|
Constantine Phokas
Constantine Phokas ( gr, Κωνσταντῖνος Φωκᾶς; died 953/954) was a Byzantine aristocrat and general. Life Constantine was the youngest son of Bardas Phokas the Elder, and brother of the general and later emperor Nikephoros II Phokas and the general Leo Phokas the Younger. When his father was appointed as Domestic of the Schools (commander-in-chief of the Byzantine army) in 945, Constantine was appointed (military governor) of the theme of Seleucia, on the Empire's southeastern border with the Muslim world. He participated in his father's campaigns against the Muslims, and was captured by the Hamdanid Emir of Aleppo, Sayf al-Dawla, at the Battle of Marash in 953. Constantine took part in Sayf al-Dawla's subsequent triumphal entry into Aleppo, but he soon fell ill and died (probably in early 954). Some Byzantine sources suggest that he was poisoned by Sayf al-Dawla after refusing to convert to Islam, while Arab sources claim that he was poisoned by Byzantine agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
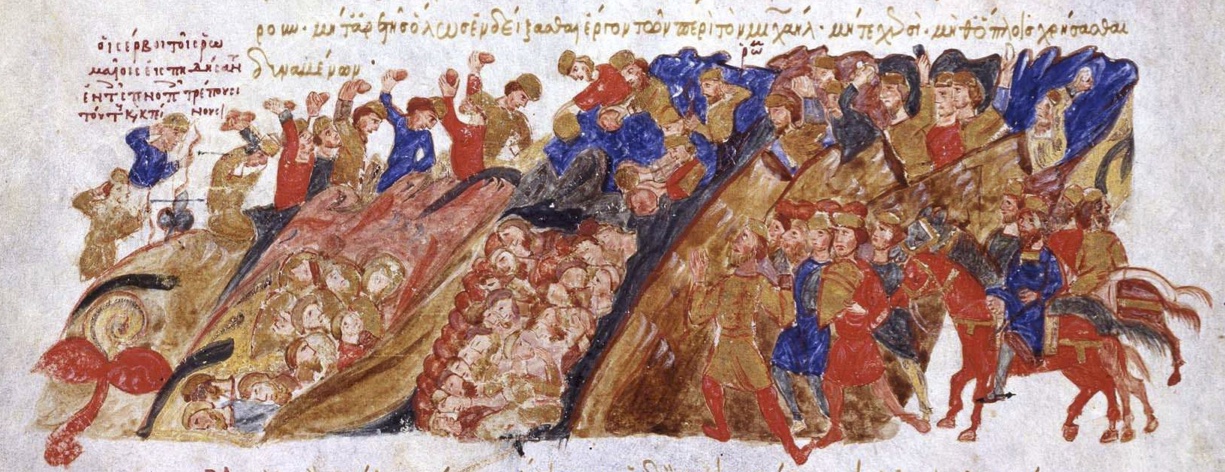
Madrid Skylitzes
The ''Madrid Skylitzes'' is a richly illustrated illuminated manuscript of the ''Synopsis of Histories'' ( el, Σύνοψις Ἱστοριῶν, ), by John Skylitzes, which covers the reigns of the Byzantine emperors from the death of Nicephorus I in 811 to the deposition of Michael VI in 1057. The manuscript was produced in Sicily in the 12th century, and is now at the Biblioteca Nacional de España in Madrid, with the shelfmark MS Graecus Vitr. 26–2. Other names for it are and . Apart from the very fragmentary 6th-century Alexandrian World Chronicle, it is the only surviving illustrated manuscript of a Greek chronicle, and includes 574 miniatures. It is unclear whether these illustrations are copies of earlier Byzantine images or were newly created specifically for this copy. Bibliography * Color facsimile edition by Militos (Μίλητος) Publishers, . * Vasiliki Tsamakda, The Illustrated Chronicle of Ioannes Skylitzes, Leiden 2002. * Bente Bjørnholt and J. Burke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamdanid
The Hamdanid dynasty ( ar, الحمدانيون, al-Ḥamdāniyyūn) was a Twelver Shia Arab dynasty of Northern Mesopotamia and Syria (890–1004). They descended from the ancient Banu Taghlib Christian tribe of Mesopotamia and Eastern Arabia. History The Hamdanid dynasty was founded by Hamdan ibn Hamdun. By 892–893, he was in possession of Mardin, after fighting the Kharijites of the Jazira. In 895, Caliph al-Mutadid invaded and Hamdan fled Mardin. Hamdan's son, Husayn, who was at Ardumusht, joined the caliph's forces. Hamdan later surrendered to the caliph and was imprisoned. In December 908, Husayn conspired to establish Ibn al-Mu'tazz as Caliph. Having failed, Husayn fled until he asked for mediation through his brother Ibrahim. Upon his return, he was made governor of Diyar Rabi'a. In 916, Husayn, due to a disagreement with vizier Ali b. Isa, revolted, was captured, imprisoned, and executed in 918. Hamdan's other son, Abdallah, was made governor of Mosul i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine People Of The Arab–Byzantine Wars
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phokas Family
Phokas ( grc-gre, Φωκᾶς, ''Phōkâs'') or Phocas (from Latin), feminine form Phokaina or Phocaina (, ''Phṓkaina''), was the name of a Byzantine aristocratic clan from Cappadocia, which in the 9th and 10th centuries provided a series of high-ranking generals and an emperor, Nikephoros II Phokas (963–969). Its members and their clients monopolized the high-command positions of the Byzantine army for much of the 10th century and led the successful Byzantine offensive against the Arabs in the East. As one of the leading families of the Anatolian military aristocracy, the Phokades were also involved in a series of rebellions that laid claim to power and challenged the emperors at Constantinople. Their power was eventually broken by Basil II (r. 976–1025), and the family declined in importance after the 11th century. History Origin and early members According to Michael Attaleiates, the family descended from the ancient Roman '' gens Fabia'', while Ali ibn al-Athir ascribed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Governors
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Generals
A Byzantine fault (also Byzantine generals problem, interactive consistency, source congruency, error avalanche, Byzantine agreement problem, and Byzantine failure) is a condition of a computer system, particularly distributed computing systems, where components may fail and there is imperfect information on whether a component has failed. The term takes its name from an allegory, the "Byzantine generals problem", developed to describe a situation in which, in order to avoid catastrophic failure of the system, the system's actors must agree on a concerted strategy, but some of these actors are unreliable. In a Byzantine fault, a component such as a server can inconsistently appear both failed and functioning to failure-detection systems, presenting different symptoms to different observers. It is difficult for the other components to declare it failed and shut it out of the network, because they need to first reach a consensus regarding which component has failed in the first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th-century Byzantine Military Personnel
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
950s Deaths
{{Numberdis ...
95 or 95th may refer to: * 95 (number) * one of the years 95 BC, AD 95, 1995, 2095, etc. * 95th Division (other) * 95th Regiment ** 95th Regiment of Foot (other) * 95th Squadron (other) * Atomic number 95: americium *Microsoft Office 95 * Saab 95 * Windows 95 See also * 9 to 5 (other) * * List of highways numbered A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marash (953)
The Battle of Marash was fought in 953 near Marash (modern Kahramanmaraş) between the forces of the Byzantine Empire under the Domestic of the Schools Bardas Phokas the Elder, and of the Hamdanid Emir of Aleppo, Sayf al-Dawla, the Byzantines' most intrepid enemy during the mid-10th century. Despite being outnumbered, the Arabs defeated the Byzantines who broke and fled. Bardas Phokas himself barely escaped through the intervention of his attendants, and suffered a serious wound on his face, while his youngest son and governor of Seleucia, Constantine Phokas, was captured and held a prisoner in Aleppo until his death of an illness some time later. This debacle, coupled with defeats in 954 and again in 955, led to Bardas Phokas' dismissal as Domestic of the Schools, and his replacement by his eldest son, Nikephoros Phokas (later emperor in 963–969). Background In the period from 945 to 967, the Hamdanid Emir of Aleppo, Sayf al-Dawla, was the Byzantines' most persistent oppone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emir Of Aleppo
The rulers of Aleppo ruled as kings, emirs and sultans of the city and its surrounding region since the later half of the 3rd millennium BC, starting with the kings of Armi, followed by the Amorite dynasty of Yamhad. Muslim rule of the city ended with the Ayyubid dynasty which was ousted by the Mongol conquest in 1260. The rulers of Yamhad used the titles of king and Great King, while the Hittite dynasty monarchs used the titles of king and viceroy. The Emirate of Halab was established in 945 by the Hamdanid dynasty and lasted until 1086, when it became a sultanate under the Seljuq dynasty. The sultanate was sometimes ruled together with Damascus under the same sultan. The Artuqids rulers used the titles of Malik and emir, as did the Zengid rulers which added the title atabeg. The Ayyubid monarchs used the titles of sultan and malik. The dates for Yamhad and the Hittite Dynasties are proximate and calculated by the Middle chronology. Yamhad Dynasty Yamhad was the name o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucia (theme)
The Theme of Seleucia ( el, θέμα Σελευκείας, ''thema Seleukeias'') was a Byzantine theme (a military-civilian province) in the southern coast of Asia Minor (modern Turkey), headquartered at Seleucia (modern Silifke). History In Late Antiquity, the port of Seleucia was the chief city of the Roman province of Isauria and seat of the ''comes Isauriae''.. In the 8th century, it is attested as a subordinate command, first under a ''tourmarches'' and then under a ''droungarios'', of the naval theme of the Cibyrrhaeots. In the early 9th century, however, it appears as a small ''kleisoura'' (a fortified frontier command) sandwiched between the larger Byzantine themes of the Cibyrrhaeots, the Anatolics, and Cappadocia and the sea, and bordering on the Abbasid Caliphate's domains in Cilicia along the river Lamos... According to the Arab geographers Qudamah ibn Ja'far and Ibn Khordadbeh, in the 9th century the ''kleisoura'' comprised Seleucia as capital and ten other fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |