|
Concubines Of Charlemagne
Concubinage is an interpersonal and sexual relationship between a man and a woman in which the couple does not want, or cannot enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarded as similar but mutually exclusive. Concubinage was a formal and institutionalized practice in China until the 20th century that upheld concubines' rights and obligations. A concubine could be freeborn or of slave origin, and their experience could vary tremendously according to their masters' whim. During the Mongol conquests, both foreign royals and captured women were taken as concubines. Concubinage was also common in Meiji Japan as a status symbol, and in Indian society, where the intermingling of castes and religions was frowned upon and a taboo, and concubinage could be practiced with women with whom marriage was considered undesirable, such as those from a lower caste and Muslim women who wouldn't be accepted in a Hindu household and Hindu women who wouldn't be accepted in a M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François-Joseph Navez - Agar Et Ismaël Dans Le Désert
François-Joseph is a given name, and may refer to: * François-Joseph Amon d'Aby (1913–2007), Ivoirian playwright and essayist * François-Joseph de Beaupoil de Sainte-Aulaire (1643-1742), French poet and army officer * François-Joseph Bélanger (1744-1818), French architect and decorator * François-Joseph Bérardier de Bataut (1720-1794), French teacher, writer and translator * François-Joseph Bissot (1673–1737), Canadian merchant, navigator and a co-seigneur of Mingan; son of François Byssot de la Rivière * François-Joseph Bressani (1612-1672), Jesuit priest * Général François-Joseph Chaussegros de Léry (1754-1824), Canadian Engineer-in-Chief and Commander-in-Chief of Napoleon's Armies Armies in Holland * François-Joseph d'Offenstein (1760-1837), French general and military commander * François-Joseph de Champagny (1804–1882), French author and historian * François-Joseph Duret (1732-1816), French sculptor * François-Joseph Fétis (1784-1871), Belgian musicolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abolitionism
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people. The British abolitionist movement started in the late 18th century when English and American Quakers began to question the morality of slavery. James Oglethorpe was among the first to articulate the Enlightenment case against slavery, banning it in the Province of Georgia on humanitarian grounds, and arguing against it in Parliament, and eventually encouraging his friends Granville Sharp and Hannah More to vigorously pursue the cause. Soon after Oglethorpe's death in 1785, Sharp and More united with William Wilberforce and others in forming the Clapham Sect. The Somersett case in 1772, in which a fugitive slave was freed with the judgement that slavery did not exist under English common law, helped launch the British movement to abolish slavery. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feminine (grammar)
In linguistics, grammatical gender system is a specific form of noun class system, where nouns are assigned with gender categories that are often not related to their real-world qualities. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns inherently carry one value of the grammatical category called ''gender''; the values present in a given language (of which there are usually two or three) are called the ''genders'' of that language. Whereas some authors use the term "grammatical gender" as a synonym of "noun class", others use different definitions for each; many authors prefer "noun classes" when none of the inflections in a language relate to sex. Gender systems are used in approximately one half of the world's languages. According to one definition: "Genders are classes of nouns reflected in the behaviour of associated words." Overview Languages with grammatical gender usually have two to four different genders, but some are attested with up to 20. Common gender ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the ''Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I. Roman law forms the basic framework for Civil law (legal system), civil law, the most widely used legal system today, and the terms are sometimes used synonymously. The historical importance of Roman law is reflected by the continued use of List of legal Latin terms, Latin legal terminology in many legal systems influenced by it, including common law. After the dissolution of the Western Roman Empire, the Roman law remained in effect in the Eastern Roman Empire. From the 7th century onward, the legal language in the East was Greek. ''Roman law'' also denoted the legal system applied in most of Western Europe until the end of the 18th century. In Germany, Roman law practice remained in place longer under the Holy Roman Empire ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Society
The culture of ancient Rome existed throughout the almost 1200-year history of the civilization of Ancient Rome. The term refers to the culture of the Roman Republic, later the Roman Empire, which at its peak covered an area from present-day Lowland Scotland and Morocco to the Euphrates. Life in ancient Rome revolved around the city of Rome, its famed seven hills, and its monumental architecture such as the Colosseum, Trajan's Forum, and the Pantheon. The city also had several theaters and gymnasia, along with many taverns, baths and brothels. Throughout the territory under ancient Rome's control, residential architecture ranged from very modest houses to country villas, and in the capital city of Rome, there were imperial residences on the elegant Palatine Hill, from which the word ''palace'' is derived. The vast majority of the population lived in the city center, packed into ''insulae'' (apartment blocks). The city of Rome was the largest megalopolis of that time, with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohabitation
Cohabitation is an arrangement where people who are not married, usually couples, live together. They are often involved in a romantic or sexually intimate relationship on a long-term or permanent basis. Such arrangements have become increasingly common in Western countries since the late 20th century, being led by changing social views, especially regarding marriage, gender roles and religion. More broadly, the term ''cohabitation'' can mean any number of people living together. To "cohabit", in a broad sense, means to "coexist". The origin of the term comes from the mid 16th century, from the Latin ''cohabitare'', from co- 'together' + habitare 'dwell'. Social changes leading to increase Today, cohabitation is a common pattern among people in the Western world. In Europe, the Scandinavian countries have been the first to start this leading trend, although many countries have since followed. Mediterranean Europe has traditionally been very conservative, with religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judeo-Christian
The term Judeo-Christian is used to group Christianity and Judaism together, either in reference to Christianity's derivation from Judaism, Christianity's borrowing of Jewish Scripture to constitute the "Old Testament" of the Christian Bible, or due to the parallels or commonalities in Judaeo-Christian ethics shared by the two religions. The term "Judæo Christian" first appeared in the 19th century as a word for Jewish converts to Christianity. In the United States the term was widely used during the Cold War in an attempt to suggest that the United States had a unified American identity which was opposed to communism. Theologian and author Arthur A. Cohen, in ''The Myth of the Judeo-Christian Tradition'', questioned the theological validity of the Judeo-Christian concept, instead, he suggested that it was essentially an invention of American politics. The use of Abrahamic religions as a term for the common grouping of faiths which are attributed to Abraham, the Baháʼí Fait ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
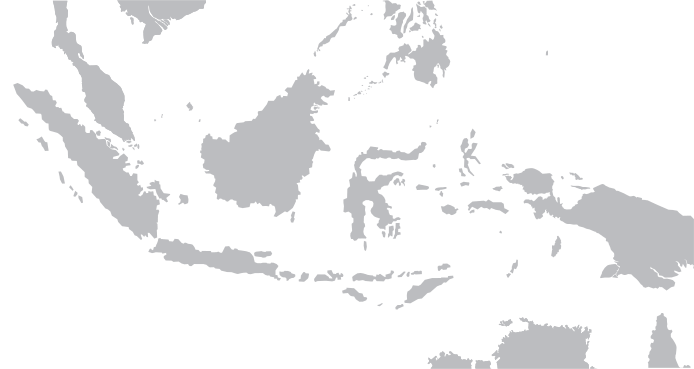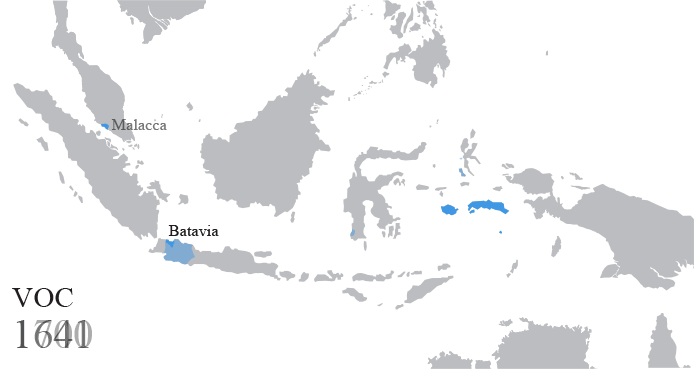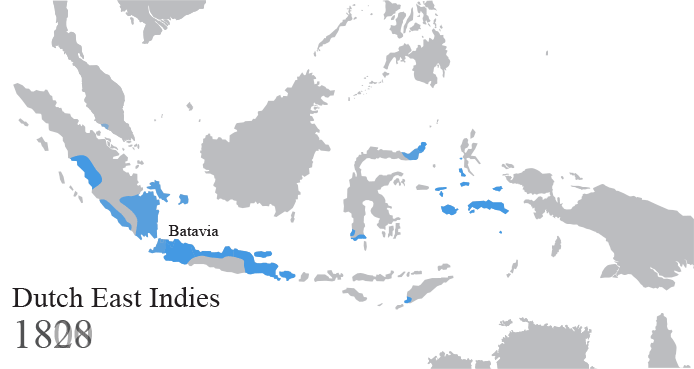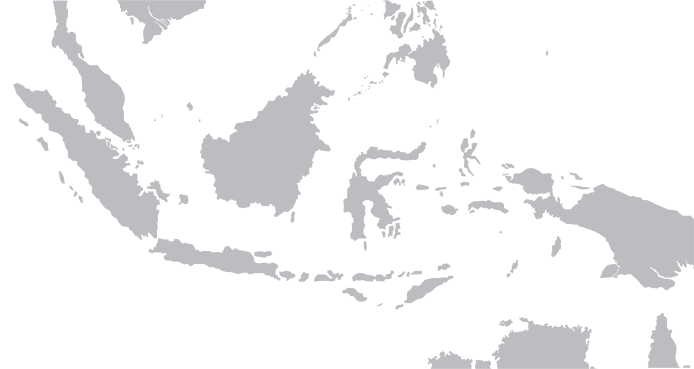
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
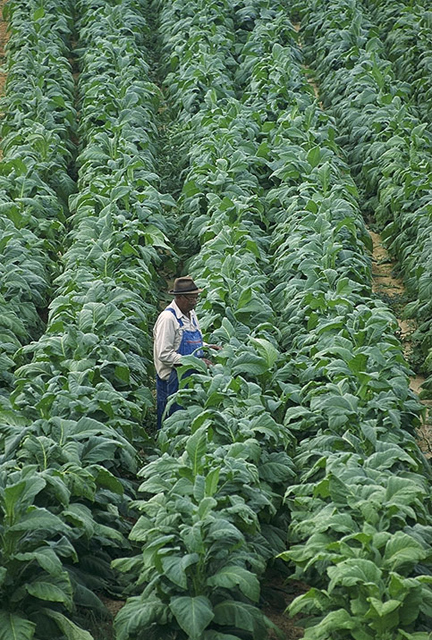
Slave Plantation
A slave plantation was an agricultural farm that used enslaved people for labour. The practice was abolished in most places during the 19th century. Slavery Planters embraced the use of slaves mainly because indentured labor became expensive. Some indentured servants were also leaving to start their own farms as land was widely available. Colonists tried to use Native Americans for labor, but they were susceptible to European diseases and died in large numbers. The plantation owners then turned to enslaved Africans for labor. In 1665, there were fewer than 500 Africans in Virginia but by 1750, 85 percent of the 235,000 slaves lived in the Southern colonies, Virginia included. Africans made up 40 percent of the South’s population. According to the 1840 United States Census, one out of every four families in Virginia owned slaves. There were over 100 plantation owners who owned over 100 slaves. The number of slaves in the 15 States was just shy of 4 million in a total po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Colonies
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs. Colonialism in the modern sense began with the "Age of Discovery", led by Portuguese, who became increasingly adventuresome following the conquest of Ceuta in 1415, aiming to control navigation through the Strait of Gibraltar, expand Christianity, obtain plunder, and suppress predation on Portuguese populations by Barbary pirates as part of a longstanding African slave trade; at that point a minor trade, one the Portuguese would soon reverse and surpass. Around 1450, based on North African fishing boats, a lighter ship was developed, the caravel, which could sail further and faster, was highly maneuverable, and could sail " into the wind". Enabled by new nautical technology, with the added incentive to find an alternative "Silk Road" after the Fall of Constantinople in 1453 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)