|
Computational Epidemiology
Computational epidemiology is a multidisciplinary field that uses techniques from computer science, mathematics, geographic information science and public health to better understand issues central to epidemiology such as the spread of diseases or the effectiveness of a public health intervention. Computational epidemiology traces its origins to mathematical epidemiology, but began to experience significant growth with the rise of big data and the democratization of high-performance computing through cloud computing. Introduction In contrast with traditional epidemiology Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent dise ..., computational epidemiology looks for patterns in unstructured sources of data, such as social media. It can be thought of as the hypothesis-generating antecedent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information Science
Geographic information science (GIScience, GISc) or geoinformation science is a scientific discipline at the crossroads of computational science, social science, and natural science that studies geographic information, including how it represents phenomena in the real world, how it represents the way humans understand the world, and how it can be captured, organized, and analyzed. It is a sub-field of geography, specifically part of technical geography. It has applications to both physical geography and human geography, although its techniques can be applied to many other fields of study as well as many different industries. As a field of study or profession, it can be contrasted with geographic information systems (GIS), which are the actual repositories of geospatial data, the software tools for carrying out relevant tasks, and the profession of GIS users. That said, one of the major goals of GIScience is to find practical ways to improve GIS data, software, and profess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a pandemic it may encompass several continents. The concept of ''health'' takes into account physical, psychological, and Well-being, social well-being, among other factors.What is the WHO definition of health? from the Preamble to the Constitution of WHO as adopted by the Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent diseases. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying Risk factor (epidemiology), risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission (medicine), transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Epidemiology
Mathematical models can project how infectious diseases progress to show the likely outcome of an epidemic (including in plants) and help inform public health and plant health interventions. Models use basic assumptions or collected statistics along with mathematics to find parameters for various infectious diseases and use those parameters to calculate the effects of different interventions, like mass vaccination programs. The modelling can help decide which intervention(s) to avoid and which to trial, or can predict future growth patterns, etc. History The modelling of infectious diseases is a tool that has been used to study the mechanisms by which diseases spread, to predict the future course of an outbreak and to evaluate strategies to control an epidemic. The first scientist who systematically tried to quantify causes of death was John Graunt in his book ''Natural and Political Observations made upon the Bills of Mortality'', in 1662. The bills he studied were listings of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
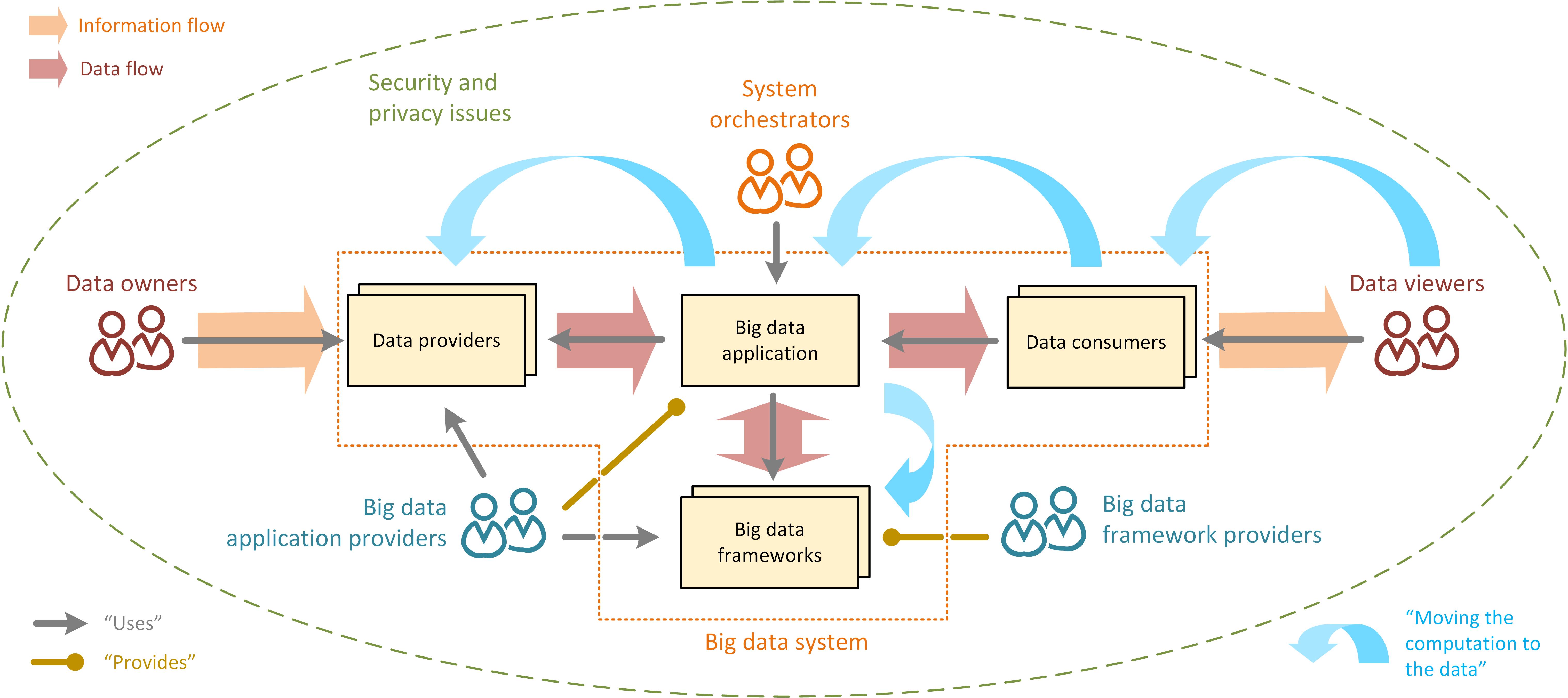
Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include Automatic identification and data capture, capturing data, Computer data storage, data storage, data analysis, search, Data sharing, sharing, Data transmission, transfer, Data visualization, visualization, Query language, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampling. Thus a fourth concept, ''veracity,'' refers to the quality or insightfulness of the data. Without sufficient investm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to International Organization for Standardization, ISO. Essential characteristics In 2011, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) identified five "essential characteristics" for cloud systems. Below are the exact definitions according to NIST: * On-demand self-service: "A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider." * Broad network access: "Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations)." * Pooling (resource management), Resource pooling: " The provider' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Science
Computational science, also known as scientific computing, technical computing or scientific computation (SC), is a division of science, and more specifically the Computer Sciences, which uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex physical problems. While this typically extends into computational specializations, this field of study includes: * Algorithms ( numerical and non-numerical): mathematical models, computational models, and computer simulations developed to solve sciences (e.g, physical, biological, and social), engineering, and humanities problems * Computer hardware that develops and optimizes the advanced system hardware, firmware, networking, and data management components needed to solve computationally demanding problems * The computing infrastructure that supports both the science and engineering problem solving and the developmental computer and information science In practical use, it is typically the application of compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |