing, bench step aerobics, hiking, in-line skating, rope skipping, swimming, and water aerobics. Exercise intensities As the below examples illustrate, exercise intensity is measured in different ways and is defined inconsistently across studies. Forms of continuous exercise may be performed at multiple intensities fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Training
Physical fitness is a state of health and well-being and, more specifically, the ability to perform aspects of sports, occupations and daily activities. Physical fitness is generally achieved through proper nutrition, moderate-vigorous physical exercise, and sufficient rest along with a formal recovery plan. Before the Industrial Revolution, fitness was defined as the capacity to carry out the day's activities without undue fatigue or lethargy. However, with automation and changes in lifestyles, physical fitness is now considered a measure of the body's ability to function efficiently and effectively in work and leisure activities, to be healthy, to resist hypokinetic diseases, improve immune system and to meet emergency situations. Overview Fitness is defined as the quality or state of being fit and healthy. Around 1950, perhaps consistent with the Industrial Revolution and the treatise of World War II, the term "fitness" increased in western vernacular by a factor of ten. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dancing
Dance is a performing art art form, form consisting of sequences of movement, either improvised or purposefully selected. This movement has aesthetic and often symbolism (arts), symbolic value. Dance can be categorized and described by its choreography, by its repertoire of movements, or by its History of dance, historical period or List of ethnic, regional, and folk dances by origin, place of origin. An important distinction is to be drawn between the contexts of Concert dance, theatrical and Participation dance, participatory dance, although these two categories are not always completely separate; both may have special functions, whether Social dance, social, ceremonial dance, ceremonial, competitive dance, competitive, erotic dance, erotic, war dance, martial, or sacred dance, sacred/liturgical dance, liturgical. Other forms of human movement are sometimes said to have a dance-like quality, including martial arts, gymnastics, cheerleading, figure skating, synchronised swimmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
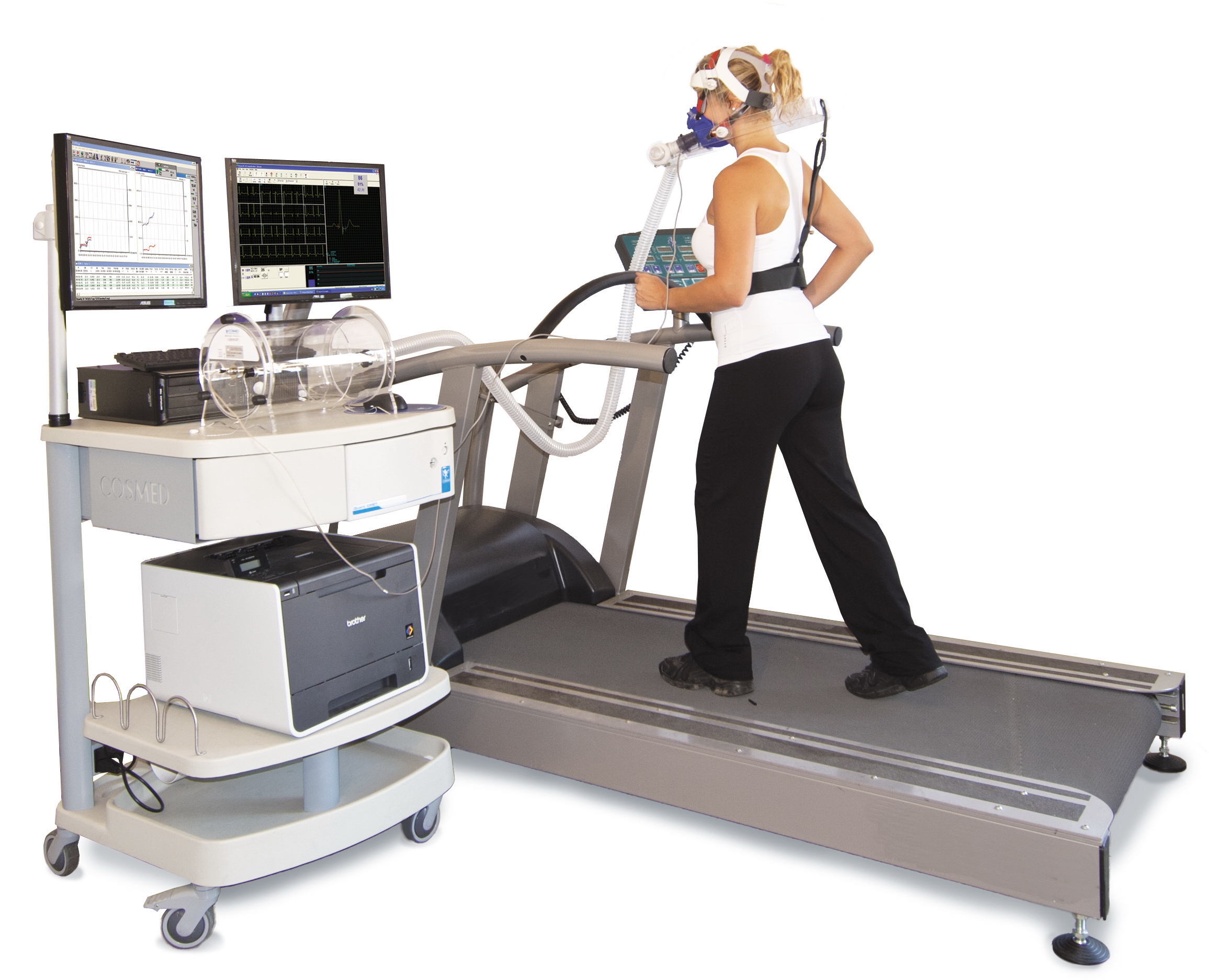
VO2 Max
VO2 max (also maximal oxygen consumption, maximal oxygen uptake or maximal aerobic capacity) is the maximum rate of oxygen consumption attainable during physical exertion. The name is derived from three abbreviations: "V̇" for volume (the dot appears over the V to indicate "per unit of time"), "O2" for oxygen, and "max" for maximum. A similar measure is VO2 peak (peak oxygen consumption), which is the measurable value from a session of physical exercise, be it incremental or otherwise. It could match or underestimate the actual VO2 max. Confusion between the values in older and popular fitness literature is common. The measurement of V̇O2 max in the laboratory provides a quantitative value of endurance fitness for comparison of individual training effects and between people in endurance training. Maximal oxygen consumption reflects cardiorespiratory fitness and endurance capacity in exercise performance. Elite athletes, such as competitive distance runners, racing cyclists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
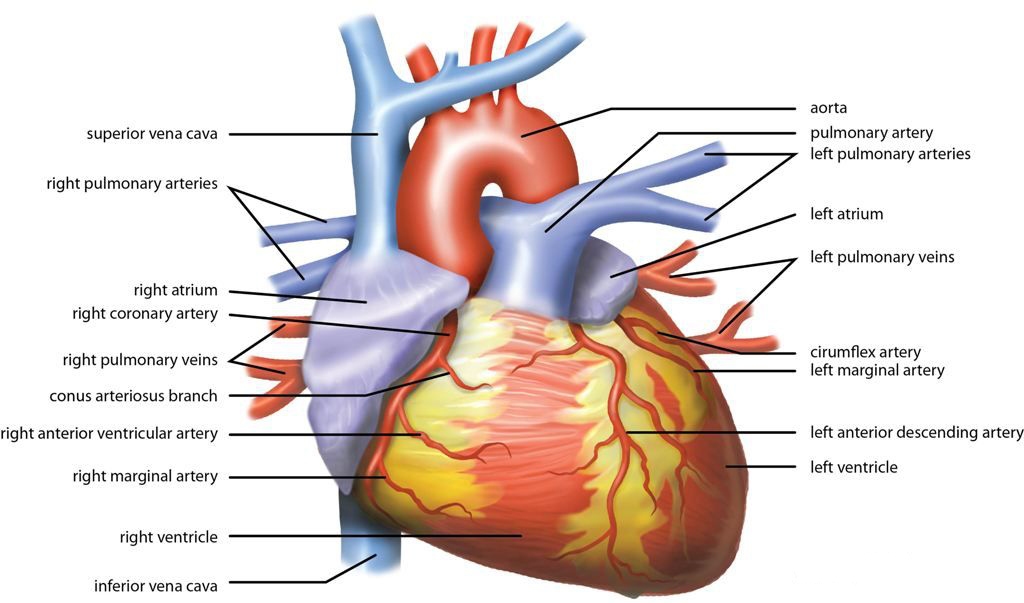
Heart Rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide, but is also modulated by numerous factors, including, but not limited to, genetics, physical fitness, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness as well as the interaction between and among these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. Tachycardia is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. Bradycardia is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with rates around 40–50 bpm is common and is considered normal. When the heart is not beating in a regular pattern, this i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Power Output
Peak power output (PPO), also known as "peak work rate" is a common measure of exercise intensity. For example, researchers may ask subjects to complete an incremental exercise test where VO2max is measured while the person cycles at increasingly difficult power generation levels as measured by a cycle ergometer. See also *Human power Human power is work or energy that is produced from the human body. It can also refer to the power (rate of work per time) of a human. Power comes primarily from muscles, but body heat is also used to do work like warming shelters, food, or o ... References Exercise physiology Sports terminology {{sport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Slow Distance
Long slow distance (LSD) is a form of aerobic endurance training used in sports including running, rowing, skiing and cycling.Burke, Ed and Ed Pavalka. 2000. ''The complete book of long-distance cycling: build the strength, skills, and confidence to ride as far as you want.'' Rodale . It is also known as aerobic endurance training, base training and Zone 2 training. Physiological adaptations to LSD training include improved cardiovascular function, improved thermoregulatory function, improved mitochondrial energy production, increased oxidative capacity of skeletal muscle, and increased utilization of fat for fuel. Ernst van Aaken, a German physician and coach, is generally recognized as the founder of the long slow distance method of endurance training.Morris, Alfred F. 1984. ''Sports medicine: prevention of athletic injuries.'' University of Michigan Anderson, Bob and Joe Henderson. 1972. ''Guide to distance running.'' Indiana University. Long slow distance training is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Aerobics
Water aerobics (waterobics, aquarobics, aquatic fitness, aquafitness, aquafit) is the performance of aerobic exercise in water such as in a swimming pool. It is done mostly vertically and without swimming typically in waist deep or deeper water. Water aerobics is a form of aerobic exercise that requires water-immersed participants. Most water aerobics is in a group fitness class setting with a trained professional teaching for about an hour. The classes focus on aerobic endurance, resistance training, and creating an enjoyable atmosphere with music. Different forms of water aerobics include: aqua Zumba, water yoga, aqua aerobics, and aqua jog. Variation from land-based aerobics While similar to land aerobics, in that it focuses on cardiac training, water aerobics differs in that it adds the component of water resistance and buoyancy. Although heart rate does not increase as much as in land-based aerobics, the heart is working just as hard, and underwater exercise actually pumps mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swimming (sport)
Swimming is an individual or team racing sport that requires the use of one's entire body to move through water. The sport takes place in pools or open water (e.g., in a sea or lake). Competitive swimming is one of the most popular Olympic sports, with varied distance events in butterfly, backstroke, breaststroke, freestyle, and individual medley. In addition to these individual events, four swimmers can take part in either a freestyle or medley relay. A medley relay consists of four swimmers who will each swim a different stroke, ordered as backstroke, breaststroke, butterfly and freestyle. Swimming each stroke requires a set of specific techniques; in competition, there are distinct regulations concerning the acceptable form for each individual stroke. There are also regulations on what types of swimsuits, caps, jewelry and injury tape that are allowed at competitions. Although it is possible for competitive swimmers to incur several injuries from the sport, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rope Skipping
A skipping rope (British English) or jump rope (American English) is a tool used in the sport of skipping/jump rope where one or more participants jump over a rope swung so that it passes under their feet and over their heads. There are multiple subsets of skipping/jump rope, including single freestyle, single speed, pairs, three-person speed (Double Dutch), and three-person freestyle (Double Dutch freestyle). Rope skipping is commonly performed as an exercise or recreational activity, and there are also several major organizations that support jump rope as a competitive sport. Often separated by sex and age, events include hundreds of competitive teams all around the world. In the US, schools rarely have jump rope teams, and few states have sanctioned official events at the elementary school level. In freestyle events, jumpers use a variety of basic and advanced techniques in a routine of one minute, which is judged by a head judge, content judges, and performance judges. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In-line Skating
Inline skating is a multi-disciplinary sport and can refer to a number of activities practiced using inline skates. Inline skates typically have two to five polyurethane wheels depending on the style of practice, arranged in a single line by a metal or plastic frame on the underside of a boot. The in-line design allows for greater speed and maneuverability than traditional (or "quad") roller skates. Following this basic design principle, inline skates can be modified to varying degrees to accommodate niche disciplines. Inline skating is commonly referred to by the proprietary eponym ''rollerblading'', or just ''blading'', due to the popular brand of inline skates, Rollerblade. History An inline skate appeared in a Paris patent in 1819, but were overtaken in popularity by quad skates. The German branch of SKF developed and produced inline-skates in 1978 with wheels for hockey or for the street. The product was stopped after one year as the management did not want a consume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiking
Hiking is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century.AMATO, JOSEPH A. "Mind over Foot: Romantic Walking and Rambling." In ''On Foot: A History of Walking'', 101-24. NYU Press, 2004. Accessed March 1, 2021. http://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt9qg056.7. Religious pilgrimages have existed much longer but they involve walking long distances for a spiritual purpose associated with specific religions. "Hiking" is the preferred term in Canada and the United States; the term " walking" is used in these regions for shorter, particularly urban walks. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, the word "walking" describes all forms of walking, whether it is a walk in the park or backpacking in the Alps. The word hiking is also often used in the UK, along with rambling , hillwalking, and fell walking (a term mostly used for hillwalking in northern England). The term bushwalking i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Step Aerobics
Step aerobics, also known as bench aerobics and step training, is a form of aerobic exercise that involves stepping on and off a small platform. Step aerobics was studied by physiologists in the 1980s, and in 1990 it swiftly grew in popularity in the U.S. as a style of health club exercise, largely because of promotion by Reebok of the Step Reebok device and associated exercise routines, prominently advocated by Gin Miller. Step aerobics attracted more men to group exercise classes. At its peak in 1995, there were 11.4 million people doing step aerobics. Today, step aerobics classes are carried by many health clubs. Exercise routines include weights held in the hands for upper body development. Music with a medium (not fast) tempo often accompanies the routine, and learning a choreography sequence can hold the participants' interest. History Background Aerobics traces its origin to the 1968 book ''Aerobics'' by Dr. Kenneth H. Cooper, which inspired Jacki Sorensen to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |