|
Constance Jones (actress)
Emily Elizabeth Constance Jones (19 February 1848 – 9 April 1922) known as Constance Jones or E.E. Constance Jones, was an English philosopher and educator. She worked in logic and ethics and served as mistress of Girton College, Cambridge from 1903 to 1916. Life and career Emily Elizabeth Constance Jones was born at Langstone Court, Llangarron, Herefordshire, to John Jones and his wife, Emily, daughter of Thomas Oakley JP, of Monmouthshire. She was the eldest of ten children. Constance was mostly tutored at home. She spent her early teenage years with her family in Cape Town, South Africa, and when they returned to England in 1865 she attended a small school, Miss Robinson's, in Cheltenham, for a year. She was coached for the entrance examination for Girton College, Cambridge by Miss Alice Grüner, a former student of Newnham College at her home in Sydenham, Kent. She went up to Girton in 1875 where, prompted by having read Henry Fawcett's ''Political Economy'' (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some sources claim the term was coined by Pythagoras ( BCE), although this theory is disputed by some. Philosophical methods include questioning, critical discussion, rational argument, and systematic presentation. in . Historically, ''philosophy'' encompassed all bodies of knowledge and a practitioner was known as a ''philosopher''."The English word "philosophy" is first attested to , meaning "knowledge, body of knowledge." "natural philosophy," which began as a discipline in ancient India and Ancient Greece, encompasses astronomy, medicine, and physics. For example, Newton's 1687 ''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'' later became classified as a book of physics. In the 19th century, the growth of modern research universiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A System Of Logic
''A System of Logic, Ratiocinative and Inductive'' is an 1843 book by English philosopher John Stuart Mill. Overview In this work, he formulated the five principles of inductive reasoning that are known as Mill's Methods. This work is important in the philosophy of science, and more generally, insofar as it outlines the empirical principles Mill would use to justify his moral and political philosophies. An article in "Philosophy of Recent Times" has described this book as an "attempt to expound a psychological system of logic within empiricist principles.” This work was important to the history of science, being a strong influence on scientists such as Dirac. ''A System of Logic'' also had an impression on Gottlob Frege, who rebuked many of Mill's ideas about the philosophy of mathematics in his work ''The Foundations of Arithmetic''. Mill revised the original work several times over the course of thirty years in response to critiques and commentary by Whewell, Bain Bain may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
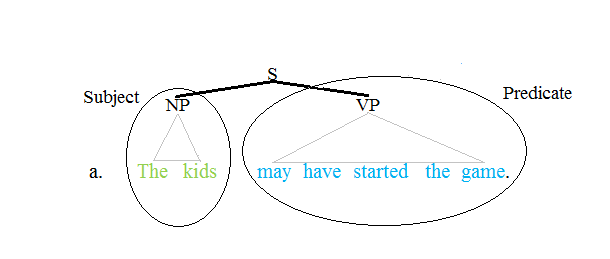
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in one of two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject, and the other views it as just the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake''. By the second definition, the predicate of the same sentence is just the content verb ''likes'', whereby ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the arguments of this predicate. Differences between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of predicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Categorical Proposition
In logic, a categorical proposition, or categorical statement, is a proposition that asserts or denies that all or some of the members of one category (the ''subject term'') are included in another (the ''predicate term''). The study of arguments using categorical statements (i.e., syllogisms) forms an important branch of deductive reasoning that began with the Ancient Greeks. The Ancient Greeks such as Aristotle identified four primary distinct types of categorical proposition and gave them standard forms (now often called ''A'', ''E'', ''I'', and ''O''). If, abstractly, the subject category is named ''S'' and the predicate category is named ''P'', the four standard forms are: *All ''S'' are ''P''. (''A'' form, \forall _\rightarrow P_xequiv \forall neg S_\lor P_x/math>) *No ''S'' are ''P''. (''E'' form, \forall _\rightarrow \neg P_xequiv \forall neg S_\lor \neg P_x/math>) *Some ''S'' are ''P''. (''I'' form, \exists _\land P_x/math>) *Some ''S'' are not ''P''. (''O'' form, \ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Moral Sciences Club
The Cambridge University Moral Sciences Club, founded in October 1878, is a philosophy discussion group that meets weekly at the University of Cambridge during term time. Speakers are invited to present a paper with a strict upper time limit of 45 minutes, after which there is discussion for an hour. Several Colleges have hosted the Club: Trinity College, King's College, Clare College, Darwin College, St John's College, and from 2014 Newnham College. The club has been highly influential in analytic philosophy because of the concentration of philosophers at Cambridge. Members have included many of British philosophy's top names, such as Henry Sidgwick, J.M.E. McTaggart, Bertrand Russell, G.E. Moore, and Ludwig Wittgenstein, and several papers regarded as founding documents of various schools of thoughts had their first airing at a club meeting. Moore's "The Nature of Judgment" was first read to the club on 21 October 1898. "Knowledge by acquaintance and knowledge by description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotelian Society
The Aristotelian Society for the Systematic Study of Philosophy, more generally known as the Aristotelian Society, is a philosophical society in London. History Aristotelian Society was founded at a meeting on 19 April 1880, at 17 Bloomsbury Square, London. It resolved "to constitute a society of about twenty and to include ladies; the society to meet fortnightly, on Mondays at 8 o'clock, at the rooms of the Spelling Reform Association…" The rules of the society stipulated: According to H. Wildon Carr, in choosing a name for the society, it was: The society's first president was Mr. Shadworth H. Hodgson. He was president for fourteen years from 1880 until 1894, when he proposed Dr. Bernard Bosanquet as his replacement. Professor Alan Willard Brown noted in 1947 that 'he Societys members were not all men of established intellectual position. It welcomed young minds just out of university as well as older amateur philosophers with serious interests and purposes. But many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Martineau
James Martineau (; 21 April 1805 – 11 January 1900) was a British religious philosopher influential in the history of Unitarianism. For 45 years he was Professor of Mental and Moral Philosophy and Political Economy in Manchester New College (now Harris Manchester College, of the University of Oxford), the principal training college for British Unitarianism. Many portraits of Martineau, including one painted by George Frederick Watts, are held at London's National Portrait Gallery. In 2014, the gallery revealed that its patron, Catherine, Princess of Wales, was related to Martineau. The Princess's great-great-grandfather, Francis Martineau Lupton, was Martineau's grandnephew. The gallery also holds written correspondence between Martineau and Poet Laureate, Alfred, Lord Tennyson - who records that he "regarded Martineau as the mastermind of all the remarkable company with whom he engaged". Martineau and Lord Tennyson were familiar with Queen Victoria's son, Prince Leopol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer (27 April 1820 – 8 December 1903) was an English philosopher, psychologist, biologist, anthropologist, and sociologist famous for his hypothesis of social Darwinism. Spencer originated the expression "survival of the fittest", which he coined in ''Principles of Biology'' (1864) after reading Charles Darwin's 1859 book ''On the Origin of Species''. The term strongly suggests natural selection, yet Spencer saw evolution as extending into realms of sociology and ethics, so he also supported Lamarckism. Riggenbach, Jeff (24 April 2011The Real William Graham Sumner, Mises Institute. Spencer developed an all-embracing conception of evolutionism, evolution as the progressive development of the physical world, biological organisms, the human mind, and human culture and societies. As a polymath, he contributed to a wide range of subjects, including ethics, religion, anthropology, economics, political theory, philosophy, literature, astronomy, biology, sociology, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Hill Green
Thomas Hill Green (7 April 183626 March 1882), known as T. H. Green, was an English philosopher, political radical and temperance reformer, and a member of the British idealism movement. Like all the British idealists, Green was influenced by the metaphysical historicism of G. W. F. Hegel. He was one of the thinkers behind the philosophy of social liberalism. Life Green was born on 7 April 1836 at Birkin, in the West Riding of Yorkshire, England, where his father was rector. On his paternal side, he was descended from Oliver Cromwell. His education was conducted entirely at home until, at the age of 14, he entered Rugby, where he remained for five years. In 1855, he became an undergraduate member of Balliol College, Oxford, and was elected fellow in 1860. He began a life of teaching (mainly philosophical) in the university—first as college tutor, afterwards, from 1878 until his death, as Whyte's Professor of Moral Philosophy. The lectures he delivered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methods Of Ethics
''The Methods of Ethics'' is a book on ethics first published in 1874 by the English philosopher Henry Sidgwick. The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' indicates that ''The Methods of Ethics'' "in many ways marked the culmination of the classical utilitarian tradition." Noted moral and political philosopher John Rawls, writing in the Forward to the Hackett reprint of the 7th edition, says ''Methods of Ethics'' "is the clearest and most accessible formulation of ... 'the classical utilitarian doctrine'". Contemporary utilitarian philosopher Peter Singer has said that the ''Methods'' "is simply the best book on ethics ever written." The main aim of the book is to provide a systematic account of the principles of ''commonsense morality''. The three general methods of making ethical choices commonly used in ordinary morality are intuitionism (following general principles), egoism (promoting one's own well-being) and utilitarianism (promoting everyone's well-being). Accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Hamilton (writer)
Elizabeth Hamilton (1756 or 1758 – 23 July 1816) was a Scottish essayist, poet, satirist and novelist, who in both her prose and fiction entered into the French-revolutionary era controversy in Britain over the education and rights of women. Early life She was most probably born on 25 July 1756, though the date is often given as 1758. She was born in Belfast, the third and youngest child of Charles Hamilton (''d''.1759), a Scottish merchant, and his wife Katherine Mackay (''d''.1767). In Belfast Hamilton's parents were on familiar terms with the town's prominent "New Light" Presbyterian families and with their Scottish Enlightenment social and political ideas. Her later thoughts on child education were greatly influenced by David Manson's co-educational English Grammar School, which her older sister Katherine attended with other children from this progressive milieu. Manson advertised the school's capacity to teach children to read and understand the English tongue "without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Lotze
Rudolf Hermann Lotze (; ; 21 May 1817 – 1 July 1881) was a German philosopher and logician. He also had a medical degree and was well versed in biology. He argued that if the physical world is governed by mechanical laws and relations, then developments in the universe could be explained as the functioning of a world mind. His medical studies were pioneering works in scientific psychology. Biography Lotze was born in Bautzen, Saxony, Germany, the son of a physician. He was educated at the grammar school of Zittau; he had an enduring love of the classical authors, publishing a translation of Sophocles' ''Antigone'' into Latin verse in his middle life. He attended the University of Leipzig as a student of philosophy and natural sciences, but entered officially as a student of medicine when he was seventeen. Lotze's early studies were mostly governed by two distinct interests: the first was scientific, based upon mathematical and physical studies under the guidance of E. H. Web ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |