|
Concentrated Solar Still
A concentrated solar still is a system that uses the same quantity of solar heat input (same solar collection area) as a simple solar still but can produce a volume of freshwater that is many times greater. While a simple solar still is a way of distilling water by using the heat of the sun to drive evaporation from a water source and ambient air to cool a condenser film, a concentrated solar still uses a concentrated solar thermal collector to concentrate solar heat and deliver it to a multi-effect evaporation process for distillation, thus increasing the natural rate of evaporation. The concentrated solar still is capable of large-scale water production in areas with plentiful solar energy. Performance The concentrated solar still can produce as much as twenty times more water than the theoretical maximum of a standard solar still and in practice, can produce as much as 30x the volume. A typically 25% efficiency standard solar still (not allowing for any recovery of rejected l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diss ME
Diss or DISS may refer to: * Diss, Alberta, a place in Canada *Diss, Norfolk, a market town in England, United Kingdom **Diss railway station ** Diss Rugby Club **Diss Town F.C. * Diss grass, a Mediterranean grass *Diss (music) A diss track, diss record or diss song (diss – abbr. from ''disrespect'') is a song whose primary purpose is to verbally attack someone else, usually another artist. Diss tracks are often the result of an existing, escalating feud between the t ..., a song whose primary purpose is to verbally attack someone else, usually another artist *Department of Internal State Security, a fictional organization from the 2009 film '' District 13: Ultimatum'' * Directorate of Intelligence and Security Services, Botswana, an intelligence agency * Smaïl Diss (born 1976), Algerian football player * Dissertation See also * Dis (other) * Disrespect {{disambiguation, geo, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
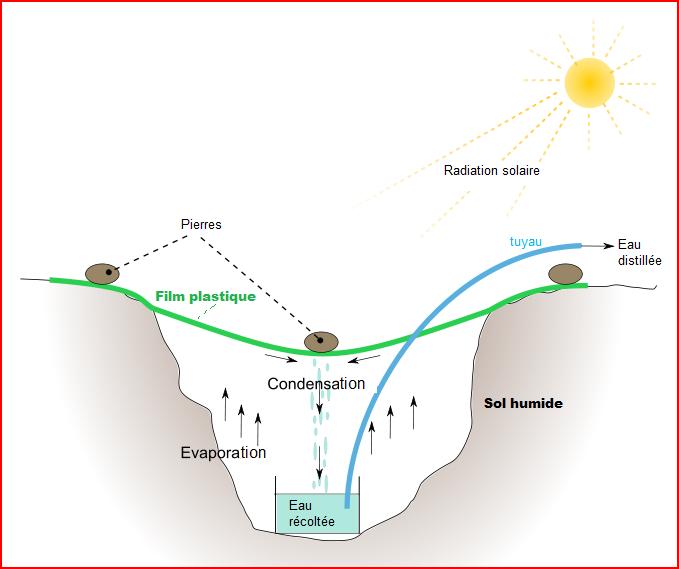
Solar Still
A solar still distills water with substances dissolved in it by using the heat of the Sun to evaporate water so that it may be cooled and collected, thereby purifying it. They are used in areas where drinking water is unavailable, so that clean water is obtained from dirty water or from plants by exposing them to sunlight. Still types include large scale concentrated solar stills and condensation traps. In a solar still, impure water is contained outside the collector, where it is evaporated by sunlight shining through a transparent collector. The pure water vapour condenses on the cool inside surface and drips into a tank. Distillation replicates the way nature makes rain. The sun's energy heats water to the point of evaporation. As the water evaporates, its vapour rises, condensing into water again as it cools. This process leaves behind impurities, such as salts and heavy metals, and eliminates microbiological organisms. The end result is pure (potable) water. History C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distilling
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the heating of solid materials to produce gaseous products (which may condense into liquids or solids); this may involve chemical changes such as destructive distillation or cracking. Distillation may result in essentially complete separation (resulting in nearly pure components), or it may be a partial separation that increases the concentration of selected components; in either case, the process exploits differences in the relative volatility of the mixture's components. In industrial applications, distillation is a unit operation of practically universal importance, but is a physical separation process, not a chemical reaction. An installation used for distillation, especially of distilled beverages, is a distillery. Distillation includes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentrated Solar Thermal
Concentrated solar power (CSP, also known as concentrating solar power, concentrated solar thermal) systems generate solar power by using mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight into a receiver. Electricity is generated when the concentrated light is converted to heat (solar thermal energy), which drives a heat engine (usually a steam turbine) connected to an electrical power generator or powers a thermochemical reaction. CSP had a global total installed capacity of 6,800 MW in 2021, up from 354 MW in 2005. Spain accounted for almost one third of the world's capacity, at 2,300 MW, despite no new capacity entering commercial operation in the country since 2013. The United States follows with 1,740 MW. Interest is also notable in North Africa and the Middle East, as well as China and India. The global market was initially dominated by parabolic-trough plants, which accounted for 90% of CSP plants at one point. Since about 2010, central p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple-effect Distillation
Multiple-effect distillation or multi-effect distillation (MED) is a distillation process often used for sea water desalination. It consists of multiple stages or "effects". In each stage the feed water is heated by steam in tubes, usually by spraying saline water onto them. Some of the water evaporates, and this steam flows into the tubes of the next stage (effect), heating and evaporating more water. Each stage essentially reuses the energy from the previous stage, with successively lower temperatures and pressures after each one. There are different configurations, such as forward-feed, backward-feed, etc. Additionally, between stages this steam uses some heat to preheat incoming saline water. Operating principles The plant can be seen as a sequence of closed spaces separated by tube walls, with a heat source in one end and a heat sink in the other end. Each space consists of two communicating subspaces, the exterior of the tubes of stage ''n'' and the interior of the tubes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Heat Of Vaporization
The enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure at which that transformation takes place. The enthalpy of vaporization is often quoted for the normal boiling temperature of the substance. Although tabulated values are usually corrected to 298 K, that correction is often smaller than the uncertainty in the measured value. The heat of vaporization is temperature-dependent, though a constant heat of vaporization can be assumed for small temperature ranges and for reduced temperature T_r \ll 1. The heat of vaporization diminishes with increasing temperature and it vanishes completely at a certain point called the critical temperature (T_r = 1). Above the critical temperature, the liquid and vapor phases are indistinguishable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Irradiation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m2) in SI units. Solar irradiance is often integrated over a given time period in order to report the radiant energy emitted into the surrounding environment (joule per square metre, J/m2) during that time period. This integrated solar irradiance is called solar irradiation, solar exposure, solar insolation, or insolation. Irradiance may be measured in space or at the Earth's surface after atmospheric absorption and scattering. Irradiance in space is a function of distance from the Sun, the solar cycle, and cross-cycle changes.Michael Boxwell, ''Solar Electricity Handbook: A Simple, Practical Guide to Solar Energy'' (2012), p. 41–42. Irradiance on the Earth's surface additionally depends on the tilt of the measuring surface, the height ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be condens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple-effect Evaporator
A multiple-effect evaporator, as defined in chemical engineering, is an apparatus for efficiently using the heat from steam to evaporate water. Water is boiled in a sequence of vessels, each held at a lower pressure than the last. Because the boiling temperature of water decreases as pressure decreases, the vapor boiled off in one vessel can be used to heat the next, and only the first vessel (at the highest pressure) requires an external source of heat. While in theory, evaporators may be built with an arbitrarily large number of stages, evaporators with more than four stages are rarely practical except in systems where the liquor is the desired product such as in chemical recovery systems where up to seven effects are used. The multiple-effect evaporator was invented by an African-American inventor and engineer Norbert Rillieux. Although he may have designed the apparatus during the 1820s and constructed a prototype in 1834, he did not build the first industrially practical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prentice Hall
Prentice Hall was an American major educational publisher owned by Savvas Learning Company. Prentice Hall publishes print and digital content for the 6–12 and higher-education market, and distributes its technical titles through the Safari Books Online e-reference service. History On October 13, 1913, law professor Charles Gerstenberg and his student Richard Ettinger founded Prentice Hall. Gerstenberg and Ettinger took their mothers' maiden names, Prentice and Hall, to name their new company. Prentice Hall became known as a publisher of trade books by authors such as Norman Vincent Peale; elementary, secondary, and college textbooks; loose-leaf information services; and professional books. Prentice Hall acquired the training provider Deltak in 1979. Prentice Hall was acquired by Gulf+Western in 1984, and became part of that company's publishing division Simon & Schuster. S&S sold several Prentice Hall subsidiaries: Deltak and Resource Systems were sold to National Education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Pump
A heat pump is a device that can heat a building (or part of a building) by transferring thermal energy from the outside using a refrigeration cycle. Many heat pumps can also operate in the opposite direction, cooling the building by removing heat from the enclosed space and rejecting it outside. Units that only provide cooling are called air conditioners. When in heating mode, a refrigerant at outside temperature is being compressed. As a result, the refrigerant becomes hot. This thermal energy can be transferred to an indoor unit. After being moved outdoors again, the refrigerant is decompressed — evaporated. It has lost some of its thermal energy and returns colder than the environment. It can now take up the surrounding energy from the air or from the ground before the process repeats. Compressors, fans, and pumps run with electric energy. Common types are air-source heat pumps, ground-source heat pumps, water-source heat pumps and exhaust air heat pumps. They are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic effect. Concentrated solar power systems use lens (optics), lenses or mirrors and solar tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight to a hot spot, often to drive a steam turbine. Photovoltaics were initially solely used as a source of electricity for small and medium-sized applications, from the calculator powered by a single solar cell to remote homes powered by an off-grid rooftop PV system. Commercial concentrated solar power plants were first developed in the 1980s. Since then, as the cost of solar electricity has fallen, grid-connected solar PV systems have Growth of photovoltaics, grown more or less exponentially. Millions of installations and gigawatt-scale photovoltaic power stations continue to be built, with half of new gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |