|
Comecrudan Language
Comecrudan refers to a group of possibly related languages spoken in the southernmost part of Texas and in northern Mexico along the Rio Grande of which ''Comecrudo'' is the best known. Very little is known about these languages or the people who spoke them. Knowledge of them primarily consists of word lists collected by European missionaries and explorers. All Comecrudan languages are extinct. Family division The three languages were: # Comecrudo (also known as Mulato or Carrizo) ''(†)'' # Garza ''(†)'' # Mamulique (also known as Carrizo de Mamulique) ''(†)'' Genetic relationships In John Wesley Powell's 1891 classification of North American languages, Comecrudo was grouped together with the Cotoname and Coahuilteco languages into a family called Coahuiltecan. John R. Swanton (1915) grouped together the Comecrudo, Cotoname, Coahuilteco, Karankawa, Tonkawa, Atakapa, and Maratino languages into a Coahuiltecan grouping. Edward Sapir (1920) accepted Swanton' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The length of the Rio Grande is . It originates in south-central Colorado, in the United States, and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. The Rio Grande drainage basin (watershed) has an area of ; however, the endorheic basins that are adjacent to and within the greater drainage basin of the Rio Grande increase the total drainage-basin area to . The Rio Grande with Rio Grande Valley (landform), its fertile valley, along with its tributaries, is a vital watersource for seven US and Mexican states, and flows primarily through arid and semi-arid lands. After traversing the length of New Mexico, the Rio Grande becomes the Mexico–United States border, between the U.S. state of Texas and the northern Mexican states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua and Coahuila, Nuevo León a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karankawa Language
Karankawa is the extinct, unclassified language of the Texas coast, where the Karankawa people migrated between the mainland and the barrier islands. It was not closely related to other known languages in the area, many of which are also poorly attested, and may have been a language isolate. A couple hundred words are preserved, collected in 1698, 1720, and 1828; in the 1880s, three lists were collected from non-Karankawa who knew some words. Karankawa has sometimes been included with neighboring languages in a Coahuiltecan family, but that is now thought to be spurious. Phonology Vocabulary Though only a few hundred words of the Karankawa language are preserved, the following are selected words recorded by Albert Gatschet, a late Victorian anthropologist and linguist, referenced from the last fluent speakers of the language. * ''Nāt’sa'' "one", counted on the right pinky * ''Haikia'' "two" or "second", counted on the right ring finger * ''Kaxayi'' "three", counted on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Families
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a biological family tree, or in a subsequent modification, to species in a phylogenetic tree of evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists therefore describe the ''daughter languages'' within a language family as being ''genetically related''. According to ''Ethnologue'' there are 7,151 living human languages distributed in 142 different language families. A living language is defined as one that is the first language of at least one person. The language families with the most speakers are: the Indo-European family, with many widely spoken languages native to Europe (such as English and Spanish) and South Asia (such as Hindi and Bengali); and the Sino-Tibetan fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comecrudan Languages
Comecrudan refers to a group of possibly related languages spoken in the southernmost part of Texas and in northern Mexico along the Rio Grande of which ''Comecrudo'' is the best known. Very little is known about these languages or the people who spoke them. Knowledge of them primarily consists of word lists collected by European missionaries and explorers. All Comecrudan languages are extinct. Family division The three languages were: # Comecrudo (also known as Mulato or Carrizo) ''(†)'' # Garza ''(†)'' # Mamulique (also known as Carrizo de Mamulique) ''(†)'' Genetic relationships In John Wesley Powell's 1891 classification of North American languages, Comecrudo was grouped together with the Cotoname and Coahuilteco languages into a family called Coahuiltecan. John R. Swanton (1915) grouped together the Comecrudo, Cotoname, Coahuilteco, Karankawa, Tonkawa, Atakapa, and Maratino languages into a Coahuiltecan grouping. Edward Sapir (1920) accepted Swanton's propos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coahuiltecan
The Coahuiltecan were various small, autonomous bands of Native Americans who inhabited the Rio Grande valley in what is now southern Texas and northeastern Mexico. The various Coahuiltecan groups were hunter-gatherers. First encountered by Europeans in the sixteenth century, their population declined due to imported European diseases, slavery, and numerous small-scale wars fought against the Spanish, criollo, Apache, and other Coahuiltecan groups. After the Texas secession from Mexico, the Coahuiltecan culture was largely forced into harsh living conditions. It is because of these harsh influences that most people in the United States and Texas are not familiar with Coahuiltecan or Tejano culture outside of the main population groups mostly located in South Texas, West Texas, and San Antonio. In 1886, ethnologist Albert Gatschet found the last known survivors of Coahuiltecan bands: 25 Comecrudo, 1 Cotoname, and 2 Pakawa. They were living near Reynosa, Mexico. Brief overview ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
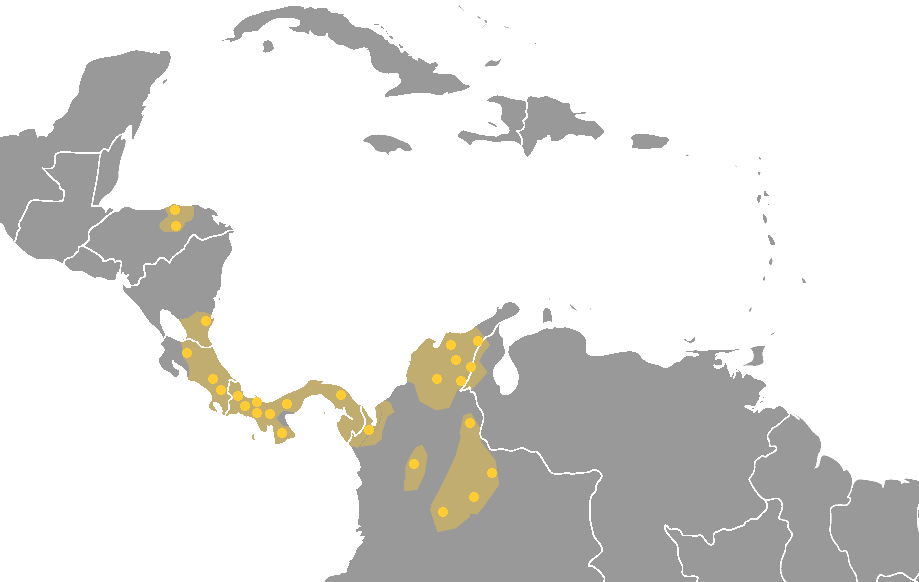
Classification Of Indigenous Languages Of The Americas
This is a list of different language classification proposals developed for the indigenous languages of the Americas. The article is divided into North, Central, and South America sections; however, the classifications do not correspond to these divisions. North America ''Glottolog'' 4.1 (2019) ''Glottolog'' 4.1 (2019) recognizes 42 independent families and 31 isolates in North America (73 total). The vast majority are (or were) spoken in the United States, with 26 families and 26 isolates (52 total). ;North American languages families proposed in ''Glottolog'' 4.1 ;Families (42) #Otomanguean (180) #Arawakan (78) # Uto-Aztecan (69) #Algic (46) # Athabaskan-Eyak-Tlingit (45) #Mayan (33) #Chibchan (27) #Salishan (25) # Mixe-Zoque (19) #Siouan (18) #Eskimo–Aleut (12) # Totonacan (12) # Cochimi-Yuman (11) #Iroquoian (11) # Miwok-Costanoan (11) #Kiowa-Tanoan (8) #Muskogean (7) # Pomoan (7) # Chumashan (6) #Wakashan (6) #Caddoan (5) #Misumalpan (5) #Sahaptian (5) # Xincan (5) #C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American Languages
Over a thousand indigenous languages are spoken by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. These languages cannot all be demonstrated to be related to each other and are classified into a hundred or so language families (including a large number of language isolates), as well as a number of extinct languages that are unclassified because of a lack of data. Many proposals have been made to relate some or all of these languages to each other, with varying degrees of success. The most notorious is Joseph Greenberg's Amerind hypothesis, which however nearly all specialists reject because of severe methodological flaws; spurious data; and a failure to distinguish cognation, contact, and coincidence. Nonetheless, there are indications that some of the recognized families are related to each other, such as widespread similarities in pronouns (e.g., ''n''/''m'' is a common pattern for 'I'/'you' across western North America, and ''ch''/''k''/''t'' for 'I'/'you'/'we' is similarly found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiktionary
Wiktionary ( , , rhyming with "dictionary") is a multilingual, web-based project to create a free content dictionary of terms (including words, phrases, proverbs, linguistic reconstructions, etc.) in all natural languages and in a number of artificial languages. These entries may contain definitions, images for illustration, pronunciations, etymologies, inflections, usage examples, quotations, related terms, and translations of terms into other languages, among other features. It is collaboratively edited via a wiki. Its name is a portmanteau of the words ''wiki'' and ''dictionary''. It is available in languages and in Simple English. Like its sister project Wikipedia, Wiktionary is run by the Wikimedia Foundation, and is written collaboratively by volunteers, dubbed "Wiktionarians". Its wiki software, MediaWiki, allows almost anyone with access to the website to create and edit entries. Because Wiktionary is not limited by print space considerations, most of Wiktio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Louis Berlandier
Jean-Louis Berlandier (1803 – 1851) was a French-Mexican naturalist, physician, and anthropologist. Early life Berlandier was born in Geneva, and later trained as a botanist there. During this time he probably served an apprenticeship to a pharmacist. Career In his early 20s on the recommendation of his mentor, Auguste Pyrame De Candolle, he joined a Mexican scientific expedition as a biologist and plant specialist. Berlandier arrived at Pánuco, in the Mexican state of Veracruz, in December 1826. He collected plants in the surrounding area before continuing into Texas as part of the Mexican Boundary Commission. The commission left Mexico City on November 10, 1827, under the command of Manuel de Mier y Terán. Berlandier made botanical collections around Laredo, Texas, in February 1828 and around San Antonio, Gonzales, and San Felipe in March, April, and May 1828. After a brief trip to the interior of the country after he contacted malaria, he returned to San Antonio. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core Vocabulary
Core or cores may refer to: Science and technology * Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages * Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding * Core (optical fiber), the signal-carrying portion of an optical fiber * Core, the central part of a fruit * Hydrophobic core, the interior zone of a protein * Nuclear reactor core, a portion containing the fuel components * Pit (nuclear weapon) or core, the fissile material in a nuclear weapon * Semiconductor intellectual property core (IP core), is a unit of design in ASIC/FPGA electronics and IC manufacturing * Atomic core, an atom with no valence electrons Geology and astrophysics * Core sample, in Earth science, a sample obtained by coring ** Ice core * Core, the central part of a galaxy; see Mass deficit * Core (anticline), the central part of an anticline or syncline * Planetary core, the center of a planet ** Earth's inner core ** Earth's outer core * Stellar core, the region of a star where nuclear fusion take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Sapir
Edward Sapir (; January 26, 1884 – February 4, 1939) was an American Jewish anthropologist-linguist, who is widely considered to be one of the most important figures in the development of the discipline of linguistics in the United States. Sapir was born in German Pomerania, in what is now northern Poland. His family emigrated to the United States of America when he was a child. He studied Germanic linguistics at Columbia, where he came under the influence of Franz Boas, who inspired him to work on Native American languages. While finishing his Ph.D. he went to California to work with Alfred Kroeber documenting the indigenous languages there. He was employed by the Geological Survey of Canada for fifteen years, where he came into his own as one of the most significant linguists in North America, the other being Leonard Bloomfield. He was offered a professorship at the University of Chicago, and stayed for several years continuing to work for the professionalization of the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |