|
Computer Simulation Technology
Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp. is a computer-aided engineering (CAE) vendor. Formerly known as Abaqus Inc. and previously Hibbitt, Karlsson & Sorensen, Inc., (HKS), the company was founded in 1978 by David Hibbitt, Bengt Karlsson and Paul Sorensen, and has its headquarters in Providence, Rhode Island. In October 2005, Dassault Systèmes acquired Abaqus, Inc. and announced Simulia, the brand encompassing all DS simulation solutions, including Abaqus and Catia Analysis applications. Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp. is the legal entity that encompasses the Simulia brand of Dassault Systèmes. Abaqus product suite The Abaqus suite consists of three core products - Abaqus/Standard, Abaqus/Explicit and Abaqus/CAE (Complete Abaqus Environment). In addition to this, recent versions of Abaqus (6.10 onwards) also contain Abaqus/CFD for computational fluid dynamic simulations. Each of these packages offers additional, optional modules that address specialized capabilities require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dassault Systèmes
Dassault Systèmes SE () (abbreviated 3DS) is a French software corporation which develops software for 3D product design, simulation, manufacturing and other 3D related products. Founded in 1981, it is headquartered in Vélizy-Villacoublay, France, and has around 20,000 employees in 140 countries. History 1980s Dassault Systèmes (3DS) grew out of the aerospace industry’s search for more sophisticated drafting tools to streamline the development process and aid in the increasing complexity of aviation design. Dassault Systemes spun out in 1981 (as part of Dassault Group.) to develop and market Dassault's 3D surface design software CATI, later renamed CATIA. That same year, 3DS signed a sales and marketing agreement with IBM, allowing IBM to resell the CATIA CAD software. 1990s In the 1990s, 3DS’ software was used to develop seven out of every ten new airplanes and four out of every ten new cars worldwide. Major players in the aviation and automotive industries, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle-in-cell
In plasma physics, the particle-in-cell (PIC) method refers to a technique used to solve a certain class of partial differential equations. In this method, individual particles (or fluid elements) in a Lagrangian frame are tracked in continuous phase space, whereas moments of the distribution such as densities and currents are computed simultaneously on Eulerian (stationary) mesh points. PIC methods were already in use as early as 1955, even before the first Fortran compilers were available. The method gained popularity for plasma simulation in the late 1950s and early 1960s by Buneman, Dawson, Hockney, Birdsall, Morse and others. In plasma physics applications, the method amounts to following the trajectories of charged particles in self-consistent electromagnetic (or electrostatic) fields computed on a fixed mesh. Technical aspects For many types of problems, the classical PIC method invented by Buneman, Dawson, Hockney, Birdsall, Morse and others is relatively intuitiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types Of Mesh
A mesh is a representation of a larger geometric domain by smaller discrete cells. Meshes are commonly used to compute solutions of partial differential equations and render computer graphics, and to analyze geographical and cartographic data. A mesh partitions space into ''elements'' (or ''cells'' or ''zones'') over which the equations can be solved, which then approximates the solution over the larger domain. Element boundaries may be constrained to lie on internal or external boundaries within a model. Higher-quality (better-shaped) elements have better numerical properties, where what constitutes a "better" element depends on the general governing equations and the particular solution to the model instance. Common cell shapes Two-dimensional There are two types of two-dimensional cell shapes that are commonly used. These are the triangle and the quadrilateral. Computationally poor elements will have sharp internal angles or short edges or both. Triangle This cell shape consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesh Generation
Mesh generation is the practice of creating a polygon mesh, mesh, a subdivision of a continuous geometric space into discrete geometric and topological cells. Often these cells form a simplicial complex. Usually the cells partition the geometric input domain. Mesh cells are used as discrete local approximations of the larger domain. Meshes are created by computer algorithms, often with human guidance through a GUI , depending on the complexity of the domain and the type of mesh desired. A typical goal is to create a mesh that accurately captures the input domain geometry, with high-quality (well-shaped) cells, and without so many cells as to make subsequent calculations intractable. The mesh should also be fine (have small elements) in areas that are important for the subsequent calculations. Meshes are used for rendering (computer graphics), rendering to a computer screen and for physical simulation such as finite element analysis or computational fluid dynamics. Meshes are comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Domain
Time domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data, with respect to time. In the time domain, the signal or function's value is known for all real numbers, for the case of continuous time, or at various separate instants in the case of discrete time. An oscilloscope is a tool commonly used to visualize real-world signals in the time domain. A time-domain graph shows how a signal changes with time, whereas a frequency-domain graph shows how much of the signal lies within each given frequency band over a range of frequencies. Though most precisely referring to time in physics, the term ''time domain'' may occasionally informally refer to position in space when dealing with spatial frequencies, as a substitute for the more precise term ''spatial domain''. Origin of term The use of the contrasting terms ''time domain'' and '' frequency domain'' developed in U.S. communication engineering in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
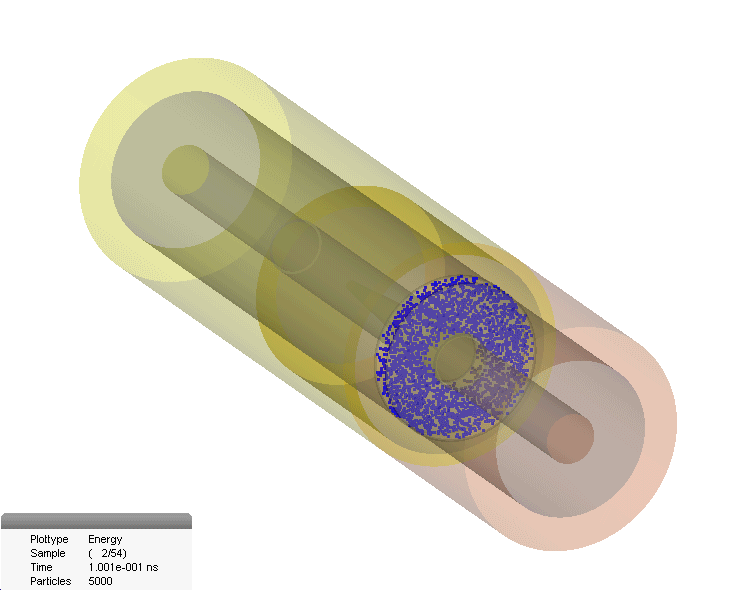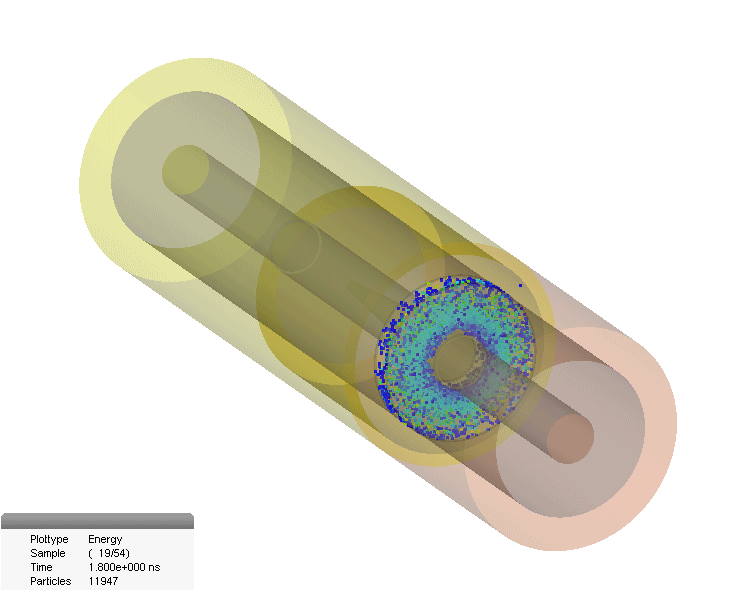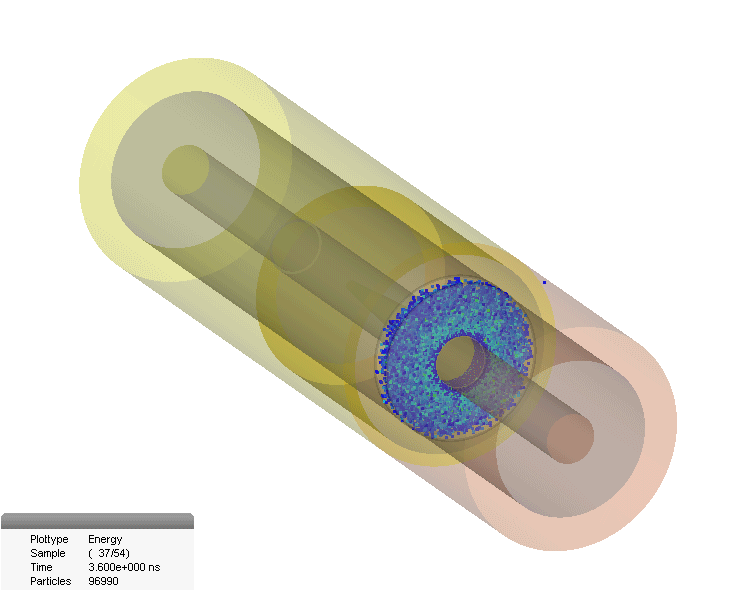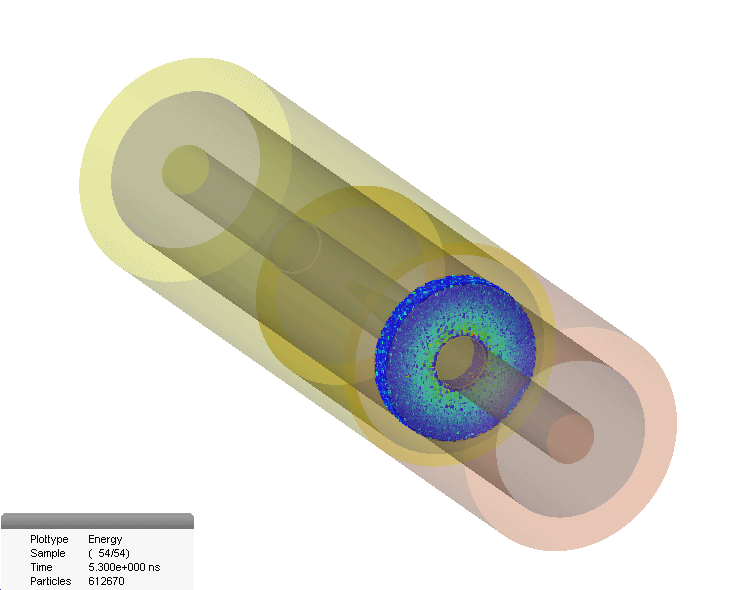
Multipaction In Coaxial Connector
The multipactor effect is a phenomenon in radio-frequency (RF) amplifier vacuum tubes and waveguides, where, under certain conditions, secondary electron emission in resonance with an alternating electric field leads to exponential electron multiplication, possibly damaging and even destroying the RF device. Description The multipactor effect occurs when electrons accelerated by radio-frequency (RF) fields are self-sustained in a vacuum (or near vacuum) via an electron avalanche caused by secondary electron emission. The impact of an electron to a surface can, depending on its energy and angle, release one or more secondary electrons into the vacuum. These electrons can then be accelerated by the RF fields and impact with the same or another surface. Should the impact energies, number of electrons released, and timing of the impacts be such that a sustained multiplication of the number of electrons occurs, the phenomenon can grow exponentially and may lead to operational problems of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises 23 member states, and Israel (admitted in 2013) is currently the only non-European country holding full membership. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2019, it had 2,660 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,400 users from institutions in more than 70 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research — consequently, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN through international collaborations. CERN is the site o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave Engineering
Microwave engineering pertains to the study and design of microwave circuits, components, and systems. Fundamental principles are applied to analysis, design and measurement techniques in this field. The short wavelengths involved distinguish this discipline from electronic engineering. This is because there are different interactions with circuits, transmissions and propagation characteristics at microwave frequencies. Some theories and devices that pertain to this field are antennas, radar, transmission lines, space based systems (remote sensing), measurements, microwave radiation hazards and safety measures. During World War II, microwave engineering played a significant role in developing radar that could accurately locate enemy ships and planes with a focused beam of EM radiation. The foundations of this discipline are found in Maxwell's equations and the work of Heinrich Hertz, William Thomson's waveguide theory, J.C. Bose, the klystron from Russel and Varian Bross, as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. The largest accelerator currently active is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, operated by the European Organization for Nuclear Research, CERN. It is a collider accelerator, which can accelerate two beams of protons to an energy of 6.5 TeV and cause them to collide head-on, creating center-of-mass energies of 13 TeV. Other powerful accelerators are, Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider, RHIC at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York and, formerly, the Tevatron at Fermilab, Batavia, Illinois. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics World
''Physics World'' is the membership magazine of the Institute of Physics, one of the largest physical societies in the world. It is an international monthly magazine covering all areas of physics, pure and applied, and is aimed at physicists in research, industry, physics outreach, and education worldwide. Overview The magazine was launched in 1988 by IOP Publishing Ltd, under the founding editorship of Philip Campbell. The magazine is sent free to members of the Institute of Physics, who can access a digital edition of the magazine; selected articles can be read by anyone for free online. It was redesigned in September 2005 and has an audited circulation of just under 35000. The current editor is Matin Durrani. Others on the team are Michael Banks (news editor) and Tushna Commissariat and Sarah Teah (features editors). Hamish Johnston, Margaret Harris and Tami Freeman are online editors. Alongside the print and online magazine, Physics World produces films and two podcasts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Weiland
Thomas Weiland (born October 24, 1951) is a German physicist, engineer and university lecturer. He is Professor of Electrical Engineering at the Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology of the Technische Universität Darmstadt in Germany. He was named a Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2012 for his development of the finite integration technique and impact of the associated software on electromagnetic engineering. Life Thomas Weiland went to the humanistic Ludwigsgymnasium in Saarbrücken. From 1970 to 1975 he studied theoretical electrical engineering at the Technische Hochschule Darmstadt (TH Darmstadt). He then worked as a research assistant at the Department of Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering at the TH Darmstadt. Weiland received his doctorate in 1977 from TH Darmstadt. After his doctorate he was a Fellow at CERN and a member of the theory group of the ISR Division. He habilitated in experimental physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technische Universität Darmstadt
The Technische Universität Darmstadt (official English name Technical University of Darmstadt, sometimes also referred to as Darmstadt University of Technology), commonly known as TU Darmstadt, is a research university in the city of Darmstadt, Germany. It was founded in 1877 and received the right to award doctorates in 1899. In 1882, it was the first university in the world to set up a chair in electrical engineering. In 1883, the university founded the first faculty of electrical engineering and introduced the world's first degree course in electrical engineering.History of the department of Electrical Engineering: (German) In 2004, it became the first German university to be declared as an autonomous university. TU Darmstadt has assumed a pioneering role in Germany. Computer science, electrical engineering, artificial intelligence, mechatronics, business informatics, political science and many more courses were introduced as scientific disciplines in Germany by Darmsta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.gif)


.jpg)