|
Conium Maculatum - Köhler–s Medizinal-Pflanzen-191
''Conium'' ( or ) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apiaceae. , Plants of the World Online accepts six species. All species of the genus are poisonous to humans. ''C. maculatum'', also known as hemlock, is infamous for being highly poisonous. Hemlock is native to temperate regions of Europe, North Africa and Western Asia. The species ''C. chaerophylloides'', ''C. fontanum'', and ''C. sphaerocarpum'' are all native to southern Africa. Description Plants of the genus ''Conium'' are eudicots, flowering plants distinguished by their two cotyledons (embryonic leaves) and tricolpate (three-pored) pollen. They are typically biennial, forming basal rosettes in the first year of growth, and sprouting a rigid, hollow flower stalk in the second. Germination occurs between spring and autumn. Occasionally, plants which germinate in early spring are annual instead of biennial. These plants grow best in wet, poorly drained areas with nutrient rich soil. They grow well in nitrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Ludwig Philipp Zeyher
Karl Ludwig Philipp Zeyher (2 August 1799 Dillenburg, Hessen, Holy Roman Empire – 13 December 1858 Cape Town), was a botanical and insect collector who collected extensively in Cape Colony. He was the author, with Christian Friedrich Ecklon, of ''Enumeratio Plantarum Africae Australis'' (1835-7), a descriptive catalogue of South African plants. In 1816 Zeyher was apprenticed to his uncle Johann Michael Zeyher who was head gardener at the ducal gardens of Schwetzingen. Here he met Franz Sieber and was talked into a partnership with the aim of collecting and selling natural history specimens - a burgeoning industry in the 19th century. They sailed for Mauritius in August 1822, however Zeyher was left at the Cape while Sieber went on to Mauritius and Australia. On his return in April 1824, Sieber picked up the specimens collected by Zeyher, assuring him of payment in due course. Sieber distributed a number of these specimens in his exsiccata named ''Flora Capensis''. No payment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
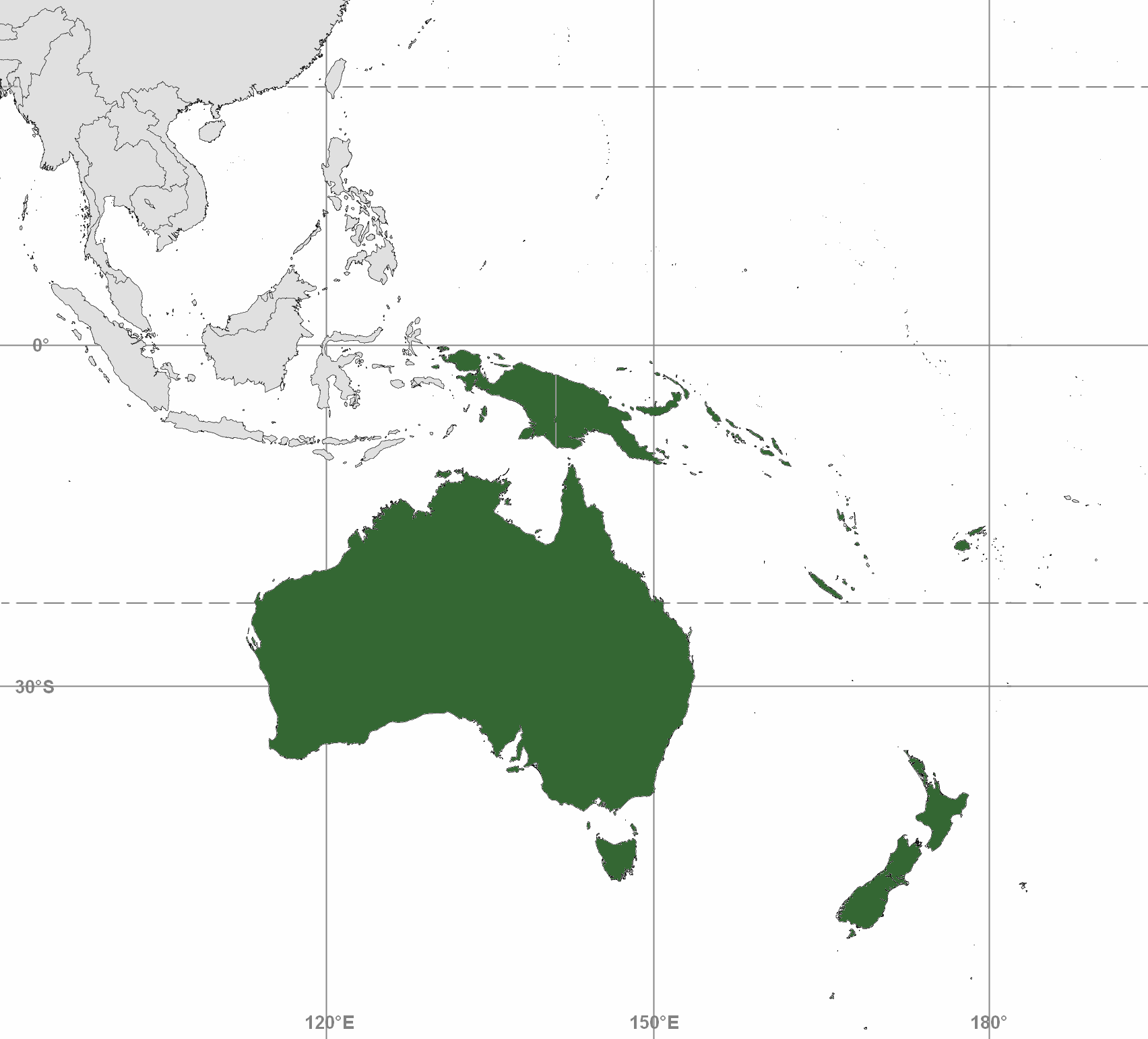
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the center (geometry), ''center'' of the sphere, and the distance is the sphere's ''radius''. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental surface in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is spherical Earth, often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conium Maculatum - Köhler–s Medizinal-Pflanzen-191
''Conium'' ( or ) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apiaceae. , Plants of the World Online accepts six species. All species of the genus are poisonous to humans. ''C. maculatum'', also known as hemlock, is infamous for being highly poisonous. Hemlock is native to temperate regions of Europe, North Africa and Western Asia. The species ''C. chaerophylloides'', ''C. fontanum'', and ''C. sphaerocarpum'' are all native to southern Africa. Description Plants of the genus ''Conium'' are eudicots, flowering plants distinguished by their two cotyledons (embryonic leaves) and tricolpate (three-pored) pollen. They are typically biennial, forming basal rosettes in the first year of growth, and sprouting a rigid, hollow flower stalk in the second. Germination occurs between spring and autumn. Occasionally, plants which germinate in early spring are annual instead of biennial. These plants grow best in wet, poorly drained areas with nutrient rich soil. They grow well in nitrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbel
UMBEL (Upper Mapping and Binding Exchange Layer) is a logically organized knowledge graph of 34,000 concepts and entity types that can be used in information science for relating information from disparate sources to one another. It was retired at the end of 2019. UMBEL was first released in July 2008. Version 1.00 was released in February 2011. Its current release is version 1.50. The grounding of this information occurs by common reference to the permanent URIs for the UMBEL concepts; the connections within the UMBEL upper ontology enable concepts from sources at different levels of abstraction or specificity to be logically related. Since UMBEL is an open-source extract of the OpenCyc knowledge base, it can also take advantage of the reasoning capabilities within Cyc. UMBEL has two means to promote the semantic interoperability of information:. It is: * An ontology of about 35,000 reference concepts, designed to provide common mapping points for relating different on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obconic
In botany, an obconic is an inverted cone shape. The term is most frequently applied to certain fruit or hypanthium structures with the apical end attached to the stem; however, less frequently the usage may apply to the pistil structure. In the case of fungi the designation is often made to the ascospore. The use of ''obconic'' in botany dates to at least as early as the nineteenth century; however, some modern usage applies to an entire plant form, such as the shape of a whole shrub. More broadly, in geometry or design, the term can be assigned in an abstract manner to shapes in the natural or man-made world which show an inverted cone design. Botanical examples The carnivorous plant '' Nepenthes deaniana'' has pitcher elements that are obconic in shape to capture insects. The hypanthium of the western USA plant '' Heuchera rubescens'' has one subspecies with an obconic structure, while several other subspecies have alternative hypantium geometries, so that the obconic characteris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conium Sphaerocarpum
''Conium'' ( or ) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apiaceae. , Plants of the World Online accepts six species. All species of the genus are poisonous to humans. ''C. maculatum'', also known as hemlock, is infamous for being highly poisonous. Hemlock is native to temperate regions of Europe, North Africa and Western Asia. The species ''C. chaerophylloides'', ''C. fontanum'', and ''C. sphaerocarpum'' are all native to southern Africa. Description Plants of the genus ''Conium'' are eudicots, flowering plants distinguished by their two cotyledons (embryonic leaves) and tricolpate (three-pored) pollen. They are typically biennial, forming basal rosettes in the first year of growth, and sprouting a rigid, hollow flower stalk in the second. Germination occurs between spring and autumn. Occasionally, plants which germinate in early spring are annual instead of biennial. These plants grow best in wet, poorly drained areas with nutrient rich soil. They grow well in nitrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conium Maculatum
''Conium maculatum'', commonly known as hemlock (British English) or poison hemlock (American English), is a highly poisonous flowering plant in the carrot family Apiaceae, native to Europe and North Africa. It is Herbaceous plant, herbaceous, with no woody parts, and has a Biennial plant, biennial lifecycle. Hemlock is a hardy plant capable of living in a variety of environments and is now widely naturalised in locations outside its native range, including parts of Australia, West Asia, and North and South America, to which it has been introduced. It is capable of spreading and thereby becoming an Invasive plant, invasive weed. All parts of the hemlock plant are Toxic plant, toxic, particularly the seeds and roots, and especially when ingested. Under the right conditions, the plant grows quite rapidly during the growing season, and can reach heights of , with a long Taproot, penetrating root. The plant has a distinctive odour that is usually considered unpleasant and carries with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conium Hilliburttorum
''Conium'' ( or ) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apiaceae. , Plants of the World Online accepts six species. All species of the genus are poisonous to humans. ''C. maculatum'', also known as hemlock, is infamous for being highly poisonous. Hemlock is native to temperate regions of Europe, North Africa and Western Asia. The species ''C. chaerophylloides'', ''C. fontanum'', and ''C. sphaerocarpum'' are all native to southern Africa. Description Plants of the genus ''Conium'' are eudicots, flowering plants distinguished by their two cotyledons (embryonic leaves) and tricolpate (three-pored) pollen. They are typically biennial, forming basal rosettes in the first year of growth, and sprouting a rigid, hollow flower stalk in the second. Germination occurs between spring and autumn. Occasionally, plants which germinate in early spring are annual instead of biennial. These plants grow best in wet, poorly drained areas with nutrient rich soil. They grow well in nitrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conium Divaricatum
''Conium divaricatum'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, native to Greece, including Crete. It was first described in 1856. The plant is phytochemically distinct from conium maculatum, and is considered a separate species. The Classical Greek philosopher Socrates Socrates (; ; – 399 BC) was a Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher from Classical Athens, Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and as among the first moral philosophers of the Ethics, ethical tradition ... is believed to have been executed with hemlock, though scholars are unsure whether it was c. maculatum or c. divaricatum. References Apioideae Flora of Crete Flora of Greece Plants described in 1856 {{Apiaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |