|
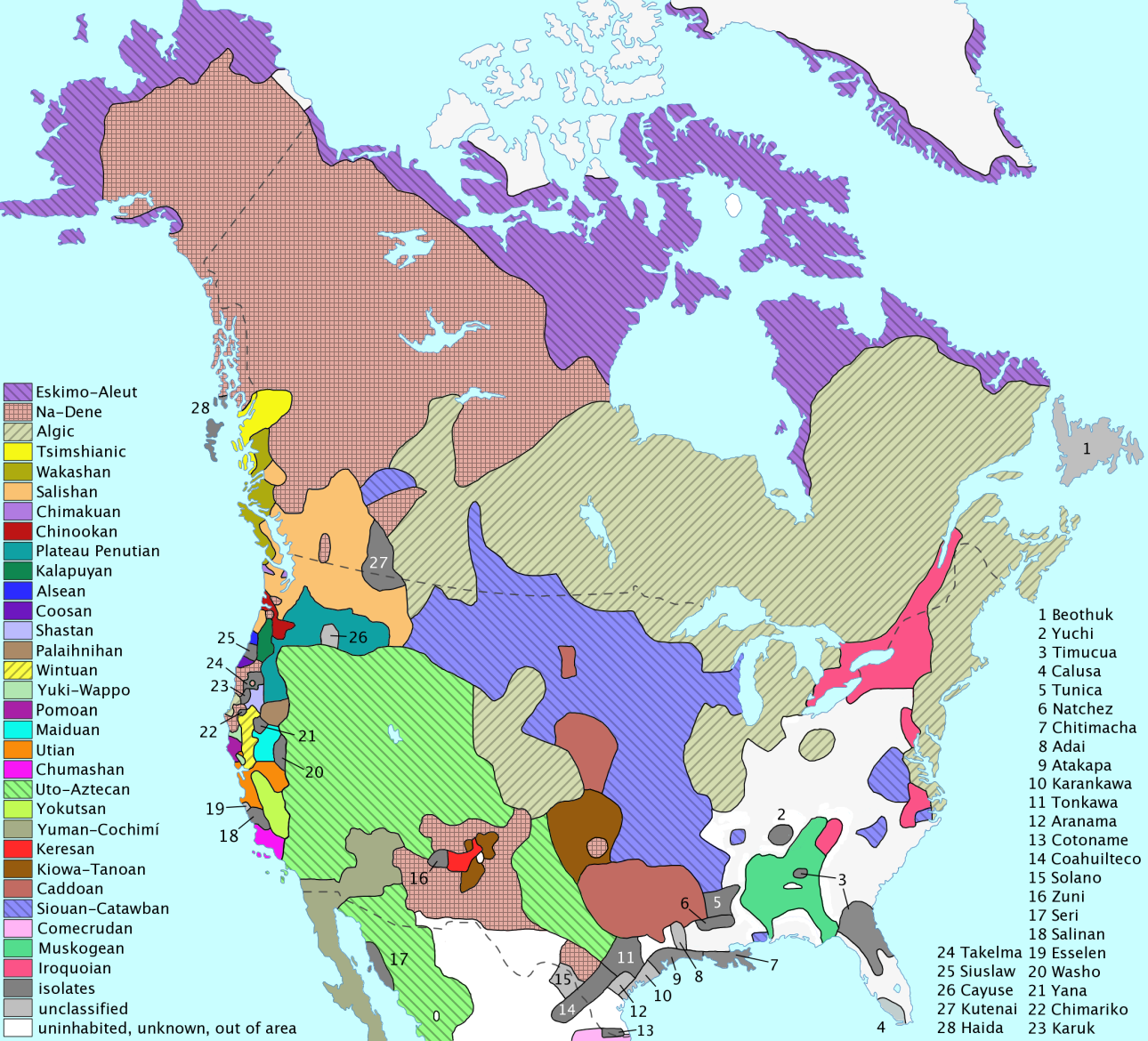
Coahuiltecan
The Coahuiltecan were various small, autonomous bands of Native Americans who inhabited the Rio Grande valley in what is now southern Texas and northeastern Mexico. The various Coahuiltecan groups were hunter-gatherers. First encountered by Europeans in the sixteenth century, their population declined due to imported European diseases, slavery, and numerous small-scale wars fought against the Spanish, criollo, Apache, and other Coahuiltecan groups. After the Texas secession from Mexico, the Coahuiltecan culture was largely forced into harsh living conditions. It is because of these harsh influences that most people in the United States and Texas are not familiar with Coahuiltecan or Tejano culture outside of the main population groups mostly located in South Texas, West Texas, and San Antonio. In 1886, ethnologist Albert Gatschet found the last known survivors of Coahuiltecan bands: 25 Comecrudo, 1 Cotoname, and 2 Pakawa. They were living near Reynosa, Mexico. Brief overview ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coahuiltecan Languages
Coahuiltecan was a proposed language family in John Wesley Powell's 1891 classification of Native American languages. Most linguists now reject the view that the Coahuiltecan peoples of southern Texas and adjacent Mexico spoke a single or related languages. Coahuiltecan continues to be a convenient collective term for the languages and people of this region. Language relationships Similarities among the cultures among the indigenous people and the physical setting of south Texas led linguists to believe that the languages of the region were also similar. The Coahuiltecan language family was proposed to include all the languages of the region, including Karankawa and Tonkawa. Linguistic connections were proposed with Hokan, a language family of several Native American peoples living in California, Arizona, and Baja California. Most modern linguists, by contrast, see the Coahuiltecan region as one of linguistic diversity. A few words are known from seven different languages: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakawa Indians
Coahuiltecan was a proposed language family in John Wesley Powell's 1891 classification of Native American languages. Most linguists now reject the view that the Coahuiltecan peoples of southern Texas and adjacent Mexico spoke a single or related languages. Coahuiltecan continues to be a convenient collective term for the languages and people of this region. Language relationships Similarities among the cultures among the indigenous people and the physical setting of south Texas led linguists to believe that the languages of the region were also similar. The Coahuiltecan language family was proposed to include all the languages of the region, including Karankawa and Tonkawa. Linguistic connections were proposed with Hokan, a language family of several Native American peoples living in California, Arizona, and Baja California. Most modern linguists, by contrast, see the Coahuiltecan region as one of linguistic diversity. A few words are known from seven different languages: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comecrudo
Comecrudan refers to a group of possibly related languages spoken in the southernmost part of Texas and in northern Mexico along the Rio Grande of which ''Comecrudo'' is the best known. Very little is known about these languages or the people who spoke them. Knowledge of them primarily consists of word lists collected by European missionaries and explorers. All Comecrudan languages are extinct. Family division The three languages were: # Comecrudo (also known as Mulato or Carrizo) ''(†)'' # Garza ''(†)'' # Mamulique (also known as Carrizo de Mamulique) ''(†)'' Genetic relationships In John Wesley Powell's 1891 classification of North American languages, Comecrudo was grouped together with the Cotoname and Coahuilteco languages into a family called Coahuiltecan. John R. Swanton (1915) grouped together the Comecrudo, Cotoname, Coahuilteco, Karankawa, Tonkawa, Atakapa, and Maratino languages into a Coahuiltecan grouping. Edward Sapir (1920) accepted Swanton's pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastia People
The Pastia people (also Pastias, Paxti; Spanish: "''chamuscados''")Text quote: ''Apparently, because of editorial oversight, no formal entry for the Pastia Indians was included in F ederickW. Hodge's Handbook of American Indians (1910), and this has led to confusion about their ethnic identity''. See ''The Handbook of Texas''. were a hunter-gatherer tribe of the Coahuiltecan. The Pastias inhabited the area south of San Antonio, largely between the Medina and San Antonio Rivers and the southward bend of the Nueces River running through modern day La Salle and McMullen counties. They were first contacted by Spanish explorers in the early eighteenth century, and were extinct as an ethnic group by the middle of the following century. History Early Spanish explorers encountered a number of ethnically distinct bands of aboriginal peoples near the Medina River who spoke a common Coahuiltecan dialect. These tribes also shared similar societal values and traditions. This group in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payaya
The Payaya people were Indigenous people whose territory encompassed the area of present-day San Antonio, Texas. The Payaya were a Coahuiltecan band and are the earliest recorded inhabitants of San Pedro Springs Park, the geographical area that became San Antonio. History The band are known to have inhabited the areas of the San Antonio River, the Frio River to the west, near the Pastia tribal lands; and Milam County to the east, where they lived among the Tonkawa. The Payaya called their village Yanaguana. It was located next to the river which the Spanish named the San Antonio. Some historians believe the band referred to the river as Yanaguana, but the Spanish Franciscan priest Damián Massanet recorded this as the name of their village. The Payaya first made contact with Spanish colonists in the 17th century, when the tribe had ten different encampments. By the year 1706, the Spanish had converted some Payaya among the Indigenous converts baptized at Mission San Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotoname
Cotoname was a Pakawan language spoken by Native Americans indigenous to the lower Rio Grande Valley of northeastern Mexico and extreme southern Texas (United States). Today it is extinct. Vocabulary The following vocabulary list of Cotoname is from John Swanton (1940).Swanton, John. 1940. ''Linguistic material from the tribes of southern Texas and northern Mexico.'' : See also *Indigenous languages of the Americas Over a thousand indigenous languages are spoken by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. These languages cannot all be demonstrated to be related to each other and are classified into a hundred or so language families (including a large num ... * Comecrudan languages References External links Native American languages (in German) {{North American languages Pakawan languages Extinct languages of North America Languages extinct in the 1900s Indigenous languages of Texas Coahuiltecan languages Language isolates of North America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra De Tamaulipas
The Sierra de Tamaulipas is an isolated, semi-tropical mountain range in the Mexican state of Tamaulipas. Its highest point is . There are no cities or towns in the Sierra and the small population is largely agricultural. The higher elevations of the Sierra have forests of oak and pine, contrasting with the semi-arid brush that dominates at lower altitudes. Several archaeological sites establish that the Sierra de Tamaulipas was the northern outpost of the agricultural Mesoamerican peoples of eastern Mexico. On 5 December 2016, the Sierra de Tamaulipas was declared a "Protected Natural Area" by the government of Mexico. The Protected Area has a core area of and a buffer zone containing . Geography The Sierra de Tamaulipas is about north to south and east to west at its widest point in the southern part of the range. The Sierra is located between 23 and 24 north latitude and 98 and 99 west longitude and has an estimated area of . Elevation ranges from . The Sierra de Tamau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both List of U.S. states and territories by area, area (after Alaska) and List of U.S. states and territories by population, population (after California). Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Houston is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas and the List of United States cities by population, fourth-largest in the U.S., while San Antonio is the second most pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monterrey, Nuevo Leon
Monterrey ( , ) is the capital and largest city of the northeastern state of Nuevo León, Mexico, and the third largest city in Mexico behind Guadalajara and Mexico City. Located at the foothills of the Sierra Madre Oriental, the city is anchor to the Monterrey metropolitan area, the second-largest in Mexico with an estimated population of 5,341,171 people as of 2020 and the second most productive metropolitan area in Mexico with a GDP ( PPP) of US$140 billion in 2015. According to the 2020 census, the city itself has a population of 1,142,194. Monterrey is one of the most livable cities in Mexico, and a 2018 study found that suburb San Pedro Garza García is the city with the best quality of life in Mexico. It serves as a commercial center of northern Mexico and is the base of many significant international corporations. Its purchasing power parity-adjusted GDP per capita is considerably higher than the rest of Mexico's at around US$35,500, compared to the country's US$18, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Grande Valley
The Lower Rio Grande Valley ( es, Valle del Río Grande), commonly known as the Rio Grande Valley or locally as the Valley or RGV, is a region spanning the border of Texas and Mexico located in a floodplain of the Rio Grande near its mouth. The region includes the southernmost tip of South Texas and a portion of northern Tamaulipas, Mexico. It consists of the Brownsville, Harlingen, Weslaco, Pharr, McAllen, Edinburg, Mission, San Juan, and Rio Grande City metropolitan areas in the United States and the Matamoros, Río Bravo, and Reynosa metropolitan areas in Mexico. The area is generally bilingual in English and Spanish, with a fair amount of Spanglish due to the region's diverse history and transborder agglomerations It is home to some of the poorest cities in the nation, as well as many unincorporated, persistent poverty communities called ''colonias''. A large seasonal influx occurs of "winter Texans" — people who come down from the north for the winter and then re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciudad Victoria, Tamaulipas
Ciudad Victoria () is the seat of the Municipality of Victoria, and the capital of the Mexican state of Tamaulipas. It is located in the northeast of Mexico at the foot of the Sierra Madre Oriental. It borders the municipality of Güémez to the north, Llera to the south, Casas Municipality to the east, and the municipality of Jaumave to the west. The city is located from Monterrey and from the US - Mexico border. Ciudad Victoria is named after the first president of Mexico, Guadalupe Victoria. In 1825 Ciudad Victoria became the state capital. It is home to higher education institutions such as the Autonomous University of Tamaulipas and the Technological Institute of Ciudad Victoria. General Pedro José Méndez International Airport is located on the outskirts of the city. As a state bureaucratic centre, it is the seat of the three political powers and has sites of tourist and cultural interest. Pre-foundation The Viceroy of New Spain, Juan Francisco Güémez and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropic Of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, which is also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun to its maximum extent. It also reaches 90 degrees below the horizon at solar midnight on the December Solstice. Using a continuously updated formula, the circle is currently north of the Equator. Its Southern Hemisphere counterpart, marking the most southerly position at which the Sun can be directly overhead, is the Tropic of Capricorn. These tropics are two of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of Earth, the others being the Arctic and Antarctic circles and the Equator. The positions of these two circles of latitude (relative to the Equator) are dictated by the tilt of Earth's axis of rotation relative to the plane of its orbit, and since the tilt changes, the location of these two circles also changes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |