|
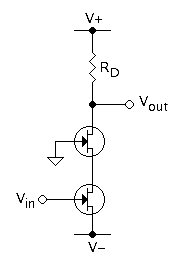
Common-gate
In electronics, a common-gate amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a current buffer or voltage amplifier. In this circuit, the source terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the drain is the output, and the gate is connected to ground, or "common," hence its name. The analogous bipolar junction transistor circuit is the common-base amplifier. Applications This configuration is used less often than the common source or source follower. It is useful in, for example, CMOS RF receivers, especially when operating near the frequency limitations of the FETs; it is desirable because of the ease of impedance matching and potentially has lower noise. Gray and Meyer provide a general reference for this circuit. Low-frequency characteristics At low frequencies and under small-signal conditions, the circuit in Figure 1 can be represented by that in Figure 2, where the hybrid-pi model for the MOSFET ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Gate
In electronics, a common-gate amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a current buffer or voltage amplifier. In this circuit, the source terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the drain is the output, and the gate is connected to ground, or "common," hence its name. The analogous bipolar junction transistor circuit is the common-base amplifier. Applications This configuration is used less often than the common source or source follower. It is useful in, for example, CMOS RF receivers, especially when operating near the frequency limitations of the FETs; it is desirable because of the ease of impedance matching and potentially has lower noise. Gray and Meyer provide a general reference for this circuit. Low-frequency characteristics At low frequencies and under small-signal conditions, the circuit in Figure 1 can be represented by that in Figure 2, where the hybrid-pi model for the MOSFET ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Source
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, common drain, or common gate is to examine where the signal enters and leaves. The remaining terminal is what is known as "common". In this example, the signal enters the gate, and exits the drain. The only terminal remaining is the source. This is a common-source FET circuit. The analogous bipolar junction transistor circuit may be viewed as a transconductance amplifier or as a voltage amplifier. (See classification of amplifiers). As a transconductance amplifier, the input voltage is seen as modulating the current going to the load. As a voltage amplifier, input voltage modulates the current flowing through the FET, changing the voltage across the output resistance according to Ohm's law. However, the FET device's output resistance typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascode
The cascode is a two-stage amplifier that consists of a common-emitter stage feeding into a common-base stage. Compared to a single amplifier stage, this combination may have one or more of the following characteristics: higher input–output isolation, higher input impedance, high output impedance, higher bandwidth. In modern circuits, the cascode is often constructed from two transistors (BJTs or FETs), with one operating as a common emitter or common source and the other as a common base or common gate. The cascode improves input–output isolation (reduces reverse transmission), as there is no direct coupling from the output to input. This eliminates the Miller effect and thus contributes to a much higher bandwidth. History The use of a cascode (sometimes verbified to ''cascoding'') is a common technique for improving analog circuit performance, applicable to both vacuum tubes and transistors. The name "cascode" was coined in an article written by Frederick Vinton Hunt an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common-source
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, common drain, or common gate is to examine where the signal enters and leaves. The remaining terminal is what is known as "common". In this example, the signal enters the gate, and exits the drain. The only terminal remaining is the source. This is a common-source FET circuit. The analogous bipolar junction transistor circuit may be viewed as a transconductance amplifier or as a voltage amplifier. (See classification of amplifiers). As a transconductance amplifier, the input voltage is seen as modulating the current going to the load. As a voltage amplifier, input voltage modulates the current flowing through the FET, changing the voltage across the output resistance according to Ohm's law. However, the FET device's output resistance typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Source
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, common drain, or common gate is to examine where the signal enters and leaves. The remaining terminal is what is known as "common". In this example, the signal enters the gate, and exits the drain. The only terminal remaining is the source. This is a common-source FET circuit. The analogous bipolar junction transistor circuit may be viewed as a transconductance amplifier or as a voltage amplifier. (See classification of amplifiers). As a transconductance amplifier, the input voltage is seen as modulating the current going to the load. As a voltage amplifier, input voltage modulates the current flowing through the FET, changing the voltage across the output resistance according to Ohm's law. However, the FET device's output resistance typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer Amplifier
A buffer amplifier (sometimes simply called a buffer) is one that provides electrical impedance transformation from one circuit to another, with the aim of preventing the signal source from being affected by whatever currents (or voltages, for a current buffer) that the load may be produced with. The signal is 'buffered from' load currents. Two main types of buffer exist: the voltage buffer and the current buffer. Voltage buffer A voltage buffer amplifier is used to transfer a voltage from a first circuit, having a high output impedance level, to a second circuit with a low input impedance level. The interposed buffer amplifier prevents the second circuit from loading the first circuit unacceptably and interfering with its desired operation, since without the voltage buffer the voltage of the second circuit is influenced by output impedance of the first circuit (as it is larger than the input impedance of the second circuit). In the ideal voltage buffer in the diagram, the input ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Base Amplifier
Common may refer to: Places * Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts * Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts * Clapham Common, originally common land, now a park in London, UK * Common Moss, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Lexington Common, a common land area in Lexington, Massachusetts * Salem Common Historic District, a common land area in Salem, Massachusetts People * Common (rapper) (born 1972), American hip hop artist, actor, and poet * Andrew Ainslie Common (born 1841), English amateur astronomer * Andrew Common (born 1889), British shipping director * John Common, American songwriter, musician and singer * Thomas Common (born 1850), Scottish translator and literary critic Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Common'' (film), a 2014 BBC One film, written by Jimmy McGovern, on the UK's Joint Enterprise Law * Dol Common, a character in ''The Alchemis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Base
In electronics, a common-base (also known as grounded-base) amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a current buffer or voltage amplifier. In this circuit the emitter terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the collector as the output, and the base is connected to ground, or "common", hence its name. The analogous field-effect transistor circuit is the common-gate amplifier. Applications This arrangement is not very common in low-frequency discrete circuits, where it is usually employed for amplifiers that require an unusually low input impedance, for example to act as a preamplifier for moving-coil microphones. However, it is popular in integrated circuits and in high-frequency amplifiers, for example for VHF and UHF, because its input capacitance does not suffer from the Miller effect, which degrades the bandwidth of the common-emitter configuration, and because of the relatively high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Base
In electronics, a common-base (also known as grounded-base) amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a current buffer or voltage amplifier. In this circuit the emitter terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the collector as the output, and the base is connected to ground, or "common", hence its name. The analogous field-effect transistor circuit is the common-gate amplifier. Applications This arrangement is not very common in low-frequency discrete circuits, where it is usually employed for amplifiers that require an unusually low input impedance, for example to act as a preamplifier for moving-coil microphones. However, it is popular in integrated circuits and in high-frequency amplifiers, for example for VHF and UHF, because its input capacitance does not suffer from the Miller effect, which degrades the bandwidth of the common-emitter configuration, and because of the relatively high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Drain
In electronics, a common-drain amplifier, also known as a source follower, is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer. In this circuit (NMOS) the gate terminal of the transistor serves as the signal input, the source is the output, and the drain is ''common'' to both (input and output), hence its name. The analogous bipolar junction transistor circuit is the common-collector amplifier. This circuit is also commonly called a "stabilizer". In addition, this circuit is used to transform impedances. For example, the Thévenin resistance of a combination of a voltage follower driven by a voltage source with high Thévenin resistance is reduced to only the output resistance of the voltage follower (a small resistance). That resistance reduction makes the combination a more ideal voltage source. Conversely, a voltage follower inserted between a driving stage and a high load (i.e. a low resistance) presents a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the voltage or current ( power, voltage or current amplifier). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a greater amplitude signal at its output. The ratio of output to input voltage, current, or power is termed gain (voltage, current, or power gain). An amplifier, by definition has gain greater than unity (if the gain is less than unity, the device is an attenuator). An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit contained within another device. Amplification is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are widely used in almost all electronic equipment. Amplifiers can be categ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gain (electronics)
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a two-port circuit (often an amplifier) to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output port by adding energy converted from some power supply to the signal. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal amplitude or power at the output port to the amplitude or power at the input port. It is often expressed using the logarithmic decibel (dB) units ("dB gain"). A gain greater than one (greater than zero dB), that is amplification, is the defining property of an active component or circuit, while a passive circuit will have a gain of less than one. The term ''gain'' alone is ambiguous, and can refer to the ratio of output to input voltage (''voltage gain''), current (''current gain'') or electric power (''power gain''). In the field of audio and general purpose amplifiers, especially operational amplifiers, the term usually refers to voltage gain, but in radio frequency amplifiers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |