|
Commonly Used Gamma-emitting Isotopes
Radionuclides which emit gamma radiation are valuable in a range of different industrial, scientific and medical technologies. This article lists some common gamma-emitting radionuclides of technological importance, and their properties. Fission products Many artificial radionuclides of technological importance are produced as fission products within nuclear reactors. A fission product is a nucleus with approximately half the mass of a uranium or plutonium nucleus which is left over after such a nucleus has been "split" in a nuclear fission reaction. Caesium-137 is one such radionuclide. It has a half-life of 30 years, and decays by beta decay without gamma ray emission to a metastable state of barium-137 (). Barium-137m has a half-life of a 2.6 minutes and is responsible for all of the gamma ray emission in this decay sequence. The ground state of barium-137 is stable. The gamma ray ( photon) energy of is about 662 keV. These gamma rays can be used, for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Radiation
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies above 30 exahertz (), it imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range from a few kiloelectronvolts (keV) to approximately 8 megaelectronvolts (MeV), corresponding to the typical energy levels in nuclei with reasonably long lifeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridium-192
There are two natural isotopes of iridium (77Ir), and 34 radioisotopes, the most stable radioisotope being 192Ir with a half-life of 73.83 days, and many nuclear isomers, the most stable of which is 192m2Ir with a half-life of 241 years. All other isomers have half-lives under a year, most under a day. All isotopes of iridium are either radioactive or observationally stable, meaning that they are predicted to be radioactive but no actual decay has been observed. List of isotopes , - , 164Ir , style="text-align:right" , 77 , style="text-align:right" , 87 , 163.99220(44)# , 1# ms , , , 2−# , , , - , style="text-indent:1em" , 164mIr , colspan="3" style="text-indent:2em" , 270(110)# keV , 94(27) µs , , , 9+# , , , - , rowspan=2, 165Ir , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 77 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 88 , rowspan=2, 164.98752(23)# , rowspan=2, 50# ns (<1 µs) , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal. Cobalt-based blue pigments ( cobalt blue) have been used since ancient times for jewelry and paints, and to impart a distinctive blue tint to glass, but the color was for a long time thought to be due to the known metal bismuth. Miners had long used the name ''kobold ore'' (German for ''goblin ore'') for some of the blue-pigment-producing minerals; they were so named because they were poor in known metals, and gave poisonous arsenic-containing fumes when smelted. In 1735, such ores were found to be reducible to a new metal (the first discovered since ancient times), and this was ultimately named for the ''kobold''. Today, some cobalt is produced specifically from one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizing radiation works by damaging the DNA of cancerous tissue l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density of as defined by experimental X-ray crystallography. It is one of the most corrosion-resistant metals, even at temperatures as high as . However, corrosion-resistance is not quantifiable in absolute terms; although only certain molten salts and halogens are corrosive to solid iridium, finely divided iridium dust is much more reactive and can be flammable, whereas gold dust is not flammable but can be attacked by substances that iridium resists, such as aqua regia. Iridium was discovered in 1803 among insoluble impurities in natural platinum. Smithson Tennant, the primary discoverer, named it after the Greek goddess Iris, personification of the rainbow, because of the striking and diverse colors of its salts. Iridium is one of the rarest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal. Cobalt-based blue pigments ( cobalt blue) have been used since ancient times for jewelry and paints, and to impart a distinctive blue tint to glass, but the color was for a long time thought to be due to the known metal bismuth. Miners had long used the name ''kobold ore'' (German for ''goblin ore'') for some of the blue-pigment-producing minerals; they were so named because they were poor in known metals, and gave poisonous arsenic-containing fumes when smelted. In 1735, such ores were found to be reducible to a new metal (the first discovered since ancient times), and this was ultimately named for the ''kobold''. Today, some cobalt is produced specifically from one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Irradiation
Neutron activation is the process in which neutron radiation induces radioactivity in materials, and occurs when atomic nuclei capture free neutrons, becoming heavier and entering excited states. The excited nucleus decays immediately by emitting gamma rays, or particles such as beta particles, alpha particles, fission products, and neutrons (in nuclear fission). Thus, the process of neutron capture, even after any intermediate decay, often results in the formation of an unstable activation product. Such radioactive nuclei can exhibit half-lives ranging from small fractions of a second to many years. Neutron activation is the only common way that a stable material can be induced into becoming intrinsically radioactive. All naturally occurring materials, including air, water, and soil, can be induced (activated) by neutron capture into some amount of radioactivity in varying degrees, as a result of the production of neutron-rich radioisotopes. Some atoms require more than one neut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RaLa Experiment
The RaLa Experiment, or RaLa, was a series of tests during and after the Manhattan Project designed to study the behavior of converging shock waves to achieve the spherical implosion necessary for compression of the plutonium pit of the nuclear weapon. The experiment used significant amounts of a short-lived radioisotope lanthanum-140, a potent source of gamma radiation; the RaLa is a contraction of Radioactive Lanthanum. The method was proposed by Robert Serber and developed by a team led by the Italian experimental physicist Bruno Rossi. The tests were performed with 1/8 inch (3.2 mm) spheres of radioactive lanthanum, equal to about and later , located in the center of a simulated nuclear device. The explosive lenses were designed primarily using this series of tests. Some 254 tests were conducted between September 1944 and March 1962. In his history of the Los Alamos project, David Hawkins wrote: “RaLa became the most important single experiment affecting the final bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the United States Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Nuclear physicist Robert Oppenheimer was the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory that designed the actual bombs. The Army component of the project was designated the Manhattan District as its first headquarters were in Manhattan; the placename gradually superseded the official codename, Development of Substitute Materials, for the entire project. Along the way, the project absorbed its earlier British counterpart, Tube Alloys. The Manhattan Project began modestly in 1939, but grew to employ more than 130,000 people and cost nearly US$2 billion (equivalent to about $ billion in ). Over 90 percent of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
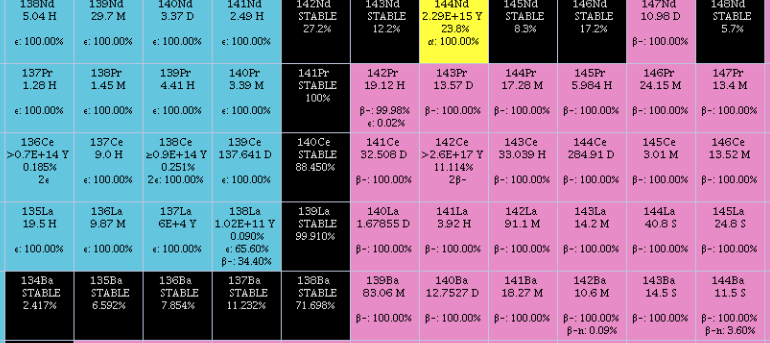
Barium-140
Naturally occurring barium (56Ba) is a mix of six stable isotopes and one very long-lived radioactive primordial isotope, barium-130, identified as being unstable by geochemical means (from analysis of the presence of its daughter xenon-130 in rocks) in 2001. This nuclide decays by double electron capture (absorbing two electrons and emitting two neutrinos), with a half-life of (0.5–2.7)×1021 years (about 1011 times the age of the universe). There are a total of thirty-three known radioisotopes in addition to 130Ba. The longest-lived of these is 133Ba, which has a half-life of 10.51 years. All other radioisotopes have half-lives shorter than two weeks. The longest-lived isomer is 133mBa, which has a half-life of 38.9 hours. The shorter-lived 137mBa (half-life 2.55 minutes) arises as the decay product of the common fission product caesium-137. Barium-114 is predicted to undergo cluster decay, emitting a nucleus of stable 12C to produce 102Sn. However this decay is not yet ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decay Product
In nuclear physics, a decay product (also known as a daughter product, daughter isotope, radio-daughter, or daughter nuclide) is the remaining nuclide left over from radioactive decay. Radioactive decay often proceeds via a sequence of steps (decay chain). For example, 238U decays to 234Th which decays to 234mPa which decays, and so on, to 206Pb (which is stable): : \ce \overbrace^\ce left, upThe decay chain from lead-212 down to lead-208, showing the intermediate decay products In this example: * 234Th, 234mPa,...,206Pb are the decay products of 238U. * 234Th is the daughter of the parent 238U. * 234mPa (234 metastable) is the granddaughter of 238U. These might also be referred to as the daughter products of 238U. (''Depleted Uranium'' — authors: Naomi H. Harley, Ernest C. Foulkes, Lee H. Hil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum-140
Naturally occurring lanthanum (57La) is composed of one stable (139La) and one radioactive (138La) isotope, with the stable isotope, 139La, being the most abundant (99.91% natural abundance). There are 38 radioisotopes that have been characterized, with the most stable being 138La, with a half-life of 1.02×1011 years; 137La, with a half-life of 60,000 years and 140La, with a half-life of 1.6781 days. The remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than a day and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 1 minute. This element also has 12 nuclear isomers, the longest-lived of which is 132mLa, with a half-life of 24.3 minutes. The isotopes of lanthanum range in atomic weight from 116.95 u (117La) to 154.96 u (155La). List of isotopes , - , rowspan=2, 117La , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 57 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 60 , rowspan=2, 116.95007(43)# , rowspan=2, 23.5(26) ms , β+ , 117Ba , rowspan=2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




-chloride-hexahydrate-sample.jpg)