Common Gate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
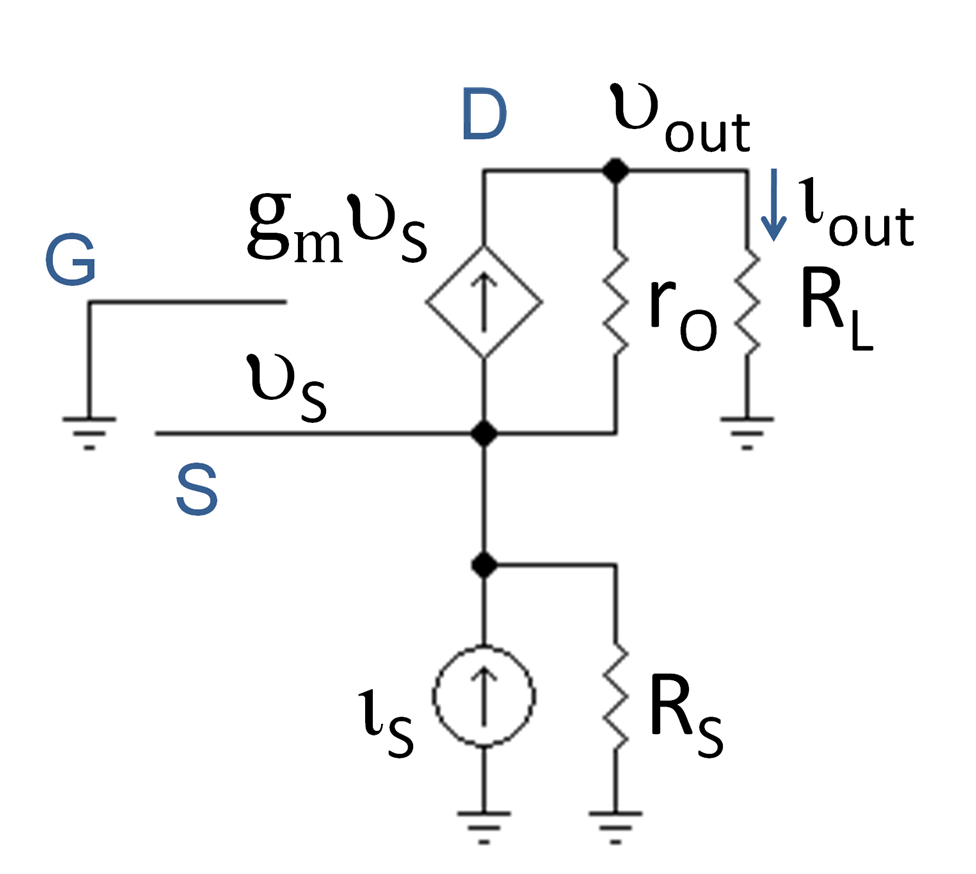 At low frequencies and under small-signal conditions, the circuit in Figure 1 can be represented by that in Figure 2, where the
At low frequencies and under small-signal conditions, the circuit in Figure 1 can be represented by that in Figure 2, where the 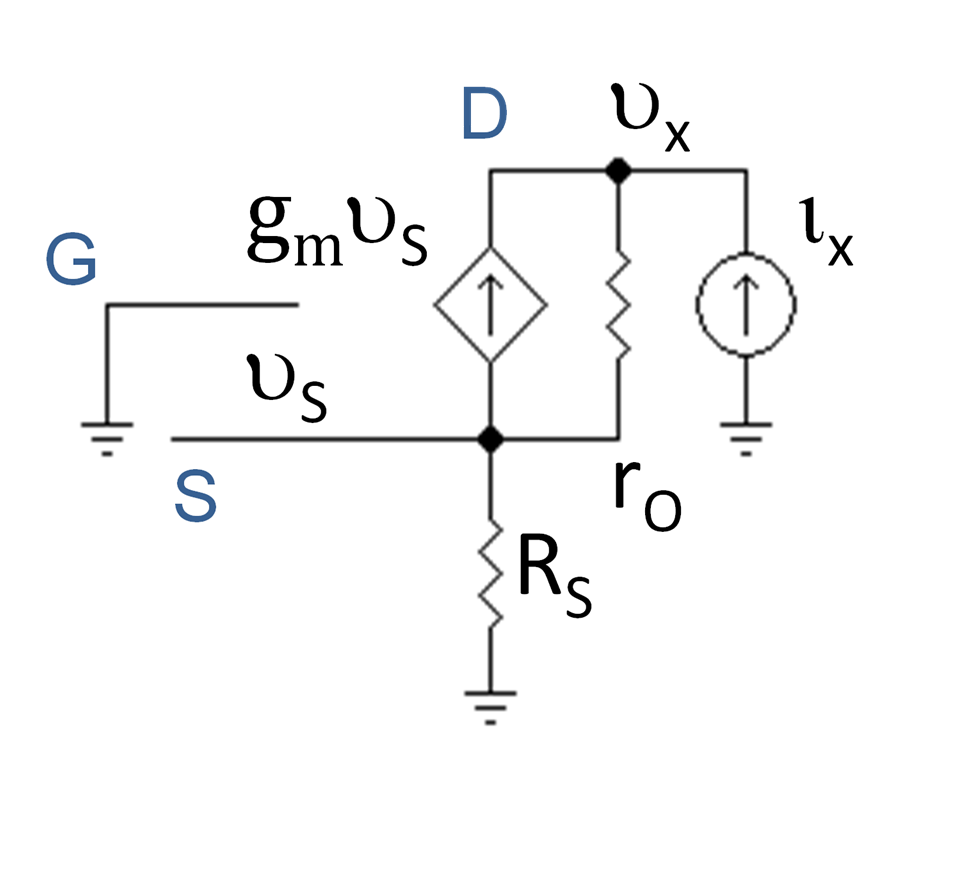 The amplifier characteristics are summarized below in Table 1. The approximate expressions use the assumptions (usually accurate) ''rO'' >> ''RL'' and ''gmrO'' >> 1.
In general, the overall voltage/current gain may be substantially less than the open/short circuit gains listed above (depending on the source and load resistances) due to the loading effect.
The amplifier characteristics are summarized below in Table 1. The approximate expressions use the assumptions (usually accurate) ''rO'' >> ''RL'' and ''gmrO'' >> 1.
In general, the overall voltage/current gain may be substantially less than the open/short circuit gains listed above (depending on the source and load resistances) due to the loading effect.
A 24GHz CMOS Front-end
{{Transistor amplifiers Single-stage transistor amplifiers
electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
, a common-gate amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost th ...
is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs ( JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs con ...
(FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
buffer
Buffer may refer to:
Science
* Buffer gas, an inert or nonflammable gas
* Buffer solution, a solution used to prevent changes in pH
* Buffering agent, the weak acid or base in a buffer solution
* Lysis buffer, in cell biology
* Metal ion buffer
* ...
or voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge t ...
amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost th ...
. In this circuit, the source terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the drain is the output, and the gate is connected to ground, or "common," hence its name.
The analogous bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipola ...
circuit is the common-base amplifier.
Applications
This configuration is used less often than thecommon source
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, comm ...
or source follower
In electronics, a common-drain amplifier, also known as a source follower, is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer. In this circuit (NMOS) the gate terminal of the ...
. It is useful in, for example, CMOS RF receivers, especially when operating near the frequency limitations of the FETs; it is desirable because of the ease of impedance matching
In electronics, impedance matching is the practice of designing or adjusting the input impedance or output impedance of an electrical device for a desired value. Often, the desired value is selected to maximize power transfer or minimize si ...
and potentially has lower noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
. Gray and Meyer
provide a general reference for this circuit.
Low-frequency characteristics
hybrid-pi model The hybrid-pi model is a popular circuit model used for analyzing the small signal behavior of bipolar junction and field effect transistors. Sometimes it is also called Giacoletto model because it was introduced by L.J. Giacoletto in 1969. The m ...
for the MOSFET has been employed.
Closed circuit voltage gain
Taking input and output loading into consideration, the closed circuit voltage gain (that is, the gain with load ''RL'' and source with resistance ''RS'' both attached) of the common gate can be written as: : , which has the simple limiting forms : , depending upon whether ''gmRS'' is much larger or much smaller than one. In the first case the circuit acts as a current follower, as understood as follows: for ''RS'' >> 1/''gm'' the voltage source can be replaced by itsNorton equivalent
In direct-current circuit theory, Norton's theorem, also called the Mayer–Norton theorem, is a simplification that can be applied to networks made of linear time-invariant resistances, voltage sources, and current sources. At a pair of ter ...
with Norton current ''vThév / RS'' and parallel Norton resistance ''RS''. Because the amplifier input resistance is small, the driver delivers by current division a current ''vThév / RS'' to the amplifier. The current gain is unity, so the same current is delivered to the output load ''RL'', producing by Ohm's law an output voltage ''vout = vThévRL / RS'', that is, the first form of the voltage gain above.
In the second case ''RS'' << 1/''gm'' and the Thévenin representation of the source is useful, producing the second form for the gain, typical of voltage amplifiers.
Because the input impedance of the common-gate amplifier is very low, the cascode
The cascode is a two-stage amplifier that consists of a common-emitter stage feeding into a common-base stage.
Compared to a single amplifier stage, this combination may have one or more of the following characteristics: higher input–outpu ...
amplifier often is used instead. The cascode places a common-source
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, comm ...
amplifier between the voltage driver and the common-gate circuit to permit voltage amplification using a driver with ''RS >> 1/gm''.
See also
* Electronic amplifier variables *Two-port network
A two-port network (a kind of four-terminal network or quadripole) is an electrical network (circuit) or device with two ''pairs'' of terminals to connect to external circuits. Two terminals constitute a port if the currents applied to them satis ...
s
* Common drain
In electronics, a common-drain amplifier, also known as a source follower, is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer. In this circuit (NMOS) the gate terminal of the ...
* Common source
In electronics, a common-source amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage or transconductance amplifier. The easiest way to tell if a FET is common source, comm ...
* Common base
In electronics, a common-base (also known as grounded-base) amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a current buffer or voltage amplifier.
In this circuit the emitter ...
* Common emitter
In electronics, a common-emitter amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar-junction-transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage amplifier. It offers high current gain (typically 200), medium input resistance an ...
* Common collector
In electronics, a common collector amplifier (also known as an emitter follower) is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer.
In this circuit the base terminal o ...
References
External links
A 24GHz CMOS Front-end
{{Transistor amplifiers Single-stage transistor amplifiers